Device manufacturers can expose extensions such as bokeh, night mode, and HDR to third-party developers through the Camera Extensions interface provided by the OEM vendor library. Developers can use the Camera2 Extensions API and the CameraX Extensions API to access the extensions implemented in the OEM vendor library.
For a list of supported extensions, which is the same across Camera2 and CameraX, see CameraX Extensions API. If you want to add an extension, file a bug with the Issue Tracker.
This page describes how to implement and enable the OEM vendor library on devices.
Architecture
The following diagram describes the architecture of the Camera Extensions
interface or extensions-interface:
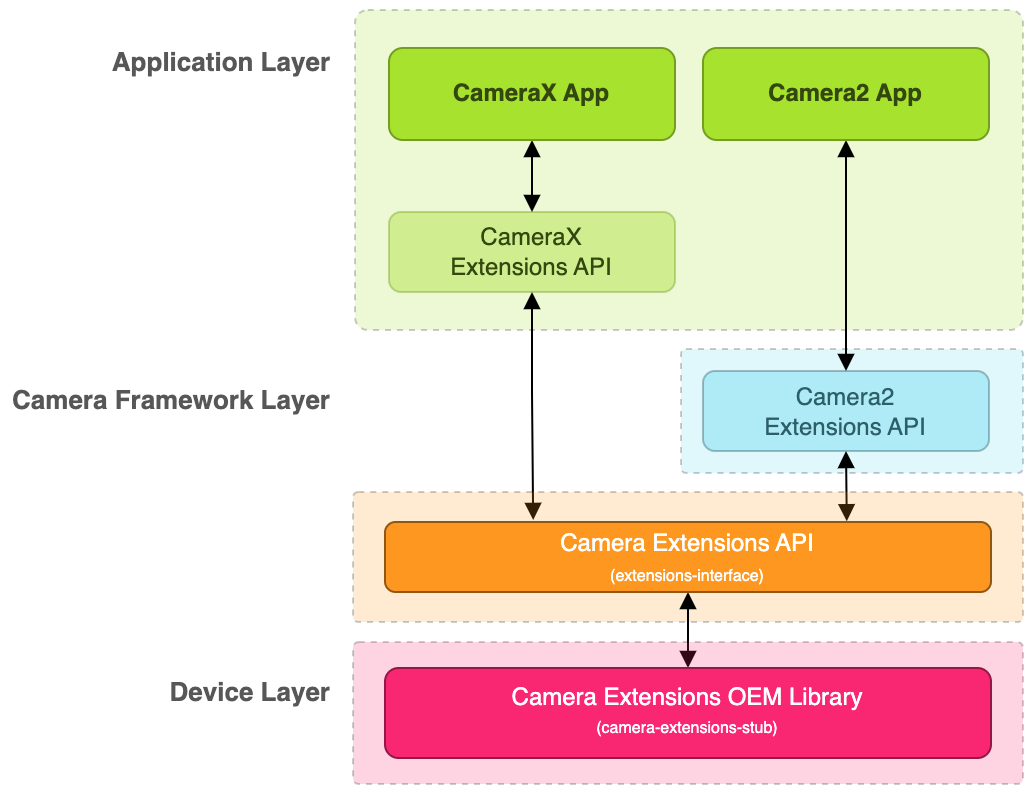
Figure 1. Camera Extensions architecture diagram
As shown in the diagram, to support Camera Extensions, you need to
implement the extensions-interface provided by the OEM vendor library. Your
OEM vendor library enables two APIs:
CameraX Extensions API and
Camera2 Extensions API,
which are used by CameraX and Camera2 apps, respectively, to access
vendor extensions.
Implement the OEM vendor library
To implement the OEM vendor library, copy the
camera-extensions-stub
files into a system library project. These files define the Camera Extensions
interface.
The camera-extensions-stub
files are divided into the following categories:
Essential interface files (don't modify)
PreviewExtenderImpl.javaImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaExtenderStateListener.javaProcessorImpl.javaPreviewImageProcessorImpl.javaCaptureProcessorImpl.javaCaptureStageImpl.javaRequestUpdateProcessorImpl.javaProcessResultImpl.javaadvanced/AdvancedExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/Camera2OutputConfigImpl.javaadvanced/Camera2SessionConfigImpl.javaadvanced/ImageProcessorImpl.javaadvanced/ImageReaderOutputConfigImpl.javaadvanced/ImageReferenceImpl.javaadvanced/MultiResolutionImageReaderOutputConfigImpl.javaadvanced/OutputSurfaceImpl.javaadvanced/RequestProcessorImpl.javaadvanced/SessionProcessorImpl.javaadvanced/SurfaceOutputConfigImpl.java
Mandatory implementations (add your implementation)
ExtensionVersionImpl.javaInitializerImpl.java
Bokeh extender classes (implement it if Bokeh extension is supported)
BokehImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaBokehPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/BokehAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Night extender classes (implement it if Night extension is supported)
NightImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaNightPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/NightAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Auto extender classes (implement it if Auto extension is supported)
AutoImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaAutoPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/AutoAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
HDR extender classes (implement it if HDR extension is supported)
HdrImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaHdrPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/HdrAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Face Retouch extender classes (implement it if Face Retouch extension is supported)
BeautyImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaBeautyPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/BeautyAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Utilities (optional, can be deleted)
advanced/Camera2OutputConfigImplBuilder.javaadvanced/Camera2SessionConfigImplBuilder.java
You aren't required to provide an implementation for every extension. If you
don't implement an extension, set isExtensionAvailable() to return false or
remove the corresponding Extender classes. The Camera2 and CameraX Extensions
APIs report to the app that the extension is unavailable.
