Questa pagina descrive in dettaglio le differenze di versione nelle HAL, nelle API e nei test associati della suite di test di compatibilità (Compatibility Test Suite, CTS). Vengono inoltre trattate diverse modifiche all'architettura apportate per rafforzare e proteggere il framework della fotocamera in Android 7.0, il passaggio a Treble in Android 8.0 e gli aggiornamenti che i fornitori devono apportare per supportare queste modifiche nelle implementazioni della fotocamera.
Terminologia
In questa pagina vengono utilizzati i seguenti termini:
- API Camera1
- Il framework della fotocamera a livello di app su dispositivi Android 4.4 e versioni precedenti, esposto
tramite la classe
android.hardware.Camera. - API Camera2
- Il framework della fotocamera a livello di app sui dispositivi Android 5.0 e versioni successive, esposto
tramite il pacchetto
android.hardware.camera2. - HAL della fotocamera
- Il livello del modulo della videocamera implementato dai fornitori di SoC. I framework pubblici a livello di app sono basati su HAL della fotocamera.
- Camera HAL3.1
- Versione dell'HAL del dispositivo videocamera rilasciata con Android 4.4.
- Camera HAL3.2
- Versione dell'HAL del dispositivo videocamera rilasciata con Android 5.0.
- Camera API1 CTS
- Set di test CTS della videocamera eseguiti sopra l'API Camera1.
- CTS API2 fotocamera
- Set aggiuntivo di test CTS della fotocamera che vengono eseguiti sopra l'API Camera2.
- Alti
- Separa l'implementazione del fornitore (software specifico per il dispositivo di livello inferiore scritto dai produttori di silicio) dal framework del sistema operativo Android tramite una nuova interfaccia del fornitore.
- HIDL
- Linguaggio di definizione dell'interfaccia HAL introdotto con Treble e utilizzato per specificare l'interfaccia tra un HAL e i suoi utenti.
- VTS
- Test Suite fornitore introdotto insieme a Treble.
API Camera
Android include le seguenti API per la fotocamera.
API Camera1
Android 5.0 ha ritirato l'API Camera1, che continua a essere eliminata man mano che il nuovo sviluppo della piattaforma si concentra sull'API Camera2. Tuttavia, il periodo di ritiro sarà lungo e le release di Android continueranno a supportare le app con API Camera1 per un po' di tempo. Nello specifico, l'assistenza continua per:
- Interfacce API1 della fotocamera per le app. Le app per la videocamera create sulla base dell'API Camera1 dovrebbero funzionare come sui dispositivi con versioni di Android precedenti.
- Versioni di Camera HAL. Include il supporto per Camera HAL1.0.
API Camera2
Il framework Camera API2 espone il controllo della fotocamera di livello inferiore all'app, inclusi flussi di streaming/scatto a raffica efficienti senza copia e controlli per frame di esposizione, guadagno, guadagni del bilanciamento del bianco, conversione del colore, riduzione del rumore, nitidezza e altro ancora. Per maggiori dettagli, guarda il video di riepilogo di Google I/O.
Android 5.0 e versioni successive includono l'API Camera2. Tuttavia, i dispositivi con Android
5.0 e versioni successive potrebbero non supportare tutte le funzionalità dell'API Camera2. La proprietà
android.info.supportedHardwareLevel che le app possono interrogare
tramite le interfacce dell'API Camera2 segnala uno dei seguenti livelli di supporto:
LEGACY: questi dispositivi espongono funzionalità alle app tramite le interfacce dell'API Camera2, che sono all'incirca le stesse funzionalità esposte alle app tramite le interfacce dell'API Camera1. Il concetto di codice dei framework legacy traduce concettualmente le chiamate dell'API Camera2 in chiamate dell'API Camera1. I dispositivi legacy non supportano le funzionalità dell'API Camera2, come i controlli per frame.LIMITED: Questi dispositivi supportano alcune funzionalità dell'API Camera2 (ma non tutte) e devono utilizzare Camera HAL 3.2 o versioni successive.FULL: questi dispositivi supportano tutte le funzionalità principali dell'API Camera2 e devono utilizzare Camera HAL 3.2 o versioni successive e Android 5.0 o versioni successive.LEVEL_3: Questi dispositivi supportano l'elaborazione YUV e l'acquisizione di immagini RAW, oltre a configurazioni aggiuntive dello stream di output.EXTERNAL: Questi dispositivi sono simili ai dispositiviLIMITEDcon alcune eccezioni; ad esempio, alcune informazioni su sensori o obiettivi potrebbero non essere segnalate o avere frame rate meno stabili. Questo livello viene utilizzato per le videocamere esterne, come le webcam USB.
