Producenci urządzeń mogą udostępniać rozszerzenia takie jak bokeh, tryb nocny i HDR deweloperom zewnętrznym za pomocą interfejsu rozszerzeń aparatu udostępnianego przez bibliotekę dostawcy OEM. Deweloperzy mogą używać interfejsu Camera2 Extensions API i interfejsu CameraX Extensions API, aby uzyskać dostęp do rozszerzeń zaimplementowanych w bibliotece dostawcy OEM.
Listę obsługiwanych rozszerzeń, która jest taka sama w przypadku interfejsów Camera2 i CameraX, znajdziesz w artykule Interfejs CameraX Extensions API. Jeśli chcesz dodać rozszerzenie, zgłoś błąd w narzędziu Issue Tracker.
Z tego artykułu dowiesz się, jak wdrożyć i włączyć bibliotekę dostawcy OEM na urządzeniach.
Architektura
Poniższy diagram przedstawia architekturę interfejsu Camera Extensions lub extensions-interface: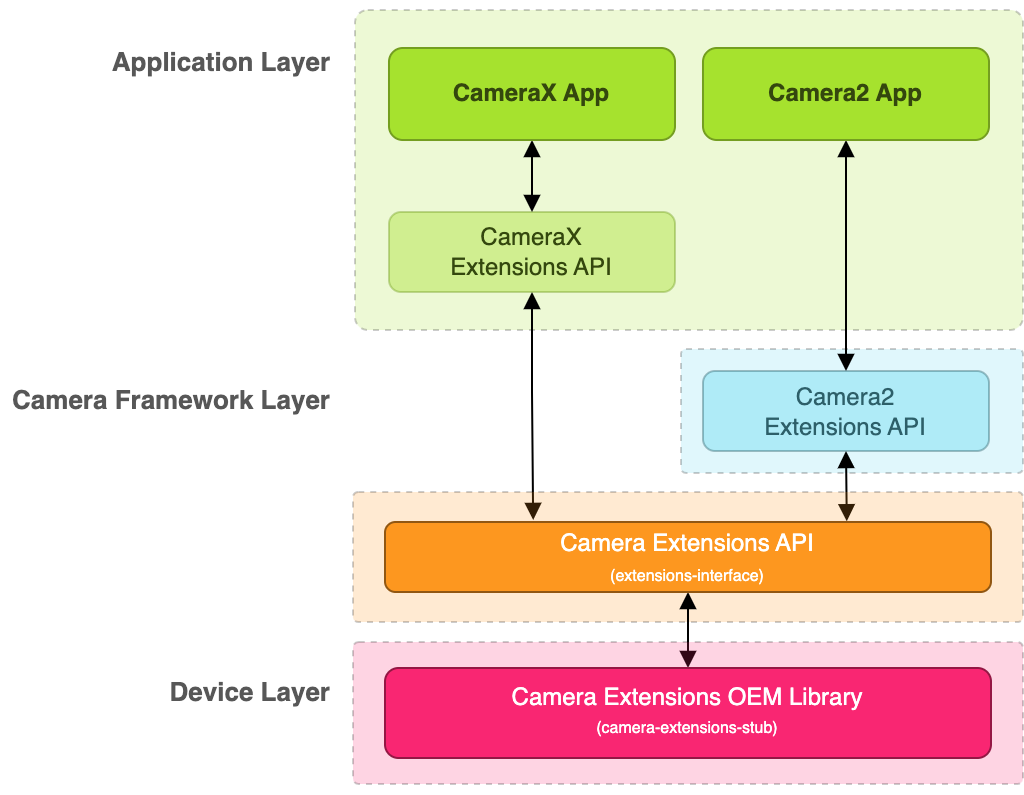
Rysunek 1. Schemat architektury rozszerzeń aparatu
Jak widać na diagramie, aby obsługiwać rozszerzenia aparatu, musisz zaimplementować interfejs extensions-interface udostępniony przez bibliotekę dostawcy OEM. Biblioteka dostawcy OEM udostępnia 2 interfejsy API: CameraX Extensions API i Camera2 Extensions API, które są używane odpowiednio przez aplikacje CameraX i Camera2 do uzyskiwania dostępu do rozszerzeń dostawcy.
Implementowanie biblioteki dostawcy OEM
Aby wdrożyć bibliotekę dostawcy OEM, skopiuj pliki
camera-extensions-stub
do projektu biblioteki systemowej. Te pliki definiują interfejs Camera Extensions.
camera-extensions-stub pliki są podzielone na te kategorie:
Niezbędne pliki interfejsu (nie modyfikuj)
PreviewExtenderImpl.javaImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaExtenderStateListener.javaProcessorImpl.javaPreviewImageProcessorImpl.javaCaptureProcessorImpl.javaCaptureStageImpl.javaRequestUpdateProcessorImpl.javaProcessResultImpl.javaadvanced/AdvancedExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/Camera2OutputConfigImpl.javaadvanced/Camera2SessionConfigImpl.javaadvanced/ImageProcessorImpl.javaadvanced/ImageReaderOutputConfigImpl.javaadvanced/ImageReferenceImpl.javaadvanced/MultiResolutionImageReaderOutputConfigImpl.javaadvanced/OutputSurfaceImpl.javaadvanced/RequestProcessorImpl.javaadvanced/SessionProcessorImpl.javaadvanced/SurfaceOutputConfigImpl.java
Obowiązkowe implementacje (dodaj swoją implementację)
ExtensionVersionImpl.javaInitializerImpl.java
Klasy rozszerzające efekt bokeh (wdrażaj je, jeśli rozszerzenie efektu bokeh jest obsługiwane)
BokehImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaBokehPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/BokehAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Klasy rozszerzające noc (wdrażaj je, jeśli rozszerzenie nocne jest obsługiwane)
NightImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaNightPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/NightAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Klasy automatycznego rozszerzania (wdrażaj je, jeśli obsługiwane jest automatyczne rozszerzanie)
AutoImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaAutoPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/AutoAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Klasy rozszerzające HDR (wdrażaj je, jeśli rozszerzenie HDR jest obsługiwane)
HdrImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaHdrPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/HdrAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Klasy rozszerzające retusz twarzy (wdrażaj je, jeśli rozszerzenie retuszu twarzy jest obsługiwane)
BeautyImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaBeautyPreviewExtenderImpl.javaadvanced/BeautyAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Narzędzia (opcjonalnie, można usunąć)
advanced/Camera2OutputConfigImplBuilder.javaadvanced/Camera2SessionConfigImplBuilder.java
Nie musisz podawać implementacji dla każdego rozszerzenia. Jeśli nie implementujesz rozszerzenia, ustaw isExtensionAvailable(), aby zwracać false, lub usuń odpowiednie klasy Extender. Interfejsy API Camera2 i CameraX Extensions informują aplikację, że rozszerzenie jest niedostępne.
Przyjrzyjmy się, jak interfejsy Camera2 i CameraX Extensions API współpracują z biblioteką dostawcy, aby włączyć rozszerzenie. Poniższy diagram ilustruje cały proces na przykładzie rozszerzenia Night:
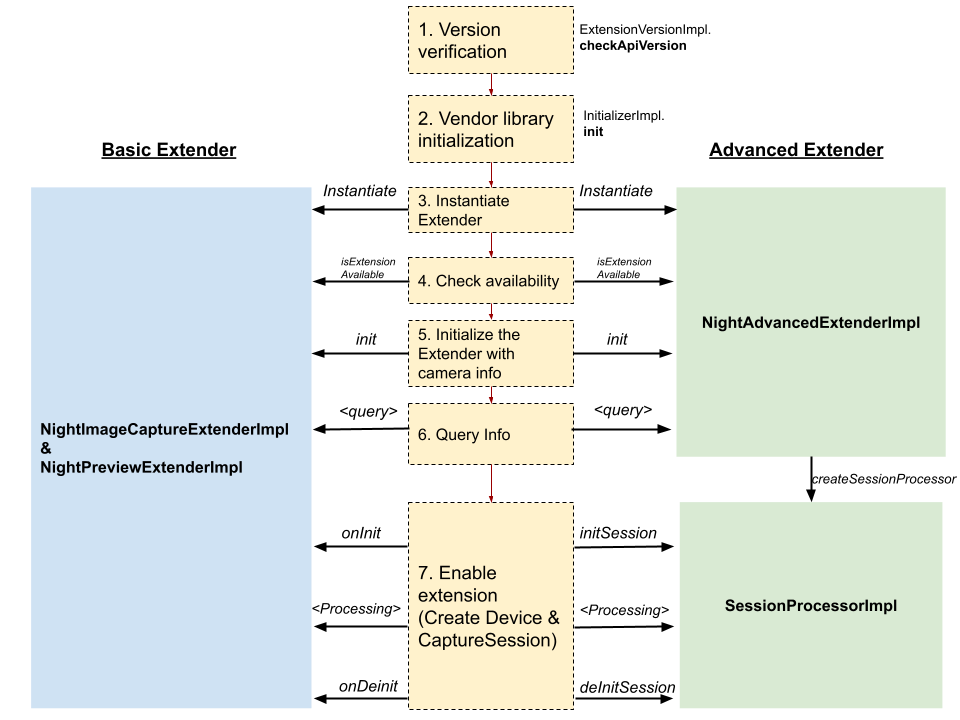
Rysunek 2. Wdrożenie rozszerzenia nocnego
Weryfikacja wersji:
Wywołania Camera2/X
ExtensionVersionImpl.checkApiVersion()zapewniają, że wersjaextensions-interfacezaimplementowana przez producenta OEM jest zgodna z wersjami obsługiwanymi przez Camera2/X.Inicjowanie biblioteki dostawcy:
InitializerImplma metodęinit(), która inicjuje bibliotekę dostawcy. Camera2/X kończy inicjowanie przed uzyskaniem dostępu do klas Extender.Utwórz instancje klas Extender:
Tworzy instancje klas Extender dla rozszerzenia. Istnieją 2 typy wzmacniaczy: podstawowy i zaawansowany. W przypadku wszystkich rozszerzeń musisz wdrożyć jeden typ Extender. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w artykule Podstawowy a zaawansowany moduł rozszerzający.