Let’s walk through how the Camera2 and CameraX Extensions APIs interact with the vendor library to enable an extension. The following diagram illustrates the end-to-end flow using the Night extension as an example:
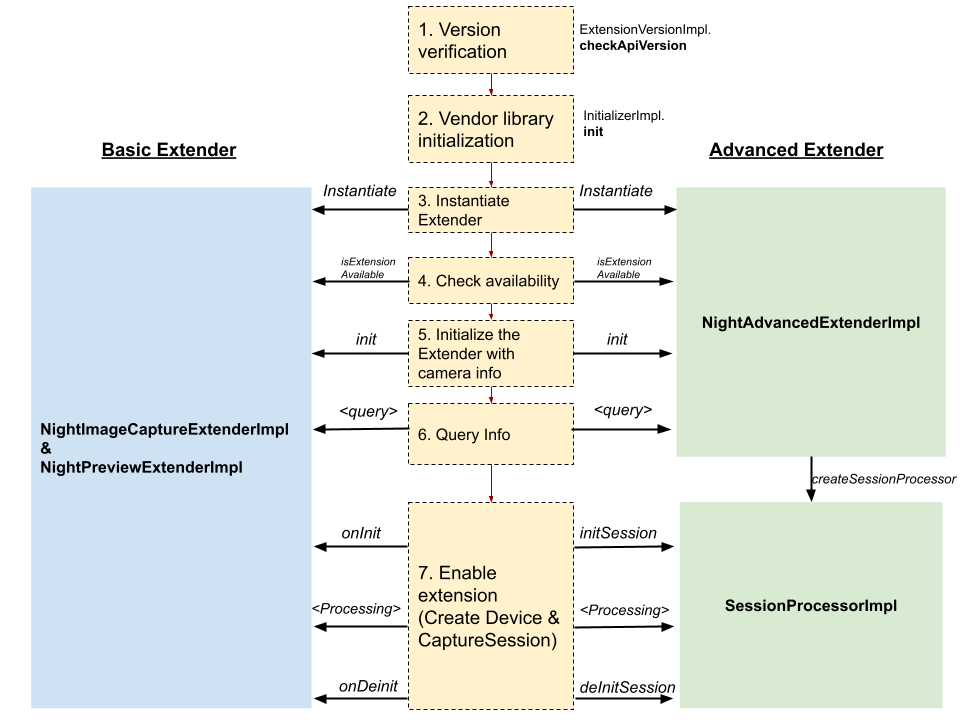
Figure 2. Night extension implementation
Version verification:
Camera2/X calls
ExtensionVersionImpl.checkApiVersion()to ensure that the OEM-implementedextensions-interfaceversion is compatible with Camera2/X supported versions.Vendor library initialization:
InitializerImplhas a methodinit()that initializes the vendor library. Camera2/X completes the initialization before accessing the Extender classes.Instantiate Extender classes:
Instantiates the Extender classes for the extension. There are two Extender types: Basic Extender and Advanced Extender. You must implement one Extender type for all Extensions. For more information, see Basic Extender versus Advanced Extender.
Camera2/X instantiates and interacts with the Extender classes to retrieve information and enable the extension. For a given extension, Camera2/X can instantiate the Extender classes multiple times. As a result, don't do heavy-lifting initialization in the constructor or the
init()call. Do the heavy lifting only when the camera session is about to start, such as whenonInit()is called in Basic Extender orinitSession()is called in Advanced Extender.For the Night extension, the following Extender classes are instantiated for the Basic Extender type:
NightImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaNightPreviewExtenderImpl.java
And for the Advanced Extender type:
NightAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Check extension availability:
Before enabling the extension,
isExtensionAvailable()checks if the extension is available on the specified camera ID through the Extender instance.Initialize the Extender with camera information:
Camera2/X calls
init()on the Extender instance and passes it the camera ID andCameraCharacteristics.Query information:
Invokes the Extender class to retrieve information such as supported resolutions, still capture estimated latency, and capture request keys from the Extender in preparation for enabling the extension.
Enable extension on the Extender:
The Extender class provides all the interfaces needed to enable the class. It offers a mechanism to hook OEM implementation into the Camera2 pipeline such as injecting capture request parameters or enabling a post processor.
For the Advanced Extender type, Camera2/X interacts with
SessionProcessorImplto enable the extension. Camera2/X retrieves theSessionProcessorImplinstance by callingcreateSessionProcessor()on the Extender.
The following sections describe the extension flow in greater detail.
Version verification
When loading the OEM vendor library from the device at runtime, Camera2/X
verifies if the library is compatible with the extensions-interface version.
The extensions-interface uses semantic versioning, or
MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH, for example, 1.1.0 or 1.2.0. However, only the
major and minor versions are used during the version verification.
To verify the version, Camera2/X calls
ExtensionVersionImpl.checkApiVersion() with the supported
extensions-interface version. Camera2/X then uses the version reported by the
OEM library to determine if the extension can be enabled and what capabilities
it should invoke.
Major version compatibility
If the major versions of the extension-interface are different between Camera2/X and the vendor library, then it's considered incompatible and the extension is disabled.
Backward compatibility
As long as the major version is identical, Camera2/X ensures
backward compatibility with OEM vendor libraries built with prior
extensions-interface versions. For example, if Camera2/X supports
extensions-interface 1.3.0, the OEM vendor libraries that implemented 1.0.0,
1.1.0, and 1.2.0 are still compatible. This also means that after you implement
a specific version of the vendor library, Camera2/X makes sure the library
is backward compatible with upcoming extension-interface versions.
Forward compatibility
Forward compatibility with vendor libraries of newer extensions-interface
depends on you, the OEM. If you need some features to implement the extensions,
you might want to enable the extensions starting from a certain version. In this
case, you can return the supported extensions-interface version when the
Camera2/X library version meets the requirements. If the Camera2/X versions
aren't supported, you can return an incompatible version such as 99.0.0 to
disable the extensions.
Vendor library initialization
After verifying the extensions-interface version implemented by the OEM
library, Camera2/X starts the initialization process. The
InitializerImpl.init() method signals to the OEM library that an app is trying
to use extensions.
Camera2/X makes no other calls to the OEM library (aside from version checking)
until the OEM vendor library calls OnExtensionsInitializedCallback.onSuccess()
to notify the completion of initialization.
You must implement
InitializerImpl
as of extensions-interface 1.1.0. Camera2/X skips the library initialization
step if the OEM vendor library implements extensions-interface 1.0.0.
Basic Extender versus Advanced Extender
There are two types of extensions-interface implementation: Basic Extender and
Advanced Extender. Advanced Extender has been supported since
extensions-interface 1.2.0.
Implement Basic Extender for extensions that process images in the camera HAL or use a post processor capable of processing YUV streams.
Implement Advanced Extender for extensions that need to customize the Camera2 stream configuration and send capture requests as needed.
See the following table for the comparison:
| Basic Extender | Advanced Extender | |
|---|---|---|
| Stream configurations | Fixed Preview: PRIVATE or YUV_420_888 (if processor exists) Still capture: JPEG or YUV_420_888 (if processor exists)
|
Customizable by OEM. |
| Sending capture request | Only Camera2/X can send capture requests. You can set the parameters to these requests. When the processor is provided for image capture, Camera2/X can send multiple capture requests and send all the images and capture results to the processor. | A RequestProcessorImpl instance is provided to you to
execute the camera2 capture request and get results and Image.
