监控定时器使用由内核在 `/proc/uid_io/stats` 位置提供的基于 UID 的磁盘 I/O 统计信息,跟踪所有应用和服务执行的磁盘 I/O 写入的总量,从而监控闪存用量。当应用或服务超出磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值时,监控定时器会对应用或服务执行相应操作。磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值和针对过度使用情况执行的相应操作在磁盘 I/O 过度使用配置中进行预定义。
过度使用阈值
- 磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值每天强制执行一次,也就是说,系统会汇总自当前世界协调时间 (UTC) 日历日开始起应用/服务执行的所有写入操作,并对照在过度使用配置中定义的阈值进行检查。
- 如果某车辆在某一天多次启动,监控定时器模块会将磁盘 I/O 用量统计信息存储在闪存中,并将自当前世界协调时间 (UTC) 日历日开始起进行汇总。
针对过度使用执行的操作
当应用反复超出定义的磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值时,监控定时器会执行过度使用配置中定义的操作。
- 所有供应商应用和服务都被认为对整体系统稳定性至关重要,因此不会因磁盘 I/O 过度使用而被终止。不过,可以在过度使用配置中定义一份可以安全终止的供应商应用和服务的列表。
- 所有第三方应用都可以安全终止。
当某个应用或服务可以安全终止时,监控定时器会停用该应用或服务,且应用组件状态将变为
PackageManager.COMPONENT_ENABLED_STATE_DISABLED_UNTIL_USED
。
过度使用配置
过度使用配置包含磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值和相应操作。默认过度使用配置在系统映像和供应商映像中定义,并且随 build 一起提供。供应商可以选择性地在供应商映像中提供供应商配置。如果不提供供应商配置,系统配置也会用于供应商应用和服务。
监控定时器通过 CarWatchdogManager 公开系统 API,以便供应商应用或服务随时更新供应商配置。
过度使用配置定义
过度使用配置按组件类型(例如系统、供应商和第三方)进行分类。OEM 仅可更新供应商组件配置。
供应商配置
供应商配置用于为所有供应商应用和服务以及所有地图和媒体应用定义磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值和相应操作。此类配置包含以下配置字段。
- 供应商软件包前缀。安装在 vendor 分区中的所有软件包均会被视为供应商软件包。除了这些软件包之外,供应商还可以将预安装软件包的前缀添加到供应商软件包前缀配置中,从而将预安装软件包归类为供应商软件包。此配置不接受正则表达式。
- 可安全终止的软件包。供应商可以向可安全终止的软件包配置添加完整的供应商软件包名称,从而指定哪些供应商软件包可以安全终止。
- 应用类别映射。供应商可以将任何软件包(包括第三方软件包)映射到以下两种受支持的应用类别之一:地图应用和媒体应用。进行这种映射是为了向地图应用和媒体应用提供更高的磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值,因为与其他应用类型相比,这些应用通常需要下载更多数据并将其写入磁盘。
- 组件级阈值。为所有供应商软件包定义通用阈值(即,特定软件包的专用阈值或特定应用类别的专用阈值未涵盖的软件包会获得这些阈值)。在定义磁盘 I/O 过度使用配置时,供应商必须定义非零组件级阈值。
- 特定软件包的专用阈值。供应商可以为特定供应商软件包定义特殊阈值。映射应包含完整的软件包名称。此配置中定义的阈值优先级高于给定软件包的其他配置中定义的阈值。
- 特定应用类别的专用阈值。供应商可以为特定应用类别指定特殊阈值。应用类别必须是受支持的类别之一:地图应用、媒体应用。此配置中定义的阈值会使用应用类别映射映射到特定软件包。
- 系统级阈值。供应商不得指定此配置。
对于供应商应用和服务,供应商软件包前缀、可安全终止的软件包、组件级阈值和特定软件包的专用阈值配置只能通过供应商配置进行更新。对于所有地图应用和媒体应用,特定应用类别的专用阈值配置只能通过供应商配置进行更新。
过度使用阈值包含在以下模式下允许写入的字节数:
- 应用/服务的前台模式与后台模式
- 系统车库模式
这种分类允许面向用户的前台应用/服务写入比后台应用/服务更多的数据。在车库模式下,应用和服务通常会下载更新,因此相较于其他模式下运行的应用和服务,这种模式下的每个应用和服务都需要更高的阈值。
系统配置和第三方配置
OEM 不得更新系统配置和第三方配置。
- 系统配置用于定义系统应用和服务的 I/O 过度使用阈值和操作。
- 此配置还可以更新应用类别映射。因此,系统配置和供应商配置之间共享此配置字段。
- 第三方配置用于为所有第三方应用定义阈值。所有未在系统中预安装的应用都是第三方应用。
- 除了地图应用和媒体应用是由供应商配置定义阈值之外,所有第三方应用都会收到相同的阈值(例如,任何第三方应用都不会收到特殊阈值)。
- 以下磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值是第三方应用的默认阈值。这些阈值随系统映像一起提供。
- 在应用前台模式下,写入阈值为 3 GiB。
- 在应用后台模式下,写入阈值为 2 GiB。
- 在系统车库模式下,写入阈值为 4 GiB。
- 这些是基本阈值。随着我们更深入地了解磁盘 I/O 用量,这些阈值会相应更新。
过度使用配置 XML 格式
可以将默认供应商配置放置在 build 映像中的 /vendor/etc/automotive/watchdog/resource_overuse_configuration.xml 位置(这属于可选操作)。如果未指定此配置,系统定义的配置也会应用于供应商应用和服务。
对于每个配置字段,XML 文件应仅包含一个标记。I/O 过度使用配置必须在 XML 文件中定义。所有阈值均应以 MiB 为单位进行指定。
下面提供了一个 XML 配置示例:
