Apps that include Dialer, Media, Car UI Library, and SMS are considered unbundled apps (that is, they are unbundled from the Android platform). Such apps include the logic for receiving data from the phone companion app and UX on the car side, including settings for association and feature enrollment. APKs built from unbundled code work with several versions of the platform.
Check out the code
To check out the unbundled code, run the following:
repo init -u https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest -b ub-automotive-masterrepo sync -cq -j4
To learn more about working with AOSP source code, see Initialize the Repo Client.
Build the code
You can build the code using Android Studio or from the command line.
Android Studio
To build the code in Android Studio:
In Android Studio, import the following build file:
packages/apps/Car/libs/aaos-apps-gradle-project/build.gradleEnsure the Gradle JDK is set to Version 11 or higher:
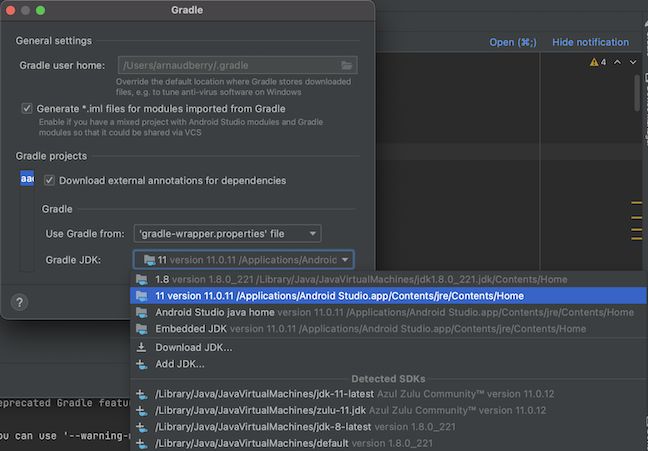
Figure 1. Set Gradle JDK to Version 11 in Android Studio.
Command line
To build the code from the command line:
Set the Android SDK location using one of the following methods:
Create
packages/apps/Car/libs/aaos-apps-gradle-project/local.propertiesand then set thesdk.dirproperty it contains. Android Studio can do this automatically when opening a project. For example, usesdk.dir=/Users/MY-USERNAME/Library/Android/sdk.or
Set the
ANDROID_SDK_ROOTenvironment variable with the path to the Android SDK.
Open a command prompt or a shell window.
Go to
packages/apps/Car/libs/aaos-apps-gradle-project.Run the following command:
./gradlew assemble
Minimum required API levels
Each unbundled app works on Android platforms with a version equal to or greater
than its
minSdkVersion. The
following table lists the minimum API version supported by each app:
| App | Minimum API level |
|---|---|
| Calendar | 29 |
| Car UI library | 29 |
| CompanionDevice | 29 |
| Dialer | 31 |
| Media | 30 |
| Messenger (SMS) | 30 |
| AOSP Host | 29 |
Integrate a prebuild into a system image
If the Android platform version is supported by the app (see the table in the previous section), you can add the APK to the system image. However, the integration steps differ between Android platform versions.
Android 13 and higher
Android 13 and higher doesn't include source code for unbundled apps, but you
can include a prebuilt APK in the platform build for use cases such as CDD
compliance testing or provisioning privileged apps. To specify the APK, use the
android_app_import
Soong rule, as shown in the following example:
android_app_import {
name: "CarMediaApp",
apk: "CarMediaApp.apk",
privileged: true,
certificate: "platform", // Media must be signed by the platform
required: ["allowed_privapp_com.android.car.media"],
}
Android 12 and lower
Android 12 and lower includes source code for unbundled apps, but you can still
specify a prebuilt APK to include. Because the Soong default is to give
precedence to the source code over a prebuilt, it's necessary to set the
prefer flag to true inside the android_app_import rule, as shown in the
following example:
android_app_import {
name: "CarDialerApp",
apk: "CarDialerApp.apk",
privileged: true,
presigned: true, // Dialer can have its own signature
required: ["allowed_privapp_com.android.car.dialer"],
overrides: ["Dialer"],
prefer: true, // The prebuilt replaces a source target with the same name
}
Unbundled app details
| App/Distribution | Privileged unbundled system signed |
Privileged unbundled non-system signed |
Unbundled don't need to be on system partition |
|---|---|---|---|
| App - Calendar | X | ||
| App - CompanionDeviceSupport | X | ||
| App - Dialer | X | ||
| App - AOSP Host | X | ||
| App - Media | X | ||
| App - Messenger (SMS) | X | ||
| Update distribution | OTA | OTA or Google Play | OTA or Google Play |