Le funzionalità individuali sono esposte tramite la proprietà
android.request.availableCapabilities nelle interfacce dell'API Camera2. I dispositivi FULL richiedono, tra le altre, le funzionalità MANUAL_SENSOR e
MANUAL_POST_PROCESSING. La funzionalità
RAW è facoltativa anche per i dispositivi FULL.
I dispositivi LIMITED possono pubblicizzare qualsiasi sottoinsieme di queste funzionalità,
incluso nessuno. Tuttavia, la funzionalità BACKWARD_COMPATIBLE
deve essere sempre definita.
Il livello hardware supportato del dispositivo, nonché le funzionalità specifiche dell'API Camera2 che supporta, sono disponibili come seguenti flag di funzionalità per consentire il filtro di Google Play delle app per fotocamere API2.
android.hardware.camera.hardware_level.fullandroid.hardware.camera.capability.rawandroid.hardware.camera.capability.manual_sensorandroid.hardware.camera.capability.manual_post_processing
Requisiti CTS
I dispositivi con Android 5.0 e versioni successive devono superare i test CTS per l'API Camera1, l'API Camera2 e CTS Verifier.
I dispositivi che non dispongono di un'implementazione di Camera HAL3.2 e non sono
in grado di supportare le interfacce complete di Camera API2 devono comunque superare i test CTS di Camera
API2. Tuttavia, il dispositivo viene eseguito in modalità API Camera2
LEGACY (in cui le chiamate API Camera2 vengono mappate concettualmente
alle chiamate API Camera1), quindi tutti i test CTS API Camera2 relativi a funzionalità o
capacità oltre l'API Camera1 vengono ignorati automaticamente.
Sui dispositivi legacy, i test CTS dell'API Camera2 eseguiti utilizzano le interfacce e le funzionalità dell'API Camera1 pubbliche esistenti senza nuovi requisiti. I bug esposti (e che causano un errore CTS dell'API Camera2) sono bug già presenti nell'HAL della fotocamera esistente del dispositivo e quindi verrebbero rilevati dalle app API Camera1 esistenti. Non prevediamo molti bug di questo tipo (tuttavia, eventuali bug di questo tipo devono essere corretti per superare i test CTS dell'API Camera2).
Requisiti VTS
I dispositivi con Android 8.0 e versioni successive con implementazioni HAL binderizzate devono superare i test VTS della fotocamera.
Rafforzamento del framework della fotocamera
Per rafforzare la sicurezza del framework di media e fotocamera, Android 7.0 sposta il servizio fotocamera fuori da mediaserver. A partire da Android 8.0, ogni HAL della fotocamera binderizzato viene eseguito in un processo separato dal servizio fotocamera. I fornitori potrebbero dover apportare modifiche all'HAL della fotocamera a seconda delle versioni dell'API e dell'HAL in uso. Le sezioni seguenti descrivono in dettaglio le modifiche all'architettura in AP1 e AP2 per HAL1 e HAL3, nonché i requisiti generali.
Modifiche all'architettura per l'API1
La registrazione video API1 potrebbe presupporre che la videocamera e il codificatore video si trovino nello stesso processo. Quando utilizzi API1 su:
- HAL3, in cui il servizio della videocamera utilizza BufferQueue per passare i buffer tra i processi, non è necessario alcun aggiornamento del fornitore.