Camera2/X tworzy instancje klas Extender i wchodzi z nimi w interakcje, aby pobierać informacje i włączać rozszerzenie. W przypadku danego rozszerzenia interfejs Camera2/X może wielokrotnie tworzyć instancje klas Extender. Dlatego nie wykonuj w konstruktorze ani w wywołaniu
init()złożonych operacji inicjowania. Wykonuj wymagające obliczenia tylko wtedy, gdy sesja aparatu ma się rozpocząć, na przykład gdy w przypadku podstawowego rozszerzenia wywoływana jest funkcjaonInit()lub w przypadku zaawansowanego rozszerzenia wywoływana jest funkcjainitSession().W przypadku rozszerzenia Night dla typu Basic Extender tworzone są te klasy Extender:
NightImageCaptureExtenderImpl.javaNightPreviewExtenderImpl.java
W przypadku typu Advanced Extender:
NightAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
Sprawdź dostępność rozszerzenia:
Przed włączeniem rozszerzenia
isExtensionAvailable()sprawdza, czy rozszerzenie jest dostępne w przypadku określonego identyfikatora kamery za pomocą instancji Extender.Zainicjuj przedłużacz, podając informacje o kamerze:
Camera2/X wywołuje funkcję
init()w instancji Extender i przekazuje jej identyfikator aparatu orazCameraCharacteristics.Informacje o zapytaniu:
Wywołuje klasę Extender, aby pobrać informacje takie jak obsługiwane rozdzielczości, szacowane opóźnienie przechwytywania obrazu i klucze żądań z klasy Extender w ramach przygotowań do włączenia rozszerzenia.
Włącz rozszerzenie na wzmacniaczu:
Klasa Extender udostępnia wszystkie interfejsy potrzebne do włączenia klasy. Umożliwia on podłączenie implementacji OEM do potoku Camera2, np. wstrzykiwanie parametrów żądania przechwytywania lub włączanie postprocesora.
W przypadku typu Advanced Extender Camera2/X wchodzi w interakcję z
SessionProcessorImpl, aby włączyć rozszerzenie. Camera2/X pobiera instancjęSessionProcessorImpl, wywołująccreateSessionProcessor()na Extenderze.
W kolejnych sekcjach znajdziesz szczegółowy opis przepływu rozszerzenia.
Weryfikacja wersji
Podczas wczytywania biblioteki dostawcy OEM z urządzenia w czasie działania Camera2/X sprawdza, czy biblioteka jest zgodna z wersją extensions-interface.
extensions-interface używa wersji semantycznej, czyli GŁÓWNA.PODRZĘDNA.POPRAWKA, np. 1.1.0 lub 1.2.0. Podczas weryfikacji wersji używane są jednak tylko wersje główne i pomocnicze.
Aby sprawdzić wersję, wywołaj Camera2/XExtensionVersionImpl.checkApiVersion() z obsługiwanąextensions-interface wersją. Camera2/X używa następnie wersji podanej przez bibliotekę OEM, aby określić, czy rozszerzenie można włączyć i jakie funkcje powinno wywoływać.
Zgodność z wersją główną
Jeśli główne wersje interfejsu rozszerzenia różnią się między Camera2/X a biblioteką dostawcy, są one uznawane za niezgodne i rozszerzenie jest wyłączane.
Zgodność wsteczna
Jeśli wersja główna jest identyczna, Camera2/X zapewnia kompatybilność wsteczną z bibliotekami dostawców OEM utworzonymi w poprzednich wersjach extensions-interface. Jeśli na przykład Camera2/X obsługuje wersję 1.3.0, biblioteki dostawcy OEM, które implementują wersje 1.0.0, 1.1.0 i 1.2.0, nadal są zgodne.extensions-interface Oznacza to również, że po wdrożeniu określonej wersji biblioteki dostawcy interfejs Camera2/X zapewnia zgodność wsteczną biblioteki z przyszłymi wersjami extension-interface.
Zgodność w przyszłości
Zgodność z bibliotekami dostawców nowszych wersji extensions-interface
zależy od Ciebie, czyli producenta OEM. Jeśli do wdrożenia rozszerzeń potrzebujesz pewnych funkcji, możesz włączyć rozszerzenia od określonej wersji. W takim przypadku możesz zwrócić obsługiwaną wersję extensions-interface, gdy wersja biblioteki Camera2/X spełnia wymagania. Jeśli wersje Camera2/X nie są obsługiwane, możesz zwrócić niezgodną wersję, np. 99.0.0, aby wyłączyć rozszerzenia.
Inicjowanie biblioteki dostawcy
Po sprawdzeniu wersji extensions-interface zaimplementowanej przez bibliotekę OEM
Camera2/X rozpoczyna proces inicjowania. Metoda
InitializerImpl.init() informuje bibliotekę OEM, że aplikacja próbuje używać rozszerzeń.
Camera2/X nie wykonuje żadnych innych wywołań biblioteki OEM (poza sprawdzaniem wersji), dopóki biblioteka dostawcy OEM nie wywoła funkcji OnExtensionsInitializedCallback.onSuccess(), aby powiadomić o zakończeniu inicjowania.
Musisz wdrożyć
InitializerImpl
od wersji extensions-interface 1.1.0. Camera2/X pomija krok inicjowania biblioteki, jeśli biblioteka dostawcy OEM implementuje extensions-interface 1.0.0.
Podstawowe i zaawansowane przedłużenie platformy
Istnieją 2 typy implementacji: extensions-interface podstawowy i zaawansowany. Wzmacniacz zaawansowany jest obsługiwany od wersji extensions-interface 1.2.0.
Zaimplementuj podstawowy moduł rozszerzający w przypadku rozszerzeń, które przetwarzają obrazy w warstwie HAL aparatu lub korzystają z procesora końcowego zdolnego do przetwarzania strumieni YUV.
Zaimplementuj zaawansowany moduł rozszerzający w przypadku rozszerzeń, które wymagają dostosowania konfiguracji strumienia Camera2 i wysyłania żądań przechwytywania w razie potrzeby.
Porównanie znajdziesz w tej tabeli:
| Podstawowy przedłużacz | Zaawansowany wzmacniacz | |
|---|---|---|
| Konfiguracje strumienia | Stały Podgląd: PRIVATE lub YUV_420_888 (jeśli jest procesor) Zdjęcie: JPEG lub YUV_420_888 (jeśli jest procesor)
|
Możliwość dostosowania przez OEM. |
| Wysyłam prośbę o zrzut | Tylko Camera2/X może wysyłać żądania przechwytywania. Możesz ustawić parametry tych żądań. Gdy procesor jest dostępny do przechwytywania obrazów, Camera2/X może wysyłać wiele żądań przechwytywania i przesyłać wszystkie obrazy oraz wyniki przechwytywania do procesora. | Otrzymasz instancję RequestProcessorImpl, która umożliwia wykonanie żądania przechwytywania camera2 i uzyskanie wyników oraz obrazu.