Camera2/X invokes |
| Hooks in the camera pipeline |
|
|
| Suitable for | Extensions implemented in the camera HAL or in a processor that processes YUV images. |
|
| Supported API version | Camera2 Extensions: Android 13 or higher CameraX Extensions: camera-extensions 1.1.0 or higher |
Camera2 Extensions: Android 12L or higher CameraX Extensions: camera-extensions 1.2.0-alpha03 or higher |
App flows
The following table shows three types of app flows and their corresponding Camera Extensions API calls. While Camera2/X provide these APIs, you must properly implement the vendor library to support these flows, which we describe in more detail in a later section.
| Camera2 extensions | CameraX extensions | |
|---|---|---|
| Query extension availability | CameraExtensionCharacteristics
.getSupportedExtensions
|
ExtensionsManager.
isExtensionAvailable
|
| Query information | CameraExtensionCharacteristics.
getExtensionSupportedSizes
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.
getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRangeMillis
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.
getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.
getAvailableCaptureResultKeys
|
ExtensionsManager.
getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRange
CameraX handles the rest of the information within the library. |
| Preview and still-capture with extension enabled | CameraDevice.
createExtensionSession
|
val cameraSelector = ExtensionsManager.
getExtensionEnabledCameraSelector
|
Basic Extender
The Basic Extender interface provides hooks into several places in the camera pipeline. Each extension type has corresponding Extender classes that OEMs need to implement.
The following table lists the Extender classes OEMS need to implement for each extension:
| Extender classes to implement | |
|---|---|
| Night | NightPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
| HDR | HdrPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
| Auto | AutoPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
| Bokeh | BokehPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
| Face retouch | BeautyPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
We use PreviewExtenderImpl and ImageCaptureExtenderImpl as placeholders
in the following example. Replace these with the names of the actual
files you're implementing.
Basic Extender has the following capabilities:
- Inject session parameters when configuring
CameraCaptureSession(onPresetSession). - Notify you of the capture session start and closing events and send a single
request to notify the HAL with the returned parameters (
onEnableSession,onDisableSession). - Inject capture parameters for the request
(
PreviewExtenderImpl.getCaptureStage,ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getCaptureStages). - Add processors for preview and still capture that's capable of processing
YUV_420_888stream.
Let’s see how Camera2/X invokes the extensions-interface to achieve the three
app flows mentioned above.
App flow 1: Check extension availability

Figure 3. App flow 1 on Basic Extender
In this flow, Camera2/X directly calls the isExtensionAvailable() method of
both PreviewExtenderImpl and ImageCaptureExtenderImpl without calling
init(). Both Extender classes must return true to enable the extensions.
This is often the first step for apps to check if the given extension type is supported for a given camera ID before enabling the extension. This is because some extensions are supported only on certain camera IDs.
App flow 2: Query information
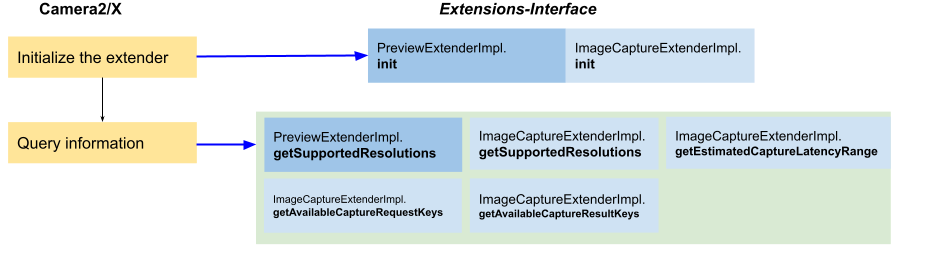
Figure 4. App flow 2 on Basic Extender
After determining if the extension is available, apps should query the following information before enabling the extension.
Still capture latency range:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRangereturns the range of the capture latency for the app to evaluate if it's appropriate to enable the extension for the current scenario.Supported sizes for the preview and capture surface:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getSupportedResolutionsandPreviewExtenderImpl.getSupportedResolutionsreturn a list of image formats and the sizes that are supported for surface format and size.Supported request and result keys: Camera2/X invokes the following methods to retrieve the supported capture request keys and result keys from your implementation:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeysImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getAvailableCapturetResultKeys
Camera2/X always calls init() first on these Extender classes before querying
for more information.
App flow 3: Preview/still capture with extension enabled (HAL implementation)
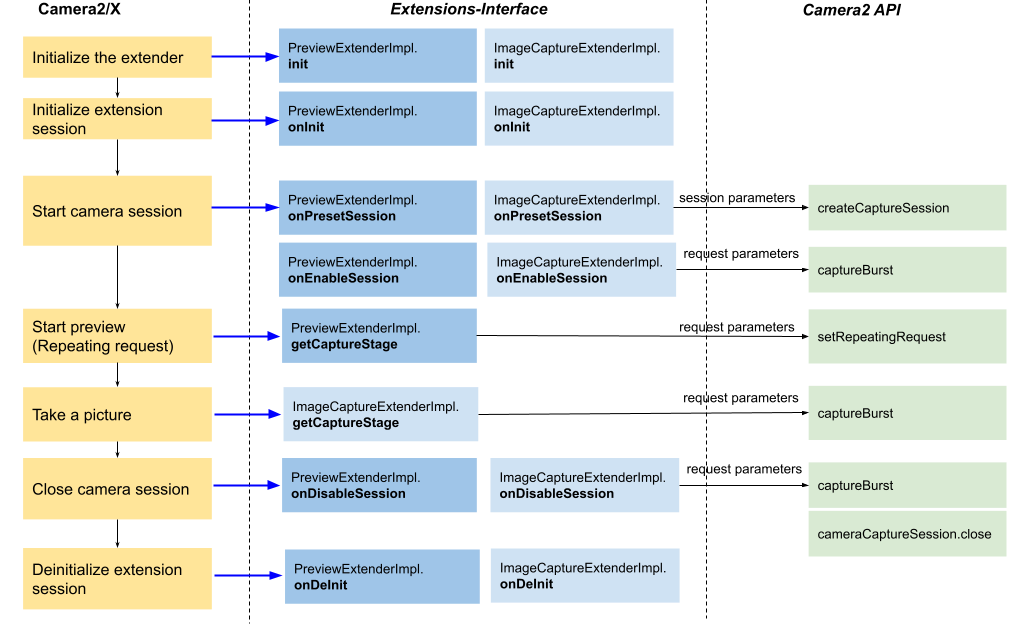
Figure 5. App flow 3 on Basic Extender
The above diagram illustrates the main flow of enabling preview and still capture with an extension without any processor. This means the camera HAL processes the extension.
In this flow, Camera2/X first calls init() then onInit, which notifies you
that a camera session is about to start with the specified extensions.
You can do heavy-lifting initialization in onInit().