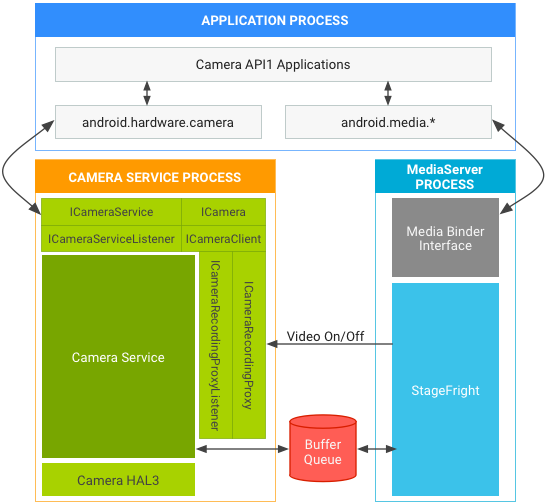
Figura 1. Stack di fotocamera e contenuti multimediali di Android 7.0 in API1 su HAL3
- HAL1, che supporta il passaggio di metadati nei buffer video, i fornitori devono
aggiornare l'HAL per utilizzare
kMetadataBufferTypeNativeHandleSource. (kMetadataBufferTypeCameraSourcenon è più supportato in Android 7.0.)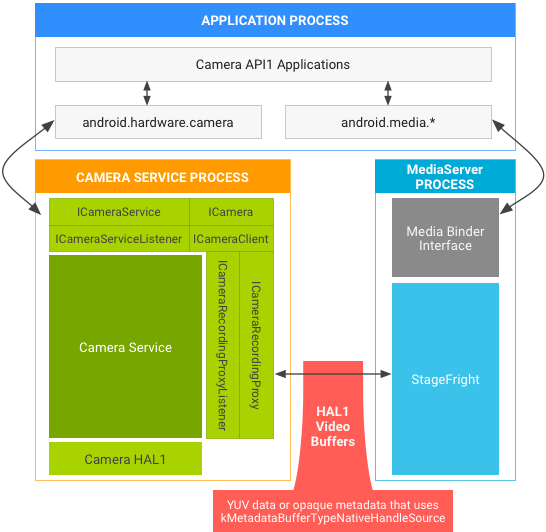
Figura 2. Stack di fotocamera e contenuti multimediali di Android 7.0 in API1 su HAL1
Modifiche all'architettura per l'API2
Per API2 su HAL1 o HAL3, BufferQueue passa i buffer, quindi questi percorsi continuano a funzionare. L'architettura di Android 7.0 per API2 su:
- HAL1 non è interessato dallo spostamento di cameraservice e non è necessario alcun aggiornamento del fornitore.
- HAL3 è interessato, ma non è necessario alcun aggiornamento del fornitore:
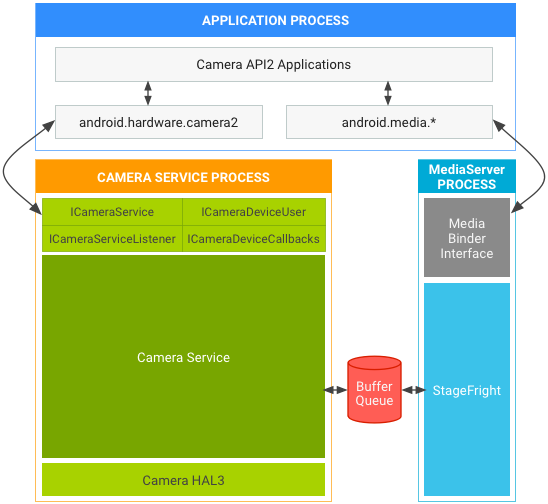
Figura 3. Stack di fotocamera e media di Android 7.0 in API2 su HAL3
Requisiti aggiuntivi
Le modifiche all'architettura apportate per rafforzare la sicurezza del framework di media e della videocamera includono i seguenti requisiti aggiuntivi per i dispositivi.
- Generale. I dispositivi richiedono una larghezza di banda aggiuntiva a causa di IPC,
che potrebbe influire sui casi d'uso della videocamera sensibili al tempo, come la registrazione
video ad alta velocità. I fornitori possono misurare l'impatto effettivo eseguendo
android.hardware.camera2.cts.PerformanceTeste l'app Google Fotocamera per la registrazione video ad alta velocità a 120/240 FPS. I dispositivi richiedono anche una piccola quantità di RAM aggiuntiva per creare il nuovo processo. - Passa i metadati nei buffer video (solo HAL1). Se HAL1
memorizza i metadati anziché i dati dei frame YUV reali nei buffer video, HAL deve
utilizzare
kMetadataBufferTypeNativeHandleSourcecome tipo di buffer di metadati e passareVideoNativeHandleMetadatanei buffer video. (kMetadataBufferTypeCameraSourcenon è più supportato su Android 7.0.) ConVideoNativeHandleMetadata, i framework di fotocamera e contenuti multimediali sono in grado di passare i buffer video tra i processi serializzando e deserializzando correttamente gli handle nativi. - L'indirizzo dell'handle del buffer non memorizza sempre lo stesso buffer (solo HAL3). Per ogni richiesta di acquisizione, HAL3 riceve gli indirizzi degli handle del buffer. HAL non può utilizzare gli indirizzi per identificare i buffer perché gli indirizzi potrebbero memorizzare un altro handle del buffer dopo che HAL restituisce il buffer. Devi aggiornare l'HAL per utilizzare gli handle dei buffer per identificare i buffer. Ad esempio, HAL riceve un indirizzo di handle del buffer A, che memorizza l'handle del buffer A. Dopo che HAL restituisce l'handle del buffer A, l'indirizzo dell'handle del buffer A potrebbe memorizzare l'handle del buffer B la volta successiva che HAL lo riceve.