Camera2/X wywołuje funkcje |
| Punkty zaczepienia w potoku kamery |
|
|
| Odpowiednie dla | Rozszerzenia zaimplementowane w warstwie HAL aparatu lub w procesorze, który przetwarza obrazy YUV. |
|
| Obsługiwana wersja interfejsu API | Rozszerzenia Camera2: Android 13 lub nowszy Rozszerzenia CameraX: camera-extensions 1.1.0 lub nowszy |
Rozszerzenia Camera2: Android 12L lub nowszy. Rozszerzenia CameraX: camera-extensions 1.2.0-alpha03 lub nowsze. |
Przepływy w aplikacji
W tabeli poniżej znajdziesz 3 typy przepływów aplikacji i odpowiadające im wywołania interfejsu Camera Extensions API. Interfejsy Camera2/X udostępniają te interfejsy API, ale aby obsługiwać te procesy, musisz prawidłowo wdrożyć bibliotekę dostawcy. Opisujemy to szczegółowo w dalszej części.
| Rozszerzenia Camera2 | Rozszerzenia CameraX | |
|---|---|---|
| Dostępność rozszerzania zapytań | CameraExtensionCharacteristics
.getSupportedExtensions
|
ExtensionsManager.
isExtensionAvailable
|
| Informacje o zapytaniu | CameraExtensionCharacteristics.
getExtensionSupportedSizes
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.
getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRangeMillis
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.
getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.
getAvailableCaptureResultKeys
|
ExtensionsManager.
getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRange
CameraX obsługuje pozostałe informacje w bibliotece. |
| Podgląd i robienie zdjęć z włączonym rozszerzeniem | CameraDevice.
createExtensionSession
|
val cameraSelector = ExtensionsManager.
getExtensionEnabledCameraSelector
|
Podstawowy przedłużacz
Interfejs Basic Extender udostępnia punkty zaczepienia w kilku miejscach w potoku kamery. Każdy typ rozszerzenia ma odpowiednie klasy Extender, które producenci OEM muszą zaimplementować.
W tabeli poniżej znajdziesz klasy Extender, które producenci OEM muszą wdrożyć w przypadku każdego rozszerzenia:
| Klasy rozszerzające do wdrożenia | |
|---|---|
| Noc | NightPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
| HDR | HdrPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
| Auto | AutoPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
| Bokeh | BokehPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
| Retusz twarzy | BeautyPreviewExtenderImpl.java
|
W poniższym przykładzie używamy zmiennych PreviewExtenderImpl i ImageCaptureExtenderImpl. Zastąp je nazwami rzeczywistych plików, które wdrażasz.
Podstawowy wzmacniacz ma te możliwości:
- Podczas konfigurowania
CameraCaptureSession(onPresetSession) wstaw parametry sesji. - Powiadamiać Cię o zdarzeniach rozpoczęcia i zamknięcia sesji przechwytywania oraz wysyłać pojedyncze żądanie powiadomienia HAL ze zwróconymi parametrami (
onEnableSession,onDisableSession). - Wstaw parametry przechwytywania do żądania (
PreviewExtenderImpl.getCaptureStage,ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getCaptureStages). - Dodaj procesory do podglądu i przechwytywania obrazu, które mogą przetwarzać strumień
YUV_420_888.
Zobaczmy, jak Camera2/X wywołuje extensions-interface, aby osiągnąć 3 wspomniane powyżej przepływy aplikacji.
Przepływ aplikacji 1. Sprawdzanie dostępności rozszerzenia

Rysunek 3. Przepływ aplikacji 1 na podstawowym wzmacniaczu
W tym procesie Camera2/X bezpośrednio wywołuje metodę isExtensionAvailable() zarówno w przypadku PreviewExtenderImpl, jak i ImageCaptureExtenderImpl, bez wywoływania init(). Aby włączyć rozszerzenia, obie klasy Extender muszą zwracać wartość true.
Jest to często pierwszy krok, który aplikacje wykonują, aby sprawdzić, czy dany typ rozszerzenia jest obsługiwany w przypadku danego identyfikatora aparatu, zanim włączą rozszerzenie. Dzieje się tak, ponieważ niektóre rozszerzenia są obsługiwane tylko w przypadku określonych identyfikatorów aparatu.
Przepływ aplikacji 2. Informacje o zapytaniu
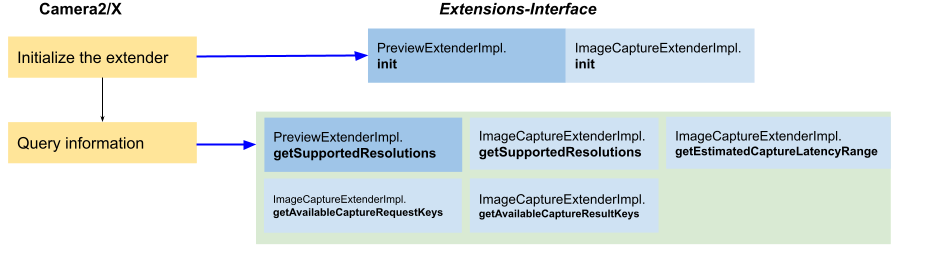
Rysunek 4. Przepływ aplikacji 2 na wzmacniaczu podstawowym
Po sprawdzeniu, czy rozszerzenie jest dostępne, aplikacje powinny przed jego włączeniem wysłać zapytanie o te informacje:
Still capture latency range:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRangezwraca zakres opóźnienia przechwytywania, aby aplikacja mogła ocenić, czy w bieżącej sytuacji warto włączyć rozszerzenie.Obsługiwane rozmiary podglądu i obszaru przechwytywania:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getSupportedResolutionsiPreviewExtenderImpl.getSupportedResolutionszwracają listę formatów obrazów i rozmiarów obsługiwanych w przypadku formatu i rozmiaru obszaru.Obsługiwane klucze żądań i wyników: Camera2/X wywołuje te metody, aby pobrać z Twojej implementacji obsługiwane klucze żądań i wyników przechwytywania:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeysImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getAvailableCapturetResultKeys
Camera2/X zawsze najpierw wywołuje init() w przypadku tych klas Extender, a potem wysyła zapytanie o więcej informacji.
Przepływ aplikacji 3. Podgląd/przechwytywanie obrazu z włączonym rozszerzeniem (implementacja HAL)
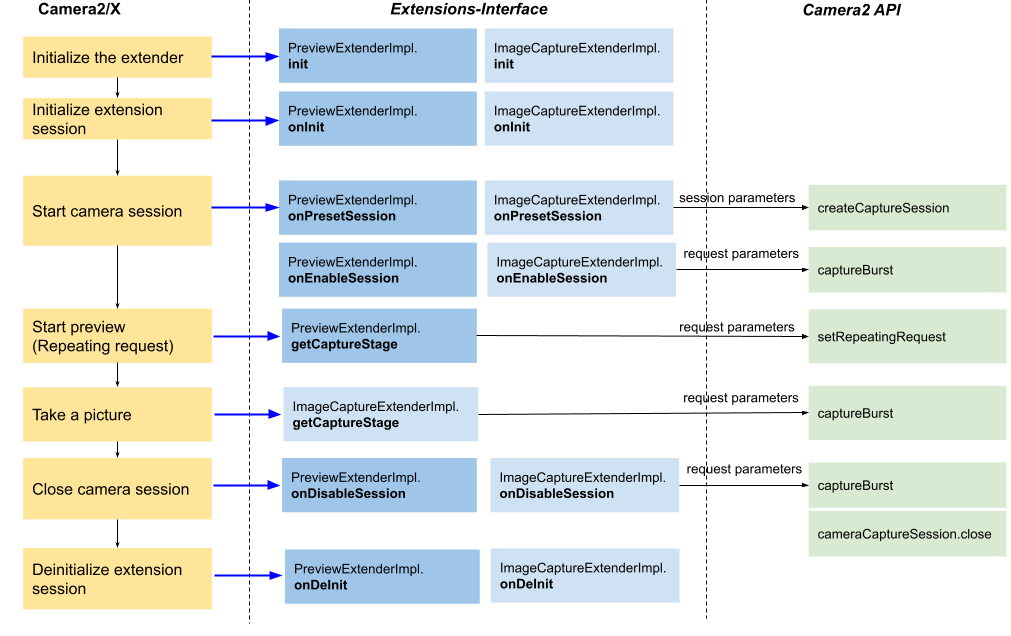
Rysunek 5. Przepływ aplikacji 3 na podstawowym wzmacniaczu
Powyższy diagram ilustruje główny proces włączania podglądu i robienia zdjęć za pomocą rozszerzenia bez procesora. Oznacza to, że rozszerzenie jest przetwarzane przez HAL aparatu.
W tym procesie Camera2/X najpierw wywołuje init(), a potem onInit, co powiadamia Cię, że sesja aparatu ma się rozpocząć z określonymi rozszerzeniami.
Inicjowanie wymagające dużego nakładu pracy możesz wykonać w onInit().