When configuring CameraCaptureSession, Camera2/X invokes
onPresetSession to get the session parameters. After the capture session is
configured successfully, Camera2/X invokes onEnableSession returning a
CaptureStageImpl
instance that contains the capture parameters. Camera2/X
immediately sends a single request with these capture parameters to notify the
HAL. Similarly, before the capture session is closed, Camera2/X invokes
onDisableSession and then sends a single request with the returned capture
parameters.
The repeating request triggered by Camera2/X contains the request parameters
returned by PreviewExtenderImpl.getCaptureStage(). Furthermore, the still
capture request contains the parameters returned by
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getCaptureStages().
Finally, Camera2/X invokes onDeInit() after the camera session has finished.
You can release resources in onDeinit().
Preview processor
In addition to the camera HAL, you can also implement extensions in a processor.
Implement PreviewExtenderImpl.getProcessorType to specify the processor type
as explained below:
PROCESSOR_TYPE_NONE: No processor. Images are processed in the camera HAL.PROCESSOR_TYPE_REQUEST_UPDATE_ONLY: The processor type lets you update the repeating request with new capture request parameters based on the latestTotalCaptureResult.PreviewExtenderImpl.getProcessormust return aRequestUpdateProcessorImplinstance that processes theTotalCaptureResultinstance and returns aCaptureStageImplinstance to update the repeating request.PreviewExtenderImpl.getCaptureStage()should also reflect the result of the processing and return the latestCaptureStageImpl.PROCESSOR_TYPE_IMAGE_PROCESSOR: This type allows you to implement a processor to processYUV_420_888images and write the output to aPRIVATEsurface.You need to implement and return a
PreviewImageProcessorImplinstance inPreviewExtenderImpl.getProcessor. The processor is responsible for processingYUV_420_888input images. It should write the output to thePRIVATEformat of preview. Camera2/X uses aYUV_420_888surface instead ofPRIVATEto configure theCameraCaptureSessionfor preview.See following illustration for the flow:
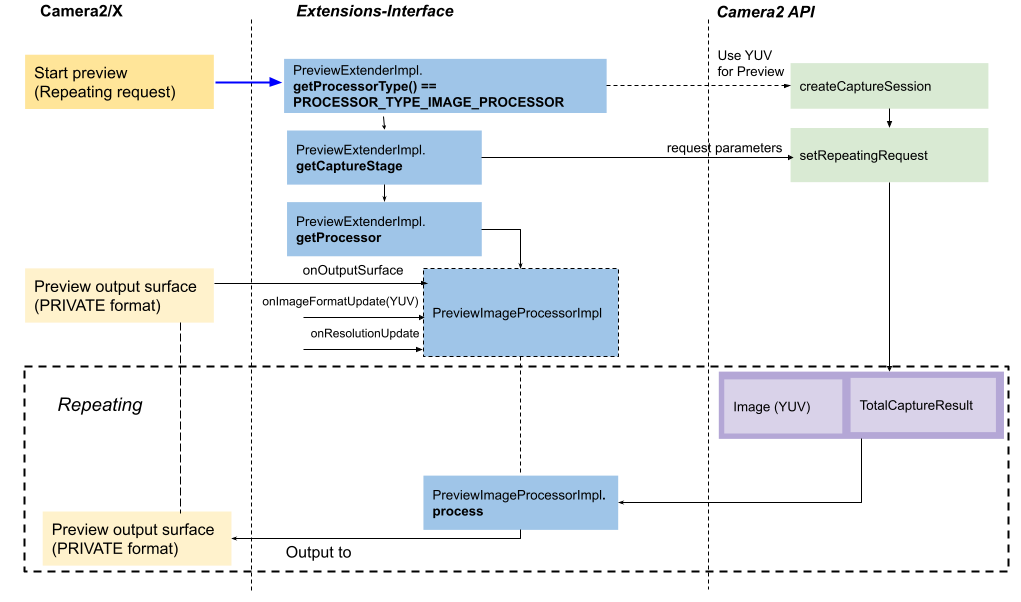
Figure 6. Preview flow with PreviewImageProcessorImpl
The PreviewImageProcessorImpl interface extends ProcessImpl and has
three important methods:
onOutputSurface(Surface surface, int imageFormat)sets the output surface for the processor. ForPreviewImageProcessorImpl,imageFormatis a pixel format such asPixelFormat.RGBA_8888.onResolutionUpdate(Size size)sets the size of the input image.onImageFormatUpdate(int imageFormat)sets the image format of the input image. Currently, it can only beYUV_420_888.
Image capture processor
For still capture, you can implement a processor by returning a
CaptureProcessorImpl
instance using ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getCaptureProcessor. The processor is
responsible to process a list of captured YUV_420_888 images and
TotalCaptureResult instances and write the output to a YUV_420_888 surface.
You can safely assume that preview is enabled and running before sending the still capture request.
See the flow in the diagram below:
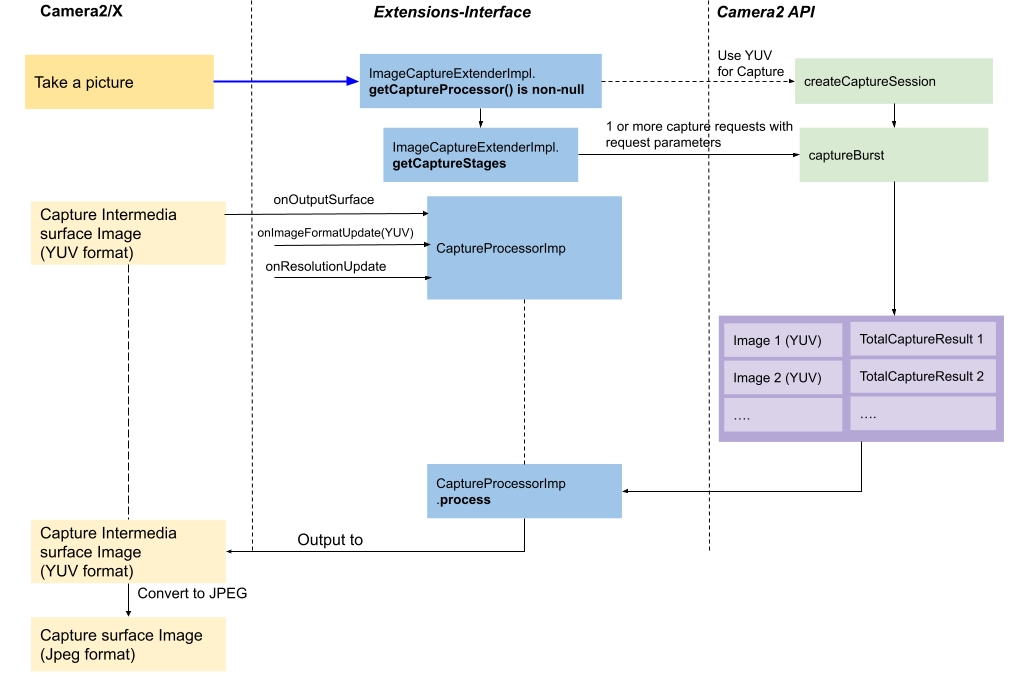
Figure 7. Still capture flow with CaptureProcessorImpl
Camera2/X uses a
YUV_420_888format surface for still capture to configure the capture session. Camera2/X preparesCaptureProcessorImplby calling:CaptureProcessorImpl.onImageFormatUpdate()withYUV_420_888.CaptureProcessorImpl.onResolutionUpdate()with the input image size.CaptureProcessorImpl.onOutputSurface()with an outputYUV_420_888surface.