- Aggiorna le policy SELinux per cameraserver. Se le policy SELinux specifiche del dispositivo concedono a mediaserver le autorizzazioni per eseguire la fotocamera, devi aggiornare le policy SELinux per concedere a cameraserver le autorizzazioni appropriate. Sconsigliamo di replicare le norme SELinux di mediaserver per cameraserver (in quanto mediaserver e cameraserver in genere richiedono risorse diverse nel sistema). Cameraserver deve disporre solo delle autorizzazioni necessarie per eseguire le funzionalità della fotocamera e tutte le autorizzazioni non necessarie relative alla fotocamera in mediaserver devono essere rimosse.
- Separazione tra Camera HAL e cameraserver. Android 8.0 e versioni successive separano inoltre l'HAL della videocamera binderizzato in un processo diverso da cameraserver. L'IPC passa attraverso interfacce definite da HIDL.
Convalida
Per tutti i dispositivi che includono una videocamera ed eseguono Android 7.0, verifica l'implementazione eseguendo il CTS di Android 7.0. Sebbene Android 7.0 non includa nuovi test CTS che verificano le modifiche al servizio fotocamera, i test CTS esistenti non riescono se non hai eseguito gli aggiornamenti indicati sopra.
Per tutti i dispositivi che includono una videocamera ed eseguono Android 8.0 e versioni successive, verifica l'implementazione del fornitore eseguendo VTS.
Cronologia delle versioni di Fotocamera HAL
Per un elenco dei test disponibili per la valutazione dell'HAL della videocamera Android, consulta l'elenco di controllo per il test dell'HAL della videocamera.
Android 10
Android 10 introduce i seguenti aggiornamenti.
API Camera
- Miglioramenti multi-camera che consentono di utilizzare le videocamere fisiche singolarmente o tramite le videocamere logiche corrispondenti nascondendo gli ID delle videocamere fisiche. Vedi Supporto della modalità multicamera.
- Possibilità di verificare se una determinata configurazione di sessione è
supportata senza il sovraccarico delle prestazioni dovuto alla creazione di una nuova sessione.
Vedi
CameraDevice. - Possibilità di recuperare le configurazioni di stream consigliate per un determinato caso d'uso per rendere il client più efficiente e performante. Vedi
getRecommendedStreamConfigurationMap. - Supporto del formato immagine JPEG con profondità. Per ulteriori dettagli, consulta la specifica Dynamic Depth.
- Supporto per il formato immagine HEIC. Consulta la sezione Immagini HEIF.
- Miglioramenti alla privacy. Perché il client disponga delle autorizzazioni
CAMERAprima di poterle recuperare daCameraCharacteristics, sono necessarie determinate chiavi. VedigetKeysNeedingPermission.
HAL della fotocamera
Le seguenti versioni di Camera HAL vengono aggiornate in Android 10.
3.5
ICameraDevice
-
getPhysicalCameraCharacteristics: Le informazioni statiche della videocamera per un ID videocamera fisica che supporta una videocamera logica. Vedi Supporto della modalità multicamera. isStreamCombinationSupported: questo metodo supporta un'API pubblica che aiuta i client a verificare se una configurazione di sessione è supportata. Consulta l'API per eseguire query sulle combinazioni di stream.
ICameraDeviceSession
-
isReconfigurationNeeded: Metodo che indica al framework della videocamera se è necessaria una riconfigurazione completa dello stream per i possibili nuovi valori dei parametri di sessione. Ciò consente di evitare ritardi non necessari nella riconfigurazione della videocamera. Consulta Query di riconfigurazione della sessione. - API di gestione dei buffer HAL: queste API consentono all'HAL della fotocamera di richiedere buffer dal framework della fotocamera solo quando necessario, anziché accoppiare ogni richiesta di acquisizione con i buffer associati durante la pipeline della fotocamera, con conseguente risparmio di memoria potenzialmente significativo.
-
signalStreamFlush: segnala all'HAL che il servizio della videocamera sta per eseguireconfigureStreams_3_5e che l'HAL deve restituire tutti i buffer degli stream designati. -
configureStreams_3_5: simile aICameraDevice3.4.configureStreams, ma in più viene fornito il contatorestreamConfigCounterper verificare una condizione di competizione tra le chiamateconfigureStreams_3_5esignalStreamFlush.
-
Aggiornamenti a ICameraDeviceCallback:
-
requestStreamBuffers: Callback sincrono che la HAL della fotocamera chiama per chiedere al server della fotocamera i buffer. VedirequestStreamBuffers. -
returnStreamBuffers: Callback sincrono per la HAL della fotocamera per restituire i buffer di output al server della fotocamera. VedireturnStreamBuffers.
3.4
Le seguenti chiavi vengono aggiunte ai metadati della videocamera in Android 10.