Podczas konfigurowania CameraCaptureSession interfejs Camera2/X wywołuje onPresetSession, aby uzyskać parametry sesji. Po pomyślnym skonfigurowaniu sesji przechwytywania interfejs Camera2/X wywołuje funkcję onEnableSession, zwracając instancję CaptureStageImpl zawierającą parametry przechwytywania. Camera2/X natychmiast wysyła pojedyncze żądanie z tymi parametrami przechwytywania, aby powiadomić HAL. Podobnie przed zamknięciem sesji przechwytywania interfejs Camera2/X wywołuje funkcję
onDisableSession, a następnie wysyła pojedyncze żądanie ze zwróconymi parametrami przechwytywania.
Powtarzające się żądanie wywoływane przez Camera2/X zawiera parametry żądania
zwrócone przez PreviewExtenderImpl.getCaptureStage(). Ponadto żądanie przechwytywania obrazu zawiera parametry zwrócone przez ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getCaptureStages().
Na koniec Camera2/X wywołuje onDeInit() po zakończeniu sesji aparatu.
Zasoby możesz zwolnić w sekcji onDeinit().
Procesor podglądu
Oprócz warstwy HAL aparatu możesz też zaimplementować rozszerzenia w procesorze.
Wdróż element PreviewExtenderImpl.getProcessorType, aby określić typ procesora, jak opisano poniżej:
PROCESSOR_TYPE_NONE: brak procesora. Obrazy są przetwarzane w warstwie HAL aparatu.PROCESSOR_TYPE_REQUEST_UPDATE_ONLY: typ procesora umożliwia aktualizowanie powtarzającego się żądania za pomocą nowych parametrów żądania przechwytywania na podstawie najnowszychTotalCaptureResult.PreviewExtenderImpl.getProcessormusi zwrócić instancjęRequestUpdateProcessorImpl, która przetwarza instancjęTotalCaptureResulti zwraca instancjęCaptureStageImpl, aby zaktualizować powtarzające się żądanie.PreviewExtenderImpl.getCaptureStage()powinna też odzwierciedlać wynik przetwarzania i zwracać najnowszą wartośćCaptureStageImpl.PROCESSOR_TYPE_IMAGE_PROCESSOR: ten typ umożliwia wdrożenie procesora do przetwarzania obrazówYUV_420_888i zapisywania danych wyjściowych na powierzchniPRIVATE.Musisz zaimplementować i zwrócić instancję
PreviewImageProcessorImplwPreviewExtenderImpl.getProcessor. Procesor odpowiada za przetwarzanieYUV_420_888obrazów wejściowych. Dane wyjściowe powinny być zapisywane wPRIVATEformacie podglądu. Camera2/X używaYUV_420_888zamiastPRIVATEdo skonfigurowaniaCameraCaptureSessionna potrzeby podglądu.Przepływ znajdziesz na poniższej ilustracji:
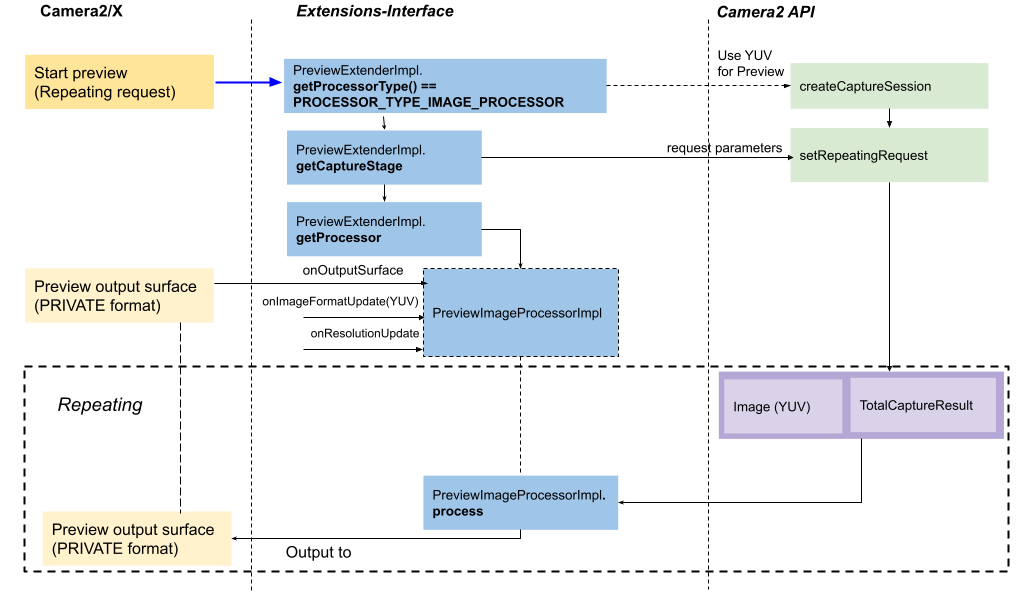
Rysunek 6. Podgląd przepływu z PreviewImageProcessorImpl
Interfejs PreviewImageProcessorImpl rozszerza interfejs ProcessImpl i ma 3 ważne metody:
onOutputSurface(Surface surface, int imageFormat)ustawia powierzchnię wyjściową procesora. W przypadkuPreviewImageProcessorImplimageFormatto format piksela, np.PixelFormat.RGBA_8888.onResolutionUpdate(Size size)ustawia rozmiar obrazu wejściowego.onImageFormatUpdate(int imageFormat)ustawia format obrazu wejściowego. Obecnie może to być tylkoYUV_420_888.
Procesor przechwytywania obrazu
W przypadku przechwytywania zdjęć możesz zaimplementować procesor, zwracając instancję CaptureProcessorImpl za pomocą ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getCaptureProcessor. Procesor jest odpowiedzialny za przetwarzanie listy zarejestrowanych YUV_420_888 obrazów i TotalCaptureResult instancji oraz zapisywanie danych wyjściowych na YUV_420_888 powierzchni.
Przed wysłaniem prośby o zrobienie zdjęcia możesz założyć, że podgląd jest włączony i działa.
Zobacz schemat poniżej:
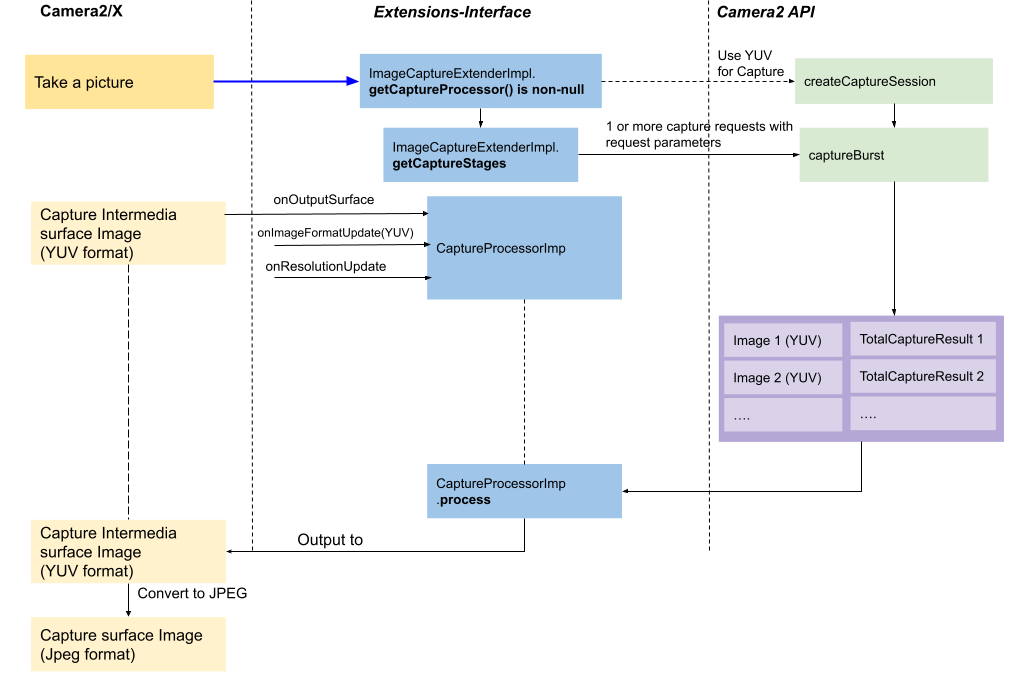
Rysunek 7. Zrób zdjęcie w aplikacji CaptureProcessorImpl
Camera2/X używa powierzchni w formacie
YUV_420_888do przechwytywania zdjęć, aby skonfigurować sesję przechwytywania. Camera2/X przygotowujeCaptureProcessorImpl, wywołując:CaptureProcessorImpl.onImageFormatUpdate()zYUV_420_888.CaptureProcessorImpl.onResolutionUpdate()z rozmiarem obrazu wejściowego.CaptureProcessorImpl.onOutputSurface()z obszarem wyjściowymYUV_420_888.