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getCaptureStagesreturns a list ofCaptureStageImpl, where each element maps to aCaptureRequestinstance with capture parameters that are sent by Camera2/X. For example, if it returns a list of threeCaptureStageImplinstances, Camera2/X sends three capture requests with corresponding capture parameters using thecaptureBurstAPI.The received images and
TotalCaptureResultinstances are bundled together and sent toCaptureProcessorImplfor processing.CaptureProcessorImplwrites the result Image (YUV_420_888format) to the output surface specified by theonOutputSurface()call. Camera2/X converts it into JPEG images if necessary.
Support capture request keys and results
In addition to camera preview and capture, apps can set zoom, flash parameters, or trigger a tap-to-focus. These parameters might not be compatible with your extension implementation.
The following methods have been added to extensions-interface 1.3.0 to allow
you to expose the parameters that your implementation supports:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys()returns the capture request keys supported by your implementation.ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureResultKeys()returns the capture result keys that are contained in the capture result.
If the camera HAL processes the extension, Camera2/X retrieves the capture
results in CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback. However, if
the processor is implemented, then Camera2/X retrieves the capture results in
ProcessResultImpl
, which is passed to the process()
method in
PreviewImageProcessorImpl
and
CaptureProcessorImpl.
You're responsible for reporting
the capture result through ProcessResultImpl to Camera2/X.
See the definition of the CaptureProcessorImpl interface below as an example.
In extensions-interface 1.3.0 or higher, the second process() call is invoked:
Interface CaptureProcessorImpl extends ProcessorImpl {
// invoked when extensions-interface version < 1.3.0
void process(Map<Integer, Pair<Image, TotalCaptureResult>> results);
// invoked when extensions-interface version >= 1.3.0
void process(Map<Integer, Pair<Image, TotalCaptureResult>> results,
ProcessResultImpl resultCallback, Executor executor);
}
For common camera operations like zoom, tap-to-focus, flash, and exposure compensation, we recommend supporting the following keys for both capture request and capture result:
- Zoom:
CaptureRequest#CONTROL_ZOOM_RATIOCaptureRequest#SCALER_CROP_REGION
- Tap-to-focus:
CaptureRequest#CONTROL_AF_MODECaptureRequest#CONTROL_AF_TRIGGERCaptureRequest#CONTROL_AF_REGIONSCaptureRequest#CONTROL_AE_REGIONSCaptureRequest#CONTROL_AWB_REGIONS
- Flash:
CaptureRequest#CONTROL_AE_MODECaptureRequest#CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGERCaptureRequest#FLASH_MODE
- Exposure compensation:
CaptureRequest#CONTROL_AE_EXPOSURE_COMPENSATION
For Basic Extenders that implement 1.2.0 or prior versions, the CameraX
Extensions API explicitly supports all the above keys. For
extensions-interface 1.3.0, both CameraX and Camera2 honor the returned list
and support only the keys contained in it. For example, if you decide to return
only CaptureRequest#CONTROL_ZOOM_RATIO and
CaptureRequest#SCALER_CROP_REGION in the 1.3.0 implementation, then that
means only zoom is supported for the app while tap-to-focus, flash, and exposure
compensation aren't allowed.
Advanced Extender
Advanced Extender is a type of vendor implementation based on the Camera2 API.
This Extender type was added in extensions-interface 1.2.0. Depending on
the device manufacturer, extensions might be implemented in the app layer,
which depends on the following factors:
Custom stream configuration: Configure custom streams like RAW stream or have multiple streams for different physical camera IDs.
Capability to send Camera2 requests: Support a complicated interaction logic that can send capture requests with parameters based on the results of previous requests.
Advanced Extender provides a wrapper, or an intermediate layer, so you can customize the stream configuration and send capture requests on demand.
Files to implement
To switch to the Advanced Extender implementation, the
isAdvancedExtenderImplemented() method in
ExtensionVersionImpl
must return true. For each extension type, OEMs must implement the
corresponding Extender classes. The Advanced Extender implementation files are
in the advanced package.
| Extender classes to implement | |
|---|---|
| Night | advanced/NightAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
| HDR | advanced/HdrAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
| Auto | advanced/AutoAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
| Bokeh | advanced/BokehAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
| Face Retouch | advanced/BeautyAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
We use AdvancedExtenderImpl as a placeholder in the following example.
Replace it with the name of the Extender file for the extension you're
implementing.
Let’s see how Camera2/X invokes the extensions-interface to achieve the three
app flows.
App flow 1: Check extensions availability
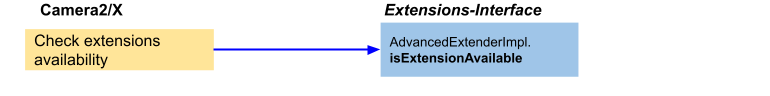
Figure 8. App flow 1 on Advanced Extender
First, the app checks if the given extension is supported.