- Formati immagine
ANDROID_SCALER_AVAILABLE_FORMATS_RAW10ANDROID_SCALER_AVAILABLE_FORMATS_RAW12ANDROID_SCALER_AVAILABLE_FORMATS_Y8
- Tag dei metadati della videocamera
ANDROID_REQUEST_CHARACTERISTIC_KEYS_NEEDING_PERMISSIONANDROID_SCALER_AVAILABLE_RECOMMENDED_STREAM_CONFIGURATIONSANDROID_SCALER_AVAILABLE_RECOMMENDED_INPUT_OUTPUT_FORMATS_MAPANDROID_INFO_SUPPORTED_BUFFER_MANAGEMENT_VERSIONANDROID_DEPTH_AVAILABLE_RECOMMENDED_DEPTH_STREAM_CONFIGURATIONSANDROID_DEPTH_AVAILABLE_DYNAMIC_DEPTH_STREAM_CONFIGURATIONSANDROID_DEPTH_AVAILABLE_DYNAMIC_DEPTH_MIN_FRAME_DURATIONSANDROID_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA_ACTIVE_PHYSICAL_IDANDROID_HEIC_AVAILABLE_HEIC_STREAM_CONFIGURATIONSANDROID_HEIC_AVAILABLE_HEIC_MIN_FRAME_DURATIONSANDROID_HEIC_AVAILABLE_HEIC_STALL_DURATIONSANDROID_HEIC_INFO_SUPPORTEDANDROID_HEIC_INFO_MAX_JPEG_APP_SEGMENTS_COUNT
- Funzionalità
-
ANDROID_REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_SECURE_IMAGE_DATA
-
- Valori per la chiave
ANDROID_SENSOR_INFO_COLOR_FILTER_ARRANGEMENTANDROID_SENSOR_INFO_COLOR_FILTER_ARRANGEMENT_MONOANDROID_SENSOR_INFO_COLOR_FILTER_ARRANGEMENT_NIR
- Configurazioni di stream di profondità dinamica disponibili
ANDROID_DEPTH_AVAILABLE_DYNAMIC_DEPTH_STREAM_CONFIGURATIONS_OUTPUTANDROID_DEPTH_AVAILABLE_DYNAMIC_DEPTH_STREAM_CONFIGURATIONS_INPUT
- Configurazioni di stream HEIC disponibili
-
ANDROID_HEIC_AVAILABLE_HEIC_STREAM_CONFIGURATIONS_OUTPUT ANDROID_HEIC_AVAILABLE_HEIC_STREAM_CONFIGURATIONS_INPUT
-
Modulo della videocamera
Le seguenti versioni del modulo della videocamera vengono aggiornate in Android 10.
2,5
- Aggiunge il metodo
notifyDeviceStateChangeper consentire ai dispositivi di notificare l'HAL della fotocamera quando modifiche fisiche, come la chiusura, influiscono sulla fotocamera e sul routing.
2.4
- I dispositivi lanciati con il livello API 29 o versioni successive DEVONO segnalare
trueperisTorchModeSupported.
Android 9
La release di Android 9 introduce i seguenti aggiornamenti all'API Camera2 e all'interfaccia HAL.
API Camera
- Introduce l'API multicamera per supportare meglio i dispositivi con più fotocamere rivolte nella stessa direzione, consentendo funzionalità come il bokeh e lo zoom continuo. Ciò consente alle app di visualizzare più videocamere su un dispositivo come un'unica unità logica (videocamera logica). Le richieste di acquisizione possono essere inviate anche a singoli dispositivi di videocamere inclusi in una videocamera logica. Vedi Supporto della modalità multicamera.
- Introduce i parametri sessione. I parametri di sessione sono un sottoinsieme dei parametri di acquisizione disponibili che possono causare gravi ritardi di elaborazione se modificati. Questi costi possono essere ridotti se i client trasmettono i valori iniziali durante l'inizializzazione della sessione di acquisizione. Consulta la sezione Parametri sessione.
- Aggiunge chiavi di dati di stabilizzazione ottica (OIS) per la stabilizzazione e gli effetti a livello di app. Vedi
STATISTICS_OIS_SAMPLES. - Aggiunge il supporto del flash esterno. Vedi
CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON_EXTERNAL_FLASH. - Aggiunge un intent di rilevamento del movimento in
CAPTURE_INTENT. VediCONTROL_CAPTURE_INTENT_MOTION_TRACKING. - Ritira
LENS_RADIAL_DISTORTIONe aggiungeLENS_DISTORTIONal suo posto. - Aggiunge modalità di correzione della distorsione in
CaptureRequest. VediDISTORTION_CORRECTION_MODE. - Aggiunge il supporto per le fotocamere esterne USB/UVC sui dispositivi supportati. Vedi
INFO_SUPPORTED_HARDWARE_LEVEL_EXTERNAL.