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getCaptureStageszwraca listęCaptureStageImpl, gdzie każdy element jest mapowany na instancjęCaptureRequestz parametrami przechwytywania wysyłanymi przez Camera2/X. Jeśli na przykład zwróci listę 3 instancji, Camera2/X wyśle 3 żądania przechwytywania z odpowiednimi parametrami przechwytywania za pomocą interfejsucaptureBurst.CaptureStageImplOtrzymane obrazy i instancje
TotalCaptureResultsą łączone w pakiet i wysyłane doCaptureProcessorImplw celu przetworzenia.CaptureProcessorImplzapisuje obraz wynikowy (w formacieYUV_420_888) na powierzchni wyjściowej określonej przez wywołanieonOutputSurface(). W razie potrzeby Camera2/X przekształca je w obrazy JPEG.
Obsługa kluczy żądań przechwytywania i wyników
Oprócz podglądu i przechwytywania obrazu z kamery aplikacje mogą ustawiać parametry zoomu i lampy błyskowej lub wywoływać funkcję dotknij, aby ustawić ostrość. Te parametry mogą być niezgodne z implementacją rozszerzenia.
Do wersji 1.3.0 interfejsu extensions-interface dodaliśmy te metody, aby umożliwić Ci udostępnianie parametrów obsługiwanych przez Twoją implementację:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys()zwraca klucze żądań przechwytywania obsługiwane przez Twoją implementację.ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureResultKeys()zwraca klucze wyników przechwytywania zawarte w wyniku przechwytywania.
Jeśli HAL kamery przetwarza rozszerzenie, Camera2/X pobiera wyniki przechwytywania w CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback. Jeśli jednak procesor jest zaimplementowany, Camera2/X pobiera wyniki przechwytywania w ProcessResultImpl, które są przekazywane do metody process() w PreviewImageProcessorImpl i CaptureProcessorImpl.
Odpowiadasz za zgłaszanie wyniku przechwytywania za pomocą ProcessResultImpl do Camera2/X.
Przykładem może być definicja interfejsu CaptureProcessorImpl poniżej.
W wersji extensions-interface 1.3.0 lub nowszej wywoływane jest drugie wywołanie process():
Interface CaptureProcessorImpl extends ProcessorImpl {
// invoked when extensions-interface version < 1.3.0
void process(Map<Integer, Pair<Image, TotalCaptureResult>> results);
// invoked when extensions-interface version >= 1.3.0
void process(Map<Integer, Pair<Image, TotalCaptureResult>> results,
ProcessResultImpl resultCallback, Executor executor);
}
W przypadku typowych funkcji aparatu, takich jak powiększenie, dotknięcie w celu ustawienia ostrości, lampa błyskowa i kompensacja ekspozycji, zalecamy obsługę tych klawiszy zarówno w przypadku żądania przechwytywania, jak i wyniku przechwytywania:
- Powiększenie:
CaptureRequest#CONTROL_ZOOM_RATIOCaptureRequest#SCALER_CROP_REGION
- Dotknij, aby ustawić ostrość:
CaptureRequest#CONTROL_AF_MODECaptureRequest#CONTROL_AF_TRIGGERCaptureRequest#CONTROL_AF_REGIONSCaptureRequest#CONTROL_AE_REGIONSCaptureRequest#CONTROL_AWB_REGIONS
- Flash:
CaptureRequest#CONTROL_AE_MODECaptureRequest#CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGERCaptureRequest#FLASH_MODE
- Kompensacja ekspozycji:
CaptureRequest#CONTROL_AE_EXPOSURE_COMPENSATION
W przypadku podstawowych rozszerzeń, które implementują wersję 1.2.0 lub starsze, interfejs CameraX Extensions API wyraźnie obsługuje wszystkie powyższe klucze. W przypadku wersji
extensions-interface 1.3.0 zarówno CameraX, jak i Camera2 uwzględniają zwróconą listę
i obsługują tylko klucze, które się na niej znajdują. Jeśli na przykład w implementacji 1.3.0 zdecydujesz się zwrócić tylko CaptureRequest#CONTROL_ZOOM_RATIO i CaptureRequest#SCALER_CROP_REGION, oznacza to, że w aplikacji obsługiwane jest tylko powiększenie, a funkcje dotknij, aby ustawić ostrość, lampa błyskowa i kompensacja ekspozycji nie są dozwolone.
Zaawansowany wzmacniacz
Zaawansowany moduł rozszerzający to typ implementacji dostawcy oparty na interfejsie Camera2 API.
Ten typ wzmacniacza został dodany w wersji extensions-interface 1.2.0. W zależności od producenta urządzenia rozszerzenia mogą być zaimplementowane w warstwie aplikacji, co zależy od tych czynników:
Konfiguracja strumienia niestandardowego: skonfiguruj strumienie niestandardowe, takie jak strumień RAW, lub używaj wielu strumieni dla różnych identyfikatorów fizycznych kamer.
Możliwość wysyłania żądań Camera2: obsługa złożonej logiki interakcji, która może wysyłać żądania przechwytywania z parametrami na podstawie wyników poprzednich żądań.
Advanced Extender zapewnia otokę lub warstwę pośrednią, dzięki czemu możesz dostosowywać konfigurację strumienia i wysyłać żądania zapisu na żądanie.
Pliki do wdrożenia
Aby przełączyć się na implementację zaawansowanego rozszerzenia, metoda
isAdvancedExtenderImplemented() w interfejsie
ExtensionVersionImpl
musi zwracać wartość true. W przypadku każdego typu rozszerzenia producenci OEM muszą wdrożyć odpowiednie klasy Extender. Pliki wdrożeniowe zaawansowanego rozszerzenia znajdują się w pakiecie advanced.
| Klasy rozszerzające do wdrożenia | |
|---|---|
| Noc | advanced/NightAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
| HDR | advanced/HdrAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
| Auto | advanced/AutoAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
| Bokeh | advanced/BokehAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
| Retusz twarzy | advanced/BeautyAdvancedExtenderImpl.java
|
W poniższym przykładzie używamy symbolu AdvancedExtenderImpl jako obiektu zastępczego.
Zastąp go nazwą pliku Extender dla wdrażanego rozszerzenia.
Zobaczmy, jak Camera2/X wywołuje extensions-interface, aby osiągnąć 3 ścieżki aplikacji.
Przepływ aplikacji 1. Sprawdzanie dostępności rozszerzeń
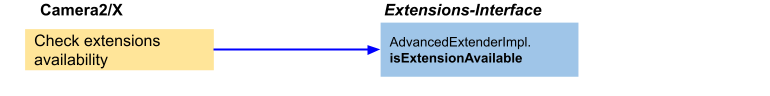
Rysunek 8. Przepływ aplikacji 1 na zaawansowanym przedłużaczu
Najpierw aplikacja sprawdza, czy dane rozszerzenie jest obsługiwane.
Przepływ aplikacji 2. Informacje o zapytaniu
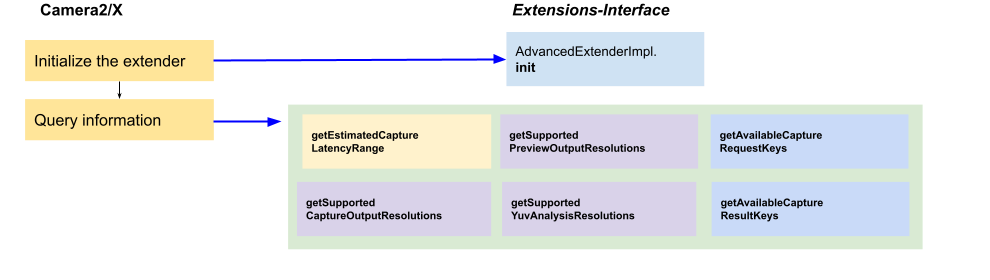
Rysunek 9. Przepływ aplikacji 2 na wzmacniaczu Advanced Extender
Po wywołaniu funkcji AdvancedExtenderImpl.init() aplikacja może wysyłać zapytania o te informacje o AdvancedExtenderImpl:
Szacowany czas oczekiwania na zrobienie zdjęcia:
AdvancedExtenderImpl.getEstimatedCaptureLatencyRange()zwraca zakres czasu oczekiwania na zrobienie zdjęcia, aby aplikacja mogła ocenić, czy w bieżącej sytuacji warto włączyć rozszerzenie.Obsługiwane rozdzielczości podglądu i robienia zdjęć:
AdvancedExtenderImpl.getSupportedPreviewOutputResolutions()zwraca mapę formatu obrazu do listy rozmiarów, które są obsługiwane w przypadku formatu i rozmiaru powierzchni podglądu. Producenci OEM muszą obsługiwać co najmniej formatPRIVATE.AdvancedExtenderImpl.getSupportedCaptureOutputResolutions()zwraca obsługiwane formaty i rozmiary powierzchni do przechwytywania zdjęć. Producenci OEM muszą obsługiwać dane wyjściowe w formatachJPEGiYUV_420_888.AdvancedExtenderImpl.getSupportedYuvAnalysisResolutions()zwraca obsługiwane rozmiary dodatkowego strumieniaYUV_420_888do analizy obrazu. Jeśli analiza obrazu w przestrzeni kolorów YUV nie jest obsługiwana, funkcjagetSupportedYuvAnalysisResolutions()powinna zwrócić wartośćnulllub pustą listę.
