Starting with Android 13, Android provides a default framework implementation for Ultra Wideband (UWB) radio technology, which enables highly secure, precise ranging between supported devices. The platform provides the AOSP UWB stack as an optional module for device manufacturers. For more details on the module, see Module: UWB.
Architecture
The UWB stack consists of the UWB mainline module and the HAL implementation provided by a UWB chip vendor. Figure 1 shows the UWB stack architecture:
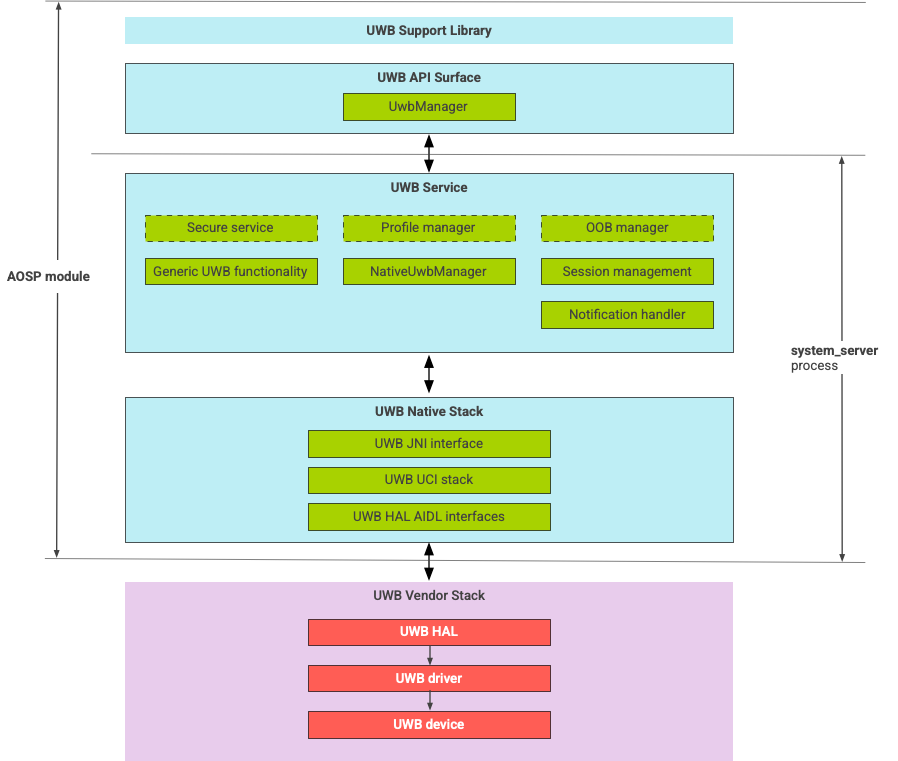
Figure 1. UWB stack architecture.
AOSP stack
The AOSP UWB stack, packaged as an optional module, com.google.android.uwb,
contains the following components:
- UWB platform API surface: Code location:
packages/modules/Uwb/framework - Support library: Code location:
packages/modules/Uwb/service/support_lib - UwbService layer and Common Service Management Layer (CSML) components
defined by FiRa Code location:
packages/modules/Uwb/service - Rust native UCI layer: Code location:
external/uwb - UWB HAL interface based on the UWB command interface (UCI) specification
defined by FiRa Code location:
hardware/interfaces/uwb
Vendor components
The vendor stack includes a UWB HAL vendor implementation, UWB driver, and a UWB device.
API surfaces for UWB
The UWB stack includes API surfaces for system apps and third-party apps.
System apps
Device manufacturers use the android.uwb.UwbManager
system API to provide low-level access for system apps. To use this API, system
apps must use the support library (packages/modules/Uwb/service/support_lib).
Third-party apps
Third-party apps use the Jetpack UWB public API,
androidx.core.uwb. For more information, see Ultra-wideband]6.
Verification
To verify your implementation of UWB, confirm that your device passes the CTS
tests in the /cts/tests/uwb directory.