HAL della fotocamera
3.4
Aggiornamenti a ICameraDeviceSession
-
configureStreams_3_4: Aggiunge il supporto persessionParameterse le videocamere logiche. -
processCaptureRequest_3_4: Aggiunge il supporto per l'inclusione degli ID videocamera fisici nella struttura dello stream.
Aggiornamenti a ICameraDeviceCallback
-
processCaptureResult_3_4: aggiunge i metadati della videocamera fisica nei risultati di acquisizione.
3.3
In Android 9 vengono aggiunte le seguenti chiavi ai metadati della fotocamera.
- Funzionalità
ANDROID_REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERAANDROID_REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_MOTION_TRACKINGANDROID_REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_MONOCHROME
- Tag dei metadati della videocamera
ANDROID_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA_PHYSICAL_IDSANDROID_LOGICAL_MULTI_CAMERA_SENSOR_SYNC_TYPEANDROID_DISTORTION_CORRECTION_AVAILABLE_MODESANDROID_LENS_POSE_REFERENCE-
ANDROID_LENS_DISTORTION ANDROID_REQUEST_AVAILABLE_SESSION_KEYSANDROID_REQUEST_AVAILABLE_PHYSICAL_CAMERA_REQUEST_KEYSANDROID_STATISTICS_OIS_DATA_MODEANDROID_STATISTICS_OIS_TIMESTAMPSANDROID_STATISTICS_OIS_X_SHIFTSANDROID_STATISTICS_OIS_Y_SHIFTS
Android 8.0
La release Android 8.0 introduce Treble. Con Treble, le implementazioni della Camera HAL del fornitore devono essere binderizzate. Android 8.0 contiene anche i seguenti miglioramenti chiave al servizio Fotocamera:
- Superfici condivise: attiva più superfici che condividono lo stesso
OutputConfiguration - API di sistema per modalità della fotocamera personalizzate
onCaptureQueueEmpty
Per saperne di più su queste funzionalità, consulta le sezioni seguenti.
Superfici condivise
Questa funzionalità consente a un solo set di buffer di gestire due output, ad esempio l'anteprima e la codifica video, riducendo il consumo di energia e memoria. Per supportare questa funzionalità, i produttori di dispositivi devono assicurarsi che le implementazioni HAL della videocamera e HAL di gralloc possano creare buffer gralloc utilizzati da più consumatori diversi (come il compositore hardware/GPU e il codificatore video), anziché da un solo consumatore. Il servizio della videocamera passa i flag di utilizzo dei consumatori all'HAL della videocamera e all'HAL gralloc; questi devono allocare i tipi giusti di buffer oppure l'HAL della videocamera deve restituire un errore che indica che questa combinazione di consumatori non è supportata.
Per ulteriori dettagli, consulta la
enableSurfaceSharingdocumentazione per sviluppatori.
API di sistema per modalità della fotocamera personalizzate
L'API fotocamera pubblica definisce due modalità di funzionamento: normale e registrazione ad alta velocità vincolata. Hanno semantiche piuttosto diverse; ad esempio,
la modalità ad alta velocità è limitata a un massimo di due uscite specifiche contemporaneamente. Diversi
OEM hanno espresso interesse a definire altre modalità personalizzate per
funzionalità specifiche dell'hardware. A livello di codice, la modalità è solo un numero intero
passato a configure_streams. Vedi:
hardware/camera/device/3.2/ICameraDeviceSession#configurestreams.
Questa funzionalità include una chiamata API di sistema che le app fotocamera OEM possono utilizzare per attivare una modalità personalizzata. Queste modalità devono iniziare con il valore intero 0x8000 per evitare conflitti con le modalità future aggiunte all'API pubblica.
Per supportare questa funzionalità, gli OEM devono semplicemente aggiungere la nuova modalità al proprio HAL, attivata da questo numero intero passato all'HAL su configure_streams, e quindi fare in modo che la propria app fotocamera personalizzata utilizzi l'API di sistema.
Il nome del metodo è
android.hardware.camera2.CameraDevice#createCustomCaptureSession.
Vedi:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/camera2/CameraDevice.
onCaptureQueueEmpty
Lo scopo di questa API è ridurre la latenza delle modifiche ai controlli, come lo zoom, mantenendo la coda delle richieste il più vuota possibile. onCaptureQueueEmpty
non richiede alcun lavoro HAL; è stata aggiunta solo al framework. Le app che
vogliono sfruttarlo devono aggiungere un listener a questo callback e rispondere
in modo appropriato. In genere, ciò avviene inviando un'altra richiesta di acquisizione al dispositivo
della videocamera.