Dostępne klucze żądań przechwytywania i wyniki (dodane w
extensions-interface1.3.0): Camera2/X wywołuje te metody, aby pobrać z Twojej implementacji obsługiwane klucze żądań przechwytywania i klucze wyników:AdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeysAdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureResultKeys
Więcej informacji znajdziesz w artykule Obsługa kluczy żądań przechwytywania i wyników.
Przepływ aplikacji 3. Podgląd/wykonywanie zdjęć z włączonym rozszerzeniem

Rysunek 10. Przepływ aplikacji 3 na zaawansowanym wzmacniaczu
Powyższy diagram przedstawia główny proces rozpoczynania podglądu i wykonywania zdjęć w przypadku zaawansowanego typu przedłużacza. Omówmy wszystkie etapy tego procesu.
SessionProcessorImplinstancjaGłówna implementacja zaawansowanego rozszerzenia znajduje się w
SessionProcessorImpl, która odpowiada za dostarczanie niestandardowej konfiguracji sesji i wysyłanie żądań przechwytywania w celu zainicjowania podglądu i przechwytywania żądań. Wywoływana jest funkcjaAdvancedExtenderImpl.createSessionProcessor(), aby zwrócić instancjęSessionProcessorImpl.initSessionSessionProcessorImpl.initSession()inicjuje sesję rozszerzenia. W tym miejscu przydzielasz zasoby i zwracasz konfigurację sesji na potrzeby przygotowaniaCameraCaptureSession.W przypadku parametrów wejściowych Camera2/X określa konfiguracje powierzchni wyjściowych na potrzeby podglądu, robienia zdjęć i opcjonalnej analizy obrazu YUV. Ta konfiguracja powierzchni wyjściowej (
OutputSurfaceImpl) zawiera powierzchnię, rozmiar i format obrazu pobrane za pomocą tych metod wAdvancedExtenderImpl:getSupportedPreviewOutputResolutions()getSupportedCaptureOutputResolutions()getSupportedYuvAnalysisResolutions()
Musisz zwrócić instancję
Camera2SessionConfigImpl, która składa się z listy instancjiCamera2OutputConfigImpli parametrów sesji użytych do skonfigurowaniaCameraCaptureSession. Odpowiadasz za przesyłanie prawidłowych obrazów z kamery do powierzchni wyjściowych przekazywanych przez Camera2/X. Oto kilka opcji włączenia danych wyjściowych:- Przetwarzanie w warstwie HAL aparatu: możesz bezpośrednio dodać powierzchnie wyjściowe do
CameraCaptureSessionza pomocą implementacjiSurfaceOutputConfigImpl. Konfiguruje to dostarczoną powierzchnię wyjściową dla potoku kamery i umożliwia HAL-owi kamery przetwarzanie obrazu. Przetwarzanie powierzchni pośredniej
ImageReader(RAW, YUV itp.): dodaj powierzchnie pośrednieImageReaderdoCameraCaptureSessionza pomocą instancjiImageReaderOutputConfigImpl.Musisz przetworzyć obrazy pośrednie i zapisać obraz wynikowy na powierzchni wyjściowej.
- Użyj udostępniania powierzchni Camera2: użyj udostępniania powierzchni z inną powierzchnią, dodając dowolną instancję
Camera2OutputConfigImpldo metodygetSurfaceSharingOutputConfigs()innej instancjiCamera2OutputConfigImpl. Format i rozmiar powierzchni muszą być identyczne.
Wszystkie
Camera2OutputConfigImpl, w tymSurfaceOutputConfigImpliImageReaderOutputConfigImpl, muszą mieć unikalny identyfikator (getId()), który służy do określania powierzchni docelowej i pobierania obrazu zImageReaderOutputConfigImpl.onCaptureSessionStartiRequestProcessorImplGdy
CameraCaptureSessionsię uruchomi i struktura aparatu wywołaonConfigured(), Camera2/X wywołaSessionProcessorImpl.onCaptureSessionStart()z otoczką żądania Camera2RequestProcessImpl. Camera2/X implementujeRequestProcessImpl, co umożliwia wykonywanie żądań przechwytywania i pobieranie obrazów, jeśli używana jest funkcjaImageReaderOutputConfigImpl.Interfejsy
RequestProcessImplsą podobne do interfejsów Camera2CameraCaptureSessionpod względem wykonywania żądań. Różnice są następujące:- Powierzchnia docelowa jest określana przez identyfikator instancji
Camera2OutputConfigImpl. - Możliwość pobrania obrazu
ImageReader.
Możesz zadzwonić pod numer
RequestProcessorImpl.setImageProcessor()z określonym identyfikatoremCamera2OutputConfigImpl, aby zarejestrować instancjęImageProcessorImpli otrzymywać obrazy.Instancja
RequestProcessImplstaje się nieprawidłowa po wywołaniach Camera2/XSessionProcessorImpl.onCaptureSessionEnd().- Powierzchnia docelowa jest określana przez identyfikator instancji
Włącz podgląd i zrób zdjęcie
W przypadku implementacji zaawansowanego rozszerzenia możesz wysyłać żądania zapisu transakcji za pomocą interfejsu
RequestProcessorImpl. Interfejs Camera2/X powiadamia Cię o konieczności rozpoczęcia powtarzającego się żądania podglądu lub sekwencji przechwytywania zdjęć, wywołując odpowiednio funkcjeSessionProcessorImpl#startRepeatingiSessionProcessorImpl#startCapture. Aby spełnić te żądania podglądu i wykonania zdjęcia, należy wysyłać żądania przechwytywania.Interfejs Camera2/X ustawia też parametry żądania przechwytywania za pomocą funkcji
SessionProcessorImpl#setParameters. Te parametry żądania (jeśli są obsługiwane) musisz ustawić zarówno w przypadku żądań powtarzanych, jak i pojedynczych.Musisz obsługiwać co najmniej
CaptureRequest.JPEG_ORIENTATIONiCaptureRequest.JPEG_QUALITY.extensions-interfacew wersji 1.3.0 obsługuje klucze żądań i wyników, które są udostępniane przez te metody:AdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys()AdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureResultKeys()
Gdy deweloperzy ustawią klucze na liście
getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys, musisz włączyć parametry i upewnić się, że wynik przechwytywania zawiera klucze z listygetAvailableCaptureResultKeys.startTriggerSessionProcessorImpl.startTrigger()jest wywoływana w celu uruchomienia wyzwalacza, takiego jakCaptureRequest.CONTROL_AF_TRIGGERiCaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRECAPTURE_TRIGGER. Możesz zignorować wszystkie klucze żądań przechwytywania, które nie były reklamowane wAdvancedExtenderImpl.getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys().startTrigger()jest obsługiwany od wersjiextensions-interface1.3.0. Umożliwia aplikacjom korzystanie z funkcji dotknij, aby ustawić ostrość, i lampy błyskowej z rozszerzeniami.Czyszczenie
Po zakończeniu sesji przechwytywania wywoływana jest funkcja
SessionProcessorImpl.onCaptureSessionEnd()przed zamknięciemCameraCaptureSession. Po zamknięciu sesji przechwytywania funkcjadeInitSession()przeprowadza czyszczenie.
obsługuje podgląd, robienie zdjęć i analizę obrazu;
Rozszerzenie należy stosować zarówno w przypadku podglądu, jak i w przypadku przechwytywania obrazów. Jeśli jednak czas oczekiwania jest zbyt duży, aby płynnie wyświetlać podgląd, możesz zastosować rozszerzenie tylko w przypadku robienia zdjęć.