App flow 2: Query information
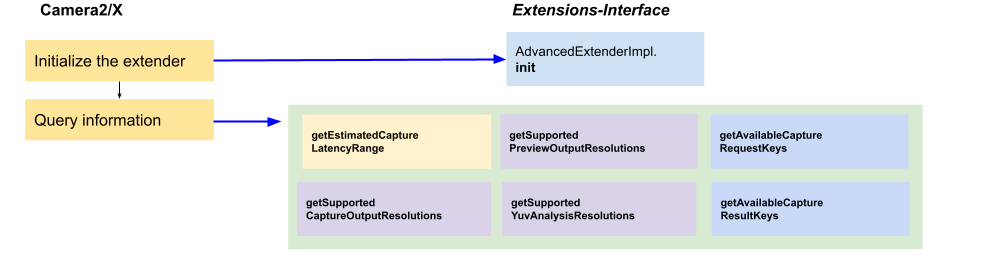
Figure 9. App flow 2 on Advanced Extender
After calling AdvancedExtenderImpl.init(), the app can query the
following the information on AdvancedExtenderImpl:
Estimated still capture latency:
AdvancedExtenderImpl.getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRange()returns the range of the capture latency for the app to evaluate if it is appropriate to enable the extension for the current scenario.Supported resolutions for preview and still capture:
AdvancedExtenderImpl.getSupportedPreviewOutputResolutions()returns a map of image format to the sizes list that are supported for preview surface format and size. OEMs must support at least thePRIVATEformat.AdvancedExtenderImpl.getSupportedCaptureOutputResolutions()returns the supported format and sizes for still capture surface. OEMs must support bothJPEGandYUV_420_888format output.AdvancedExtenderImpl.getSupportedYuvAnalysisResolutions()returns the supported sizes for an extraYUV_420_888stream for image analysis. If the image analysis YUV surface isn't supported,getSupportedYuvAnalysisResolutions()should returnnullor an empty list.
Available capture request keys/results (added in
extensions-interface1.3.0): Camera2/X invokes the following methods to retrieve the supported capture request keys and result keys from your implementation:AdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeysAdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureResultKeys
For more information, see Support capture request keys and results.
App flow 3: Preview/still capture with extension enabled
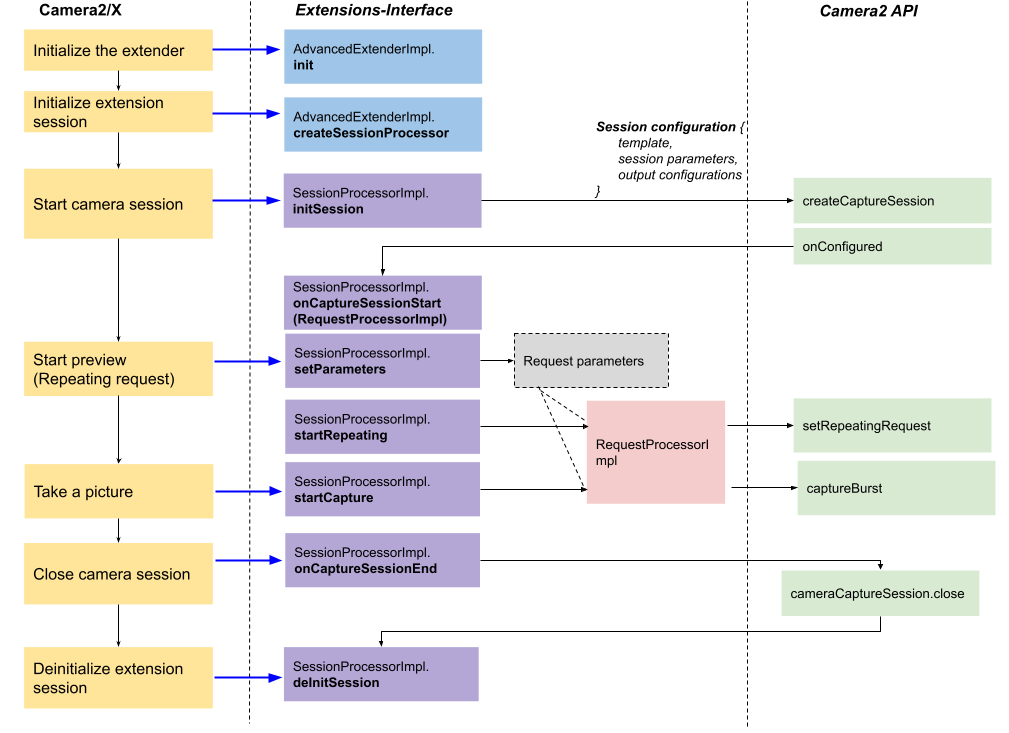
Figure 10. App flow 3 on Advanced Extender
The above diagram shows the main flow for starting preview and still capture for the Advanced Extender type. Let’s walk through each step.
SessionProcessorImplinstanceThe core Advanced Extender implementation is in
SessionProcessorImpl, which is responsible for providing customized session configuration and sending capture requests to initiate the preview and still capture request.AdvancedExtenderImpl.createSessionProcessor()is invoked to return theSessionProcessorImplinstance.initSessionSessionProcessorImpl.initSession()initializes the session for the extension. This is where you allocate resources and return a session configuration for preparing aCameraCaptureSession.For the input parameters, Camera2/X specifies the output surface configurations for preview, still capture, and an optional YUV image analysis. This output surface configuration (
OutputSurfaceImpl) contains the surface, size and image format that are retrieved by following methods inAdvancedExtenderImpl:getSupportedPreviewOutputResolutions()getSupportedCaptureOutputResolutions()getSupportedYuvAnalysisResolutions()
You must return a
Camera2SessionConfigImplinstance, which consists of a list ofCamera2OutputConfigImplinstances and the session parameters used for configuringCameraCaptureSession. You're responsible for outputting the correct camera images to the output surfaces passed in by Camera2/X. Here are some options to enable the output:- Processing in camera HAL: You can directly add the output surfaces
to
CameraCaptureSessionwith aSurfaceOutputConfigImplimplementation. This configures the supplied output surface to the camera pipeline and allows the camera HAL to process the image. Processing intermediate
ImageReadersurface (RAW, YUV, etc): Add the intermediateImageReadersurfaces to theCameraCaptureSessionwith anImageReaderOutputConfigImplinstance.You need to process the intermediate images and write the result image to the output surface.
- Use Camera2 surface sharing: Use surface sharing with another surface
by adding any
Camera2OutputConfigImplinstance to thegetSurfaceSharingOutputConfigs()method of anotherCamera2OutputConfigImplinstance. The surface format and size must be identical.
All
Camera2OutputConfigImplincludingSurfaceOutputConfigImplandImageReaderOutputConfigImplmust have a unique ID (getId()), which is used to specify the target surface and retrieve the image fromImageReaderOutputConfigImpl.onCaptureSessionStartandRequestProcessorImplWhen
CameraCaptureSessionstarts and the Camera framework invokesonConfigured(), then Camera2/X invokesSessionProcessorImpl.onCaptureSessionStart()with the Camera2 request wrapperRequestProcessImpl. Camera2/X implementsRequestProcessImpl, which enables you to execute the capture requests, and retrieve images ifImageReaderOutputConfigImplis used.The
RequestProcessImplAPIs are similar to the Camera2CameraCaptureSessionAPIs in terms of executing requests. The differences are:- The target surface is specified by the ID of the
Camera2OutputConfigImplinstance. - The capability of retrieving the image of the
ImageReader.