Interfaccia HIDL della fotocamera
L'interfaccia HIDL della fotocamera è una revisione completa dell'interfaccia HAL della fotocamera che utilizza API HIDL stabili. Tutte le funzionalità e le capacità della videocamera introdotte nelle versioni legacy più recenti 3.4 e 2.4 (per il modulo della videocamera) fanno parte anche delle definizioni HIDL.
3.4
Piccole aggiunte ai metadati supportati e modifiche al supporto di data_space:
- Aggiungi i metadati statici
ANDROID_SENSOR_OPAQUE_RAW_SIZEcome obbligatori se il formatoRAW_OPAQUEè supportato. - Aggiungi i metadati statici
ANDROID_CONTROL_POST_RAW_SENSITIVITY_BOOST_RANGEcome obbligatori se è supportato un formato RAW. - Passa al campo
camera3_stream_t data_spaceper una definizione più flessibile, utilizzando la definizione della versione 0 della codifica dello spazio dei dati. - Aggiunte di metadati generali disponibili per l'utilizzo per HAL v3.2 o versioni successive:
-
ANDROID_INFO_SUPPORTED_HARDWARE_LEVEL_3 ANDROID_CONTROL_POST_RAW_SENSITIVITY_BOOSTANDROID_CONTROL_POST_RAW_SENSITIVITY_BOOST_RANGEANDROID_SENSOR_DYNAMIC_BLACK_LEVELANDROID_SENSOR_DYNAMIC_WHITE_LEVELANDROID_SENSOR_OPAQUE_RAW_SIZEANDROID_SENSOR_OPTICAL_BLACK_REGIONS
-
3.3
Revisione secondaria dell'HAL con funzionalità estese:
- Aggiornamenti delle API di rielaborazione OPAQUE e YUV.
- Supporto di base per i buffer di output della profondità.
- Aggiunta del campo
data_spaceacamera3_stream_t. - Aggiunta del campo di rotazione a
camera3_stream_t. - Aggiunta della modalità di funzionamento della configurazione dello stream camera3 a
camera3_stream_configuration_t.
3.2
Revisione secondaria dell'HAL con funzionalità estese:
- Depreca
get_metadata_vendor_tag_ops. Utilizzaget_vendor_tag_opsincamera_common.h. - Depreca
register_stream_buffers. Tutti i buffer gralloc forniti dal framework all'HAL inprocess_capture_requestpotrebbero essere nuovi in qualsiasi momento. - Aggiungi il supporto dei risultati parziali.
process_capture_resultpotrebbe essere chiamato più volte con un sottoinsieme dei risultati disponibili prima che il risultato completo sia disponibile. - Aggiungi il modello manuale a
camera3_request_template. Le app possono utilizzare questo modello per controllare direttamente le impostazioni di acquisizione. - Rielabora le specifiche del flusso bidirezionale e di input.
- Modifica il percorso di ritorno del buffer di input. Il buffer viene restituito in
process_capture_resultanziché inprocess_capture_request.
3.1
Revisione secondaria dell'HAL con funzionalità estese:
configure_streamspassa i flag di utilizzo dei consumatori all'HAL.- Chiamata di svuotamento per eliminare tutte le richieste/buffer in corso il più rapidamente possibile.
3,0
Prima revisione dell'HAL con funzionalità estese:
- Modifica della versione principale poiché l'ABI è completamente diverso. Nessuna modifica alle funzionalità hardware richieste o al modello operativo rispetto alla versione 2.0.
- Interfacce di richiesta di input e coda di stream rielaborate: il framework chiama HAL con i buffer di richiesta e stream successivi già rimossi dalla coda. Il supporto del framework di sincronizzazione è incluso, necessario per implementazioni efficienti.
- Gli attivatori sono stati spostati nelle richieste, la maggior parte delle notifiche nei risultati.
- Consolidato tutti i callback nel framework in un'unica struttura e tutti i metodi di impostazione
in una singola chiamata
initialize(). - La configurazione dello stream è stata trasformata in una singola chiamata per semplificare la gestione dello stream.
Gli stream bidirezionali sostituiscono il costrutto
STREAM_FROM_STREAM. - Semantica della modalità limitata per dispositivi hardware meno recenti/limitati.
2,0
Versione iniziale di HAL con funzionalità estese (Android 4.2) [camera2.h]:
- Sufficienti per implementare l'API
android.hardware.Cameraesistente. - Consente la coda ZSL nel livello di servizio della fotocamera.