W przypadku typu Basic Extender, niezależnie od tego, czy rozszerzenie jest włączone w trybie podglądu, musisz wdrożyć zarówno ImageCaptureExtenderImpl, jak i PreviewExtenderImpl
w przypadku danego rozszerzenia. Aplikacja często używa też strumienia YUV do analizowania treści obrazu, np. do znajdowania kodów QR lub tekstu. Aby lepiej obsługiwać ten przypadek użycia, należy obsługiwać kombinację strumieni podglądu, przechwytywania obrazu i strumienia YUV_420_888 do konfigurowania CameraCaptureSession. Oznacza to, że jeśli zaimplementujesz procesor, musisz obsługiwać kombinację 3 strumieni YUV_420_888.
W przypadku zaawansowanego przedłużacza Camera2/X przekazuje do wywołania SessionProcessorImpl.initSession() 3 powierzchnie wyjściowe. Te powierzchnie wyjściowe służą odpowiednio do podglądu, przechwytywania obrazów i analizy obrazów. Musisz zadbać o to, aby powierzchnie wyjściowe podglądu i zdjęć pokazywały prawidłowe dane wyjściowe. W przypadku powierzchni wyjściowej analizy obrazu upewnij się jednak, że działa ona tylko wtedy, gdy nie ma wartości null. Jeśli Twoja implementacja nie obsługuje strumienia analizy obrazu, możesz zwrócić pustą listę w AdvancedExtenderImpl.getSupportedYuvAnalysisResolutions(). Dzięki temu powierzchnia wyjściowa analizy obrazu jest zawsze pusta w SessionProcessorImpl.initSession().
Obsługa nagrywania filmów
Obecna architektura rozszerzenia aparatu obsługuje tylko podgląd i robienie zdjęć. Nie obsługujemy włączania rozszerzenia na platformach MediaCodec lub MediaRecorder w celu nagrywania filmu. Aplikacje mogą jednak nagrywać podgląd.
Sprawdzamy, czy można obsługiwać platformy MediaCodec i MediaRecorder.
Metadane specyficzne dla rozszerzenia
W przypadku Androida 14 i nowszych metadane specyficzne dla rozszerzenia umożliwiają klientom rozszerzenia aparatu ustawianie i otrzymywanie ustawień żądania przechwytywania specyficznych dla rozszerzenia oraz wyników. W szczególności klienci rozszerzenia kamery mogą używać parametru żądania przechwytywania EXTENSION_STRENGTH do kontrolowania siły rozszerzenia i parametru wyniku przechwytywania EXTENSION_CURRENT_TYPE do wskazywania włączonego typu rozszerzenia.
Przechwytywanie żądań
Parametr żądania przechwytywania EXTENSION_STRENGTH
określa siłę efektu przetwarzania końcowego rozszerzenia. Odpowiedni wynik przechwytywania zawiera domyślną wartość siły, jeśli ten parametr nie jest jawnie ustawiony przez klienta. W przypadku tych typów rozszerzeń ten parametr można zastosować w ten sposób:
BOKEH: określa stopień rozmycia.HDRiNIGHT: kontroluje liczbę połączonych obrazów i jasność końcowego obrazu.FACE_RETOUCH: określa stopień poprawy wyglądu i wygładzenia skóry.
Obsługiwany zakres parametru EXTENSION_STRENGTH to 0–100. Wartość 0 oznacza brak przetwarzania rozszerzenia lub proste przekazywanie, a 100 – maksymalną siłę rozszerzenia efektu przetwarzania.
Aby dodać obsługę EXTENSION_STRENGTH, użyj interfejsów API parametrów specyficznych dla dostawcy wprowadzonych w wersji 1.3.0 interfejsu biblioteki rozszerzeń. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w sekcji getAvailableCaptureRequestKeys().
Wyniki przechwytywania
Wynik przechwytywania
EXTENSION_CURRENT_TYPE
umożliwia implementacjom rozszerzeń powiadamianie klientów o aktywnym typie rozszerzenia.
Rozszerzenia korzystające z typu AUTO dynamicznie przełączają się między typami rozszerzeń, takimi jak HDR i NIGHT, w zależności od warunków sceny. Aplikacje rozszerzeń aparatu mogą używać EXTENSION_CURRENT_TYPE do wyświetlania informacji o bieżącym rozszerzeniu wybranym przez rozszerzenie AUTO.
Szacowana latencja przechwytywania obrazu w czasie rzeczywistym
W przypadku Androida 14 i nowszych wersji klienci rozszerzeń aparatu mogą wysyłać zapytania o szacunki opóźnień w czasie rzeczywistym dotyczące przechwytywania zdjęć na podstawie sceny i warunków otoczenia za pomocą funkcji getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency(). Ta metoda zapewnia dokładniejsze szacunki niż metoda statycznagetEstimatedCaptureLatencyRangeMillis(). Na podstawie szacowanego opóźnienia aplikacje mogą zdecydować, czy pominąć przetwarzanie rozszerzenia, czy wyświetlić informację o długotrwałej operacji.
CameraExtensionSession.StillCaptureLatency latency;
latency = extensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency();
// The capture latency from ExtensionCaptureCallback#onCaptureStarted() until ExtensionCaptureCallback#onCaptureProcessStarted().
latency.getCaptureLatency();
// The processing latency from ExtensionCaptureCallback#onCaptureProcessStarted() until the processed frame returns to the client.
latency.getProcessingLatency();
Aby obsługiwać szacunki opóźnienia przechwytywania zdjęć w czasie rzeczywistym, zaimplementuj:
- Rozszerzenia podstawowe:
ImageCaptureExtenderImpl.getRealtimeCaptureLatency() - Rozszerzenia zaawansowane:
SessionProcessorImpl.getRealtimeCaptureLatency
Wywołania zwrotne postępu przetwarzania przechwytywania
W przypadku Androida 14 i nowszych klienci rozszerzeń aparatu mogą otrzymywać wywołania zwrotne dotyczące postępu długotrwałych operacji przetwarzania przechwytywania zdjęć. Aplikacje mogą wyświetlać użytkownikom bieżące postępy, aby poprawić ogólne wrażenia użytkowników.
Aby zintegrować tę funkcję, aplikacje mogą użyć tego kodu:
import android.hardware.camera2.CameraExtensionSession.
ExtensionCaptureCallback;
{
…
class AppCallbackImpl extends ExtensionCaptureCallback {
…
@Override
public void onCaptureProcessProgressed(
@NonNull CameraExtensionSession session,
@NonNull CaptureRequest request,
@IntRange(from = 0, to = 100) int progress) {
// Update app UI with current progress
}
}
…
}
Aby obsługiwać wywołania zwrotne postępu przetwarzania przechwytywania, implementacja dostawcy rozszerzenia musi wywoływać te wywołania zwrotne z bieżącą wartością postępu:
- Rozszerzenia podstawowe:
ProcessResultImpl.onCaptureProcessProgressed() - Rozszerzenia zaawansowane:
CaptureCallback.onCaptureProcessProgressed()
Zapis po obejrzeniu
W Androidzie 14 i nowszych wersjach rozszerzenia aparatu mogą dostarczać podgląd końcowy (obraz podglądu) za pomocą funkcji setPostviewOutputConfiguration.
Aby zwiększyć komfort użytkowników, aplikacje mogą wyświetlać obraz po wyświetleniu jako element zastępczy, gdy rozszerzenie ma większe opóźnienie przetwarzania, i zastępować go, gdy dostępny jest obraz końcowy. Aplikacje mogą konfigurować i wysyłać żądania przechwytywania po wyświetleniu za pomocą tego kodu referencyjnego:
{
…
if (!CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable()) {
continue;
}
…
ExtensionSessionConfiguration extensionConfiguration = new
ExtensionSessionConfiguration(
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.EXTENSION_NIGHT,
outputConfig,
backgroundExecutor,
extensionSessionStateCallback
);
extensionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration(
postviewImageOutput);
…
CaptureRequest.Builder captureRequestBuilder =
cameraDevice.createCaptureRequest(
CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_STILL_CAPTURE);
captureRequestBuilder.addTarget(stillImageReader.getSurface());
captureRequestBuilder.addTarget(postviewImageSurface);
CaptureRequest captureRequest = captureRequestBuilder.build();
…
}
Aby obsługiwać przechwytywanie obrazu po wyświetleniu, implementacja dostawcy musi zawierać te elementy:
Rozszerzenia podstawowe:
CaptureProcessorImpl.onPostviewOutputSurfaceiCaptureProcessorImpl.processWithPostviewRozszerzenia zaawansowane:
SessionProcessorImpl.startCaptureWithPostview
Obsługa danych wyjściowych SurfaceView
W przypadku Androida 14 i nowszych wersji klienci rozszerzeń aparatu mogą używać ścieżek renderowania podglądu zoptymalizowanych pod kątem mocy i wydajności, rejestrując instancję SurfaceView na potrzeby danych wyjściowych podglądu w przypadku powtarzających się żądań.