You can call
RequestProcessorImpl.setImageProcessor()with a specifiedCamera2OutputConfigImplID to register anImageProcessorImplinstance to receive images.The
RequestProcessImplinstance becomes invalid after Camera2/X callsSessionProcessorImpl.onCaptureSessionEnd().- The target surface is specified by the ID of the
Start the preview and take a picture
In the Advanced Extender implementation, you can send capture requests through the
RequestProcessorImplinterface. Camera2/X notifies you to start the repeating request for preview or the still capture sequence by callingSessionProcessorImpl#startRepeatingandSessionProcessorImpl#startCapturerespectively. You should send capture requests to satisfy these preview and still-capture requests.Camera2/X also sets the capture request parameters through
SessionProcessorImpl#setParameters. You must set these request parameters (if parameters are supported) on both the repeating and single requests.You must support at least
CaptureRequest.JPEG_ORIENTATIONandCaptureRequest.JPEG_QUALITY.extensions-interface1.3.0 supports request and result keys, which are exposed by the following methods:AdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys()AdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureResultKeys()
When developers set the keys in the
getAvailableCaptureRequestKeyslist, you must enable the parameters and ensure the capture result contains the keys in thegetAvailableCaptureResultKeyslist.startTriggerSessionProcessorImpl.startTrigger()is invoked to start the trigger such asCaptureRequest.CONTROL_AF_TRIGGERandCaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER. You can disregard any capture request keys that weren't advertised inAdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys().startTrigger()has been supported sinceextensions-interface1.3.0. It enables apps to implement tap-to-focus and flash with extensions.Clean up
When finishing a capture session,
SessionProcessorImpl.onCaptureSessionEnd()is invoked ahead of closingCameraCaptureSession. After the capture session has closed,deInitSession()performs the clean up.
Support preview, still capture, and image analysis
You should apply the extension for both the preview and still capture use cases. However, if the latency is too high to smoothly show the preview, you can apply the extension only for still capture.
For the Basic Extender type, regardless of enabling the extension for preview,
you must implement both ImageCaptureExtenderImpl and PreviewExtenderImpl
for a given extension. Often, an app also uses a YUV stream to analyze the
image content such as finding QR codes or text. To better support this use case
, you should support the stream combination of preview, still capture, and a
YUV_420_888 stream for configuring CameraCaptureSession. This means
that if you implement a processor, then you have to support the stream
combination of three YUV_420_888 streams.
For Advanced Extender, Camera2/X passes three output surfaces to the
SessionProcessorImpl.initSession() call. These output surfaces are for preview
, still capture, and image analysis, respectively. You must ensure that preview
and still capture output surfaces show the valid output. However, for the image
analysis output surface, ensure it's working only when it's non-null. If your
implementation can't support the image analysis stream, you can return an empty
list in AdvancedExtenderImpl.getSupportedYuvAnalysisResolutions(). This
ensures the image analysis output surface is always null in
SessionProcessorImpl.initSession().
Support video capture
The current Camera Extension architecture supports only the preview and still
capture use cases. We don't support enabling the extension on the MediaCodec
or MediaRecorder surfaces for recording the video. However, it's possible
for apps to record the preview output.
Supporting MediaCodec and MediaRecorder surfaces is under investigation.
Extension-specific metadata
For Android 14 and higher, extension-specific metadata
lets camera extension clients set and receive extension specific capture
request settings and results. Specifically, camera extension
clients can use the EXTENSION_STRENGTH capture request parameter to control
the extension strength and the EXTENSION_CURRENT_TYPE capture result to
indicate the enabled extension type.
Capture requests
The
EXTENSION_STRENGTH
capture request parameter
controls the strength of the extension post-processing effect. The corresponding
capture result includes the default strength value if this parameter isn't set
explicitly by the client. This parameter can be applied as follows for these
extension types:
BOKEH: Controls the amount of blur.HDRandNIGHT: Controls the amount of images fused and the brightness of the final image.FACE_RETOUCH: Controls the amount of cosmetic enhancement and skin smoothing.
The supported range for the EXTENSION_STRENGTH parameter is between 0 and
100, with 0 indicating no extension processing or simple passthrough and
100 indicating the maximum extension strength of the processing effect.
To add support for EXTENSION_STRENGTH, use the vendor
specific parameter APIs introduced in version 1.3.0 of the extension library
interface. For more information, see
getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys().
Capture results
The
EXTENSION_CURRENT_TYPE
capture result lets extension implementations notify clients about the active
extension type.
Because extensions using the AUTO type dynamically switch between extension
types such as HDR and NIGHT depending on the scene conditions, camera
extensions apps can use EXTENSION_CURRENT_TYPE to display information about
the current extension selected by the AUTO extension.
Real-time still capture latency estimate
For Android 14 and higher, camera extension clients
can query real-time still capture latency estimates based on the scene and
environment conditions using
getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency(). This
method provides more accurate estimates than the static
getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRangeMillis()
method. Based on the latency estimate, apps can decide to skip extension
processing or to display an indication to notify users about a long
running operation.
CameraExtensionSession.StillCaptureLatency latency;
latency = extensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency();
// The capture latency from ExtensionCaptureCallback#onCaptureStarted() until ExtensionCaptureCallback#onCaptureProcessStarted().
latency.getCaptureLatency();
// The processing latency from ExtensionCaptureCallback#onCaptureProcessStarted() until the processed frame returns to the client.
latency.getProcessingLatency();
To support real-time still capture latency estimates, implement the following:
- Basic extensions:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getRealtimeCaptureLatency() - Advanced extensions:
SessionProcessorImpl.getRealtimeCaptureLatency
Capture processing progress callbacks
For Android 14 and higher, camera extension clients can receive callbacks for the progress of long running still capture processing operations. Apps can display the current progress to users to improve the overall user experience.
Apps can use the following code to integrate this feature:
import android.hardware.camera2.CameraExtensionSession.
ExtensionCaptureCallback;
{
…
class AppCallbackImpl extends ExtensionCaptureCallback {
…
@Override
public void onCaptureProcessProgressed(
@NonNull CameraExtensionSession session,
@NonNull CaptureRequest request,
@IntRange(from = 0, to = 100) int progress) {
// Update app UI with current progress
}
}
…
}
To support capture processing progress callbacks, your extension vendor implementation must call the following callbacks with the current progress value:
- Basic extensions:
ProcessResultImpl.onCaptureProcessProgressed() - Advanced extensions:
CaptureCallback.onCaptureProcessProgressed()
Postview still capture
For Android 14 and higher, camera extensions can
supply a postview (preview image) using
setPostviewOutputConfiguration.