- Non testato per nuove funzionalità come il controllo manuale dell'acquisizione, l'acquisizione Bayer RAW, il ritrattamento dei dati RAW e così via.
1.0
HAL della fotocamera Android iniziale (Android 4.0) [camera.h]:
- Convertito dal livello di astrazione CameraHardwareInterface C++.
- Supporta l'API
android.hardware.Camera.
Cronologia delle versioni del modulo della videocamera
Questa sezione contiene informazioni sul controllo delle versioni dei moduli per il modulo hardware della videocamera, in base a camera_module_t.common.module_api_version. Le due cifre esadecimali
più significative rappresentano la versione principale, mentre le due meno
significative rappresentano la versione secondaria.
2.4
Questa versione del modulo della videocamera aggiunge le seguenti modifiche all'API:
- Supporto della modalità Torcia. Il framework può attivare la modalità torcia per qualsiasi
dispositivo videocamera dotato di un'unità flash, senza aprire un dispositivo videocamera. Il
dispositivo fotocamera ha una priorità più alta di accesso al flash rispetto al modulo
fotocamera; l'apertura di un dispositivo fotocamera disattiva la torcia se era stata attivata
tramite l'interfaccia del modulo. Quando si verificano conflitti di risorse, ad esempio
viene chiamato
open()per aprire un dispositivo videocamera, il modulo HAL della videocamera deve notificare al framework tramite il callback dello stato della modalità torcia che la modalità torcia è stata disattivata. - Supporto di videocamere esterne (ad esempio, videocamera USB hot-plug). Gli aggiornamenti
dell'API specificano che le informazioni statiche della videocamera sono disponibili solo quando la videocamera
è connessa e pronta per l'uso per le videocamere hot-plug esterne. Le chiamate per ottenere informazioni statiche
non sono valide quando lo stato della videocamera non è
CAMERA_DEVICE_STATUS_PRESENT. Il framework si basa esclusivamente sui callback di modifica dello stato del dispositivo per gestire l'elenco delle fotocamere esterne disponibili. - Suggerimenti per l'arbitrato della videocamera. Aggiunge il supporto per indicare esplicitamente
il numero di dispositivi videocamera che possono essere aperti e utilizzati contemporaneamente. Per specificare combinazioni valide di dispositivi, i campi
resource_costeconflicting_devicesdevono essere sempre impostati nella strutturacamera_inforestituita dalla chiamataget_camera_info. - Metodo di inizializzazione del modulo. Chiamato dal servizio della videocamera dopo il caricamento del modulo HAL per consentire l'inizializzazione una tantum di HAL. Viene chiamato prima di qualsiasi altro metodo del modulo.
2.3
Questa versione del modulo della videocamera aggiunge il supporto del dispositivo HAL della videocamera legacy aperto.
Il framework può utilizzarlo per aprire il dispositivo della videocamera come versione HAL del dispositivo inferiore
HAL se lo stesso dispositivo può supportare più versioni dell'API del dispositivo.
La chiamata aperta del modulo hardware standard
(common.methods->open) continua
ad aprire il dispositivo della videocamera con l'ultima versione supportata, che è
anche la versione elencata in camera_info_t.device_version.
2.2
Questa versione del modulo della videocamera aggiunge il supporto dei tag del fornitore dal modulo e
ritira i vecchi vendor_tag_query_ops che in precedenza erano accessibili solo
con un dispositivo aperto.
2.1
Questa versione del modulo della videocamera aggiunge il supporto per i callback asincroni al
framework dal modulo HAL della videocamera, che viene utilizzato per notificare al framework
le modifiche allo stato del modulo della videocamera. I moduli che forniscono un metodo set_callbacks() valido devono segnalare almeno questo numero di versione.
2,0
I moduli della videocamera che segnalano questo numero di versione implementano la seconda versione
dell'interfaccia HAL del modulo della videocamera. I dispositivi di videocamera apribili tramite questo
modulo potrebbero supportare la versione 1.0 o la versione 2.0 dell'interfaccia
HAL del dispositivo di videocamera. Il campo device_version di camera_info è sempre valido; il campo static_camera_characteristics di camera_info è valido se il campo device_version è 2.0 o superiore.
1.0
I moduli della videocamera che segnalano questi numeri di versione implementano l'interfaccia HAL iniziale del modulo della videocamera. Tutti i dispositivi videocamera apribili tramite questo modulo supportano solo la versione 1 di HAL del dispositivo videocamera. I campi
device_version e static_camera_characteristics
di camera_info non sono validi. Solo l'API
android.hardware.Camera può essere supportata da questo modulo e dai suoi
dispositivi.