Aby obsługiwać dane wyjściowe SurfaceView, implementacja rozszerzenia dostawcy musi umożliwiać przesyłanie strumieniowe i wyświetlanie podglądu w instancjach SurfaceView. Aby sprawdzić, czy jest to obsługiwane, uruchom moduł SurfaceViewExtensionPreviewTest.java CTS.
Typy sesji dotyczące konkretnego dostawcy
Ta funkcja umożliwia implementacjom rozszerzeń dostawcy wybór typu sesji specyficznego dla dostawcy, który zostanie ustawiony w wewnętrznej sesji przechwytywania obrazu z aparatu zamiast wartości domyślnej.
Ta funkcja działa w ramach platformy i zestawu narzędzi dostawcy i nie ma wpływu na interfejs API widoczny dla klienta lub publiczny.
Aby wybrać typ sesji specyficzny dla dostawcy, w przypadku bibliotek rozszerzeń zaimplementuj te elementy:
* ExtenderStateListener.onSessionType() w przypadku rozszerzeń podstawowych;
* Camera2SessionConfigImpl.getSessionType() w przypadku rozszerzeń zaawansowanych.
Historia wersji interfejsu rozszerzeń
W tabeli poniżej znajdziesz historię wersji interfejsu Camera Extension. Zawsze wdrażaj bibliotekę dostawcy w najnowszej wersji.
| Wersja | Dodane funkcje |
|---|---|
| 1.0.0 |
|
| 1.1.0 |
|
| 1.2.0 |
|
| 1.3.0 |
|
| 1.4.0 |
|
Implementacja referencyjna
W usłudze frameworks/ex dostępne są te implementacje bibliotek dostawców OEM:
advancedSample: podstawowa implementacja zaawansowanego przedłużenia platformy.sample: podstawowa implementacja podstawowego rozszerzenia.service_based_sample: implementacja pokazująca, jak hostować rozszerzenia aparatu wService. Ta implementacja zawiera te komponenty:oem_library: Biblioteka OEM rozszerzeń aparatu dla interfejsów Camera2 i CameraX Extensions API, która implementujeExtensions-Interface. Działa on jako przekierowanie, które przekazuje wywołania zExtensions-Interfacedo usługi. Ta biblioteka zawiera też pliki AIDL i klasy opakowujące do komunikacji z usługą.Zaawansowany wzmacniacz jest domyślnie włączony. Aby włączyć Basic Extender, zmień
ExtensionsVersionImpl#isAdvancedExtenderImplementedna returnfalse.extensions_service: przykładowa implementacja usługi rozszerzeń. Dodaj tutaj swoją implementację. Interfejs do wdrożenia w usłudze jest podobny do interfejsuExtensions-Interface. Na przykład implementacjaIAdvancedExtenderImpl.Stubwykonuje te same operacje coAdvancedExtenderImpl. Aby można było przekazywać obiektyImageiTotalCaptureResult, wymagane są polaImageWrapperiTotalCaptureResultWrapper.
Konfigurowanie biblioteki dostawcy na urządzeniu
Biblioteka dostawcy OEM nie jest wbudowana w aplikację. Jest ona wczytywana z urządzenia w czasie działania przez Camera2/X. W CameraX tag <uses-library> deklaruje, że biblioteka androidx.camera.extensions.impl, która jest zdefiniowana w pliku AndroidManifest.xml biblioteki camera-extensions, jest zależnością CameraX i musi być wczytywana w czasie działania. W Camera2 platforma wczytuje usługę rozszerzeń, która deklaruje, że <uses-library>wczytuje tę samąandroidx.camera.extensions.impl bibliotekę w czasie działania.
Umożliwia to aplikacjom innych firm korzystającym z rozszerzeń automatyczne wczytywanie biblioteki dostawcy OEM. Biblioteka OEM jest oznaczona jako opcjonalna, dzięki czemu aplikacje mogą działać na urządzeniach, które nie mają jej zainstalowanej. Camera2/X automatycznie obsługuje to zachowanie, gdy aplikacja próbuje użyć rozszerzenia aparatu, o ile producent urządzenia umieści na nim bibliotekę OEM, aby aplikacja mogła ją wykryć.
Aby skonfigurować bibliotekę OEM na urządzeniu:
- Dodaj plik uprawnień wymagany przez tag
<uses-library>w tym formacie:/etc/permissions/ANY_FILENAME.xml. Na przykład:/etc/permissions/camera_extensions.xml. Pliki w tym katalogu zawierają mapowanie biblioteki o nazwie<uses-library>na rzeczywistą ścieżkę pliku na urządzeniu. Aby dodać wymagane informacje do pliku, skorzystaj z poniższego przykładu.
namemusi byćandroidx.camera.extensions.impl, ponieważ to tej biblioteki szuka CameraX.fileto ścieżka bezwzględna do pliku, który zawiera implementację rozszerzeń (np./system/framework/androidx.camera.extensions.impl.jar).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <permissions> <library name="androidx.camera.extensions.impl" file="OEM_IMPLEMENTED_JAR" /> </permissions>
Na urządzeniach z Androidem 12 lub nowszym, które obsługują rozszerzenia CameraX, właściwość ro.camerax.extensions.enabled musi mieć wartość true. Umożliwia to sprawdzanie, czy urządzenie obsługuje rozszerzenia.
Aby to zrobić, dodaj ten wiersz do pliku make urządzenia:
PRODUCT_VENDOR_PROPERTIES += \
ro.camerax.extensions.enabled=true \
Weryfikacja
Aby przetestować implementację biblioteki dostawcy OEM na etapie rozwoju, użyj przykładowej aplikacji dostępnej pod adresem androidx-main/camera/integration-tests/extensionstestapp/, która korzysta z różnych rozszerzeń dostawcy.
Po zakończeniu implementacji użyj narzędzia do weryfikacji rozszerzeń aparatu, aby przeprowadzić testy automatyczne i ręczne i sprawdzić, czy biblioteka dostawcy została prawidłowo zaimplementowana.
Rozszerzony tryb sceny a rozszerzenia aparatu
W przypadku rozszerzenia bokeh oprócz udostępniania go za pomocą rozszerzeń aparatu możesz udostępniać je za pomocą rozszerzonego trybu sceny, który jest włączany za pomocą klawisza CONTROL_EXTENDED_SCENE_MODE.
Więcej informacji o implementacji znajdziesz w artykule Bokeh w aparacie.
Tryb rozszerzonej sceny ma mniej ograniczeń niż rozszerzenia aparatu w przypadku aplikacji camera2. Możesz na przykład włączyć rozszerzony tryb sceny w zwykłej instancji CameraCaptureSession, która obsługuje elastyczne kombinacje strumieni i parametry żądania przechwytywania. Rozszerzenia kamery obsługują tylko stały zestaw typów strumieni i mają ograniczoną obsługę parametrów żądania przechwytywania.
Wadą trybu rozszerzonej sceny jest to, że można go wdrożyć tylko w warstwie HAL aparatu. Oznacza to, że musi on być zweryfikowany pod kątem działania we wszystkich ortogonalnych elementach sterujących dostępnych dla deweloperów aplikacji.
Zalecamy udostępnianie efektu bokeh zarówno w trybie rozszerzonej sceny, jak i w interfejsie Camera Extensions, ponieważ aplikacje mogą preferować używanie określonego interfejsu API do włączania efektu bokeh. Zalecamy najpierw użycie trybu rozszerzonej sceny, ponieważ jest to najbardziej elastyczny sposób włączania rozszerzenia bokeh w aplikacjach. Następnie możesz wdrożyć interfejs rozszerzeń aparatu na podstawie rozszerzonego trybu sceny. Jeśli wdrożenie efektu bokeh w warstwie HAL aparatu jest trudne, np. dlatego, że wymaga procesora końcowego działającego w warstwie aplikacji do przetwarzania obrazów, zalecamy wdrożenie rozszerzenia bokeh za pomocą interfejsu Camera Extensions.
Najczęstsze pytania
Czy istnieją ograniczenia dotyczące poziomów interfejsu API?
Tak. Zależy to od zestawu funkcji interfejsu Android API, które są wymagane przez implementację biblioteki dostawcy OEM. Na przykład funkcja
ExtenderStateListener.onPresetSession() używa wywołania
SessionConfiguration.setSessionParameters()
do ustawienia podstawowego zestawu tagów. To wywołanie jest dostępne tylko na interfejsie API na poziomie 28 lub wyższym. Szczegółowe informacje o poszczególnych metodach interfejsu znajdziesz w dokumentacji interfejsu API.