To improve the user experience, apps can display a postview image as a
placeholder when an extension is experiencing increased processing latency,
and replace the image when the final image is available. Apps can configure
and issue postview capture requests using the following reference code:
{
…
if (!CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable()) {
continue;
}
…
ExtensionSessionConfiguration extensionConfiguration = new
ExtensionSessionConfiguration(
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.EXTENSION_NIGHT,
outputConfig,
backgroundExecutor,
extensionSessionStateCallback
);
extensionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration(
postviewImageOutput);
…
CaptureRequest.Builder captureRequestBuilder =
cameraDevice.createCaptureRequest(
CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_STILL_CAPTURE);
captureRequestBuilder.addTarget(stillImageReader.getSurface());
captureRequestBuilder.addTarget(postviewImageSurface);
CaptureRequest captureRequest = captureRequestBuilder.build();
…
}
To support postview still capture, your vendor implementation must implement the following:
Basic extensions:
CaptureProcessorImpl.onPostviewOutputSurfaceandCaptureProcessorImpl.processWithPostviewAdvanced extensions:
SessionProcessorImpl.startCaptureWithPostview
Support SurfaceView output
For Android 14 and higher, camera extension clients
can use power and performance optimized preview render paths by registering a
SurfaceView
instance for preview output for repeating requests.
To support SurfaceView output, your vendor extension implementation must be
capable of streaming and outputting preview to SurfaceView instances. To
verify that this is supported, run the SurfaceViewExtensionPreviewTest.java
CTS module.
Vendor specific session types
The feature enables vendor extension implementations to select a vendor specific session type that will be set in the internal camera capture session instead of the default value.
The feature works entirely within the framework and vendor stack and has no client/public visible API impact.
To select a vendor-specific session type, implement the following for your extension libraries:
* ExtenderStateListener.onSessionType() for basic extensions
* Camera2SessionConfigImpl.getSessionType() for advanced extensions
Extensions interface version history
The following table shows the Camera Extension interface version history. You should always implement the vendor library with the latest version.
| Version | Added features |
|---|---|
| 1.0.0 |
|
| 1.1.0 |
|
| 1.2.0 |
|
| 1.3.0 |
|
| 1.4.0 |
|
Reference implementation
The following reference OEM vendor library implementations are available in
frameworks/ex.
advancedSample: A basic implementation of Advanced Extender.sample: A basic implementation of Basic Extender.service_based_sample: An implementation that demonstrates how to host Camera Extensions in aService. This implementation contains the following components:oem_library: A Camera Extensions OEM library for Camera2 and CameraX Extensions APIs that implementsExtensions-Interface. This acts as a passthrough that forwards calls fromExtensions-Interfaceto the service. This library also provides AIDL files and wrapper classes to communicate with the service.Advanced Extender is enabled by default. To enable the Basic Extender, change
ExtensionsVersionImpl#isAdvancedExtenderImplementedto returnfalse.extensions_service: A sample implementation of the Extensions Service. Add your implementation here. The interface to implement in the service is similar to theExtensions-Interface. For example, implementing theIAdvancedExtenderImpl.Stubperforms the same operations asAdvancedExtenderImpl.ImageWrapperandTotalCaptureResultWrapperare required to makeImageandTotalCaptureResultparcelable.
Set up the vendor library on a device
The OEM vendor library isn't built into an app; it's loaded from the device
at runtime by Camera2/X. In CameraX, the <uses-library> tag declares
that the androidx.camera.extensions.impl library, which is defined in the
AndroidManifest.xml
file of the camera-extensions library, is a dependency of CameraX and must be
loaded at runtime. In Camera2, the framework loads an extensions service that
also declares that the <uses-library>loads the same
androidx.camera.extensions.impl library at runtime.
This allows third-party apps using extensions to automatically load the OEM vendor library. The OEM library is marked as optional so apps can run on devices that don't have the library on the device. Camera2/X handles this behavior automatically when an app tries to use a camera extension as long as the device manufacturer places the OEM library on the device so that it can be discovered by the app.
To set up the OEM library on a device, do the following:
- Add a permission file, which is required by the
<uses-library>tag, using the following format:/etc/permissions/ANY_FILENAME.xml. For example,/etc/permissions/camera_extensions.xml. The files in this directory provide a mapping of the library named in<uses-library>to the actual file path on the device. Use the example below to add the required information to the file.
namemust beandroidx.camera.extensions.implas that's the library that CameraX searches for.fileis the absolute path of the file that contains the extensions implementation (for example,/system/framework/androidx.camera.extensions.impl.jar).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <permissions> <library name="androidx.camera.extensions.impl" file="OEM_IMPLEMENTED_JAR" /> </permissions>
In Android 12 or higher, devices supporting CameraX
extensions must have the ro.camerax.extensions.enabled property set to true,
which allows for querying whether a device supports extensions.
To do this, add the following line in the device make file:
PRODUCT_VENDOR_PROPERTIES += \
ro.camerax.extensions.enabled=true \
Validation
To test your implementation of the OEM vendor library during the
development stage, use the example app at
androidx-main/camera/integration-tests/extensionstestapp/,
which runs through various vendor extensions.
After you complete your implementation, use the camera extensions validation tool to run automated and manual tests to verify that the vendor library is implemented correctly.
Extended scene mode versus camera extensions
For the bokeh extension, in addition to exposing it using camera extensions, you
can expose the extension using the extended scene mode, which is enabled through
the
CONTROL_EXTENDED_SCENE_MODE
key.
For more implementation details, see Camera bokeh.
Extended scene mode has fewer restrictions compared to camera extensions for
camera2 apps. For example, you can enable extended scene mode in
a regular CameraCaptureSession instance that supports flexible stream
combinations and capture request parameters. In contrast, camera extensions
support only a fixed set of stream types and have limited support for capture
request parameters.
A downside of extended scene mode is that you can only implement it in the camera HAL, which means that it must be verified to work across all orthogonal controls available to app developers.
We recommend exposing bokeh using both the extended scene mode and Camera Extensions because apps might prefer to use a particular API to enable bokeh. We recommend first using the extended scene mode because this is the most flexible way for apps to enable the bokeh extension. Then you can implement the camera extensions interface based on the extended scene mode. If implementing bokeh in the camera HAL is difficult, for example, because it requires a post processor running in the app layer to process images, we recommend implementing the bokeh extension using the Camera Extensions interface.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Are there any restrictions on API levels?
Yes. This depends on the Android API feature set that's required by the OEM
vendor library implementation. For example,
ExtenderStateListener.onPresetSession() uses the
SessionConfiguration.setSessionParameters()
call to set a baseline set of tags. This call is available only on API level
28 and higher. For details on specific interface methods, see the
API reference documentation.