<resourceOveruseConfiguration version="1.0"> <componentType> VENDOR </componentType> <!-- List of safe to kill vendor packages. --> <safeToKillPackages> <package> com.vendor.package.A </package> <package> com.vendor.package.B </package> </safeToKillPackages> <!-- List of vendor package prefixes. --> <vendorPackagePrefixes> <packagePrefix> com.vendor.package </packagePrefix> </vendorPackagePrefixes> <!-- List of unique package names to app category mappings. --> <packagesToAppCategoryTypes> <packageAppCategory type="MEDIA"> com.vendor.package.A </packageAppCategory> <packageAppCategory type="MAPS"> com.google.package.B </packageAppCategory> <packageAppCategory type="MEDIA"> com.third.party.package.C </packageAppCategory> </packagesToAppCategoryTypes> <ioOveruseConfiguration> <!-- Thresholds in MiB for all vendor packages that don't have package specific thresholds. --> <componentLevelThresholds> <state id="foreground_mode"> 1024 </state> <state id="background_mode"> 512 </state> <state id="garage_mode"> 3072 </state> </componentLevelThresholds> <packageSpecificThresholds> <!-- IDs must be unique --> <perStateThreshold id="com.vendor.package.C"> <state id="foreground_mode"> 400 </state> <state id="background_mode"> 100 </state> <state id="garage_mode"> 200 </state> </perStateThreshold> <perStateThreshold id="com.vendor.package.D"> <state id="foreground_mode"> 1024 </state> <state id="background_mode"> 500 </state> <state id="garage_mode"> 2048 </state> </perStateThreshold> </packageSpecificThresholds> <!-- Application category specific thresholds. --> <appCategorySpecificThresholds> <!-- One entry per supported application category --> <perStateThreshold id="MEDIA"> <state id="foreground_mode"> 600 </state> <state id="background_mode"> 700 </state> <state id="garage_mode"> 1024 </state> </perStateThreshold> <perStateThreshold id="MAPS"> <state id="foreground_mode"> 800 </state> <state id="background_mode"> 900 </state> <state id="garage_mode"> 2048 </state> </perStateThreshold> </appCategorySpecificThresholds> </ioOveruseConfiguration> </resourceOveruseConfiguration>
通过 CarWatchdogManager 系统 API 更新过度使用配置
仅可在 build 映像中提供上述 XML 配置。如果 OEM 选择在 build 发布后更新设备端配置,可以使用以下 API 更改设备端配置。
- 向调用方授予
Car.PERMISSION_CONTROL_CAR_WATCHDOG_CONFIG权限。 - 必须使用现有配置来更新和设置新配置。使用 API
CarWatchdogManager.getResourceOveruseConfigurations可获取现有配置。如果未使用现有配置,所有配置(包括系统配置和第三方配置)都会被覆盖,建议不要这样做。 - 使用增量更改更新现有配置,并设置新配置。请勿更新系统组件配置和第三方组件配置。
- 使用 API
CarWatchdogManager.setResourceOveruseConfigurations设置新配置。 - 如需获取和设置磁盘 I/O 过度使用配置,请使用
CarWatchdogManager.FLAG_RESOURCE_OVERUSE_IO标志。
下面展示了更新资源过度使用配置的实现示例。
void updateResourceOveruseConfigurations() { CarWatchdogManager manager = (CarWatchdogManager) car.getCarManager(Car.CAR_WATCHDOG_SERVICE); List<ResourceOveruseConfiguration> resourceOveruseConfigurations = manager.getResourceOveruseConfigurations( CarWatchdogManager.FLAG_RESOURCE_OVERUSE_IO); List<ResourceOveruseConfiguration> newResourceOveruseConfigurations = new List<>(); ResourceOveruseConfiguration vendorConfiguration; for(ResourceOveruseConfiguration config : resourceOveruseConfigurations) { // Do not update the configurations of the system and third-party component types. if (config.getComponentType() != ResourceOveruseConfiguration.COMPONENT_TYPE_VENDOR) { newResourceOveruseConfigurations.add(config); continue; } vendorConfiguration = config; } if (vendorConfiguration == null) { ResourceOveruseConfiguration.Builder vendorConfigBuilder = new ResourceOveruseConfiguration.Builder(); initializeConfig(vendorConfigBuilder); newResourceOveruseConfigurations.add(vendorConfigBuilder.build()); } else { ResourceOveruseConfiguration newVendorConfig = updateConfig(vendorConfiguration); newResourceOveruseConfigurations.add(newVendorConfig); } int result = manager.setResourceOveruseConfigurations( newResourceOveruseConfigurations, if (result != CarWatchdogManager.RETURN_CODE_SUCCESS) { // Failed to set the resource overuse configurations. } } /** Sets the delta between the old configuration and the new configuration. */ ResourceOveruseConfiguration updateConfig( ResourceOveruseConfiguration oldConfiguration) { // Replace com.vendor.package.A with com.vendor.package.B in the safe-to-kill list. List<String> safeToKillPackages = oldConfiguration.getSafeToKillPackages(); safeToKillPackages.remove("com.vendor.package.A"); safeToKillPackages.add("com.vendor.package.B"); ResourceOveruseConfiguration.Builder configBuilder = new ResourceOveruseConfiguration.Builder( oldConfiguration.getComponentType(), safeToKillPackages, oldConfiguration.getVendorPackagePrefixes(), oldConfiguration.getPackagesToAppCategoryTypes()); configBuilder.addVendorPackagePrefixes("com.vendor."); configBuilder.addPackagesToAppCategoryTypes("com.vendor.package.B", ResourceOveruseConfiguration.APPLICATION_CATEGORY_TYPE_MAPS); IoOveruseConfiguration oldIoConfiguration = oldConfiguration.getIoOveruseConfiguration(); IoOveruseConfiguration.Builder ioConfigBuilder = new IoOveruseConfiguration.Builder( oldIoConfiguration.getComponentLevelThresholds(), oldIoConfiguration.getPackageSpecificThresholds(), oldIoConfiguration.getAppCategorySpecificThresholds(), oldIoConfiguration.getSystemWideThresholds()); // Define the amount of bytes based on the flash memory specification, expected lifetime, // and estimated average amount of bytes written by a package during different modes. ioConfigBuilder.addPackageSpecificThresholds("com.vendor.package.B", new PerStateBytes(/* foregroundModeBytes= */ 2 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024, /* backgroundModeBytes= */ 500 * 1024 * 1024, /* garageModeBytes= */ 3 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024)); return configBuilder.setIoOveruseConfiguration(ioConfigBuilder.build()).build(); }
监控资源过度使用情况的应用
供应商和第三方应用可以监听来自监控定时器的应用特定资源过度使用通知,或轮询 CarWatchdogManager 以获取最近 30 天内的应用特定资源过度使用统计信息。
监听资源过度使用通知
应用可以实现资源过度使用监听器,并向 CarWatchdogManager 注册监听器,以便在超出其磁盘 I/O 过度使用阈值的 80% 或 100% 时收到应用特定通知。应用可以使用这类通知实现以下目的:
- 记录磁盘 I/O 过度使用统计信息以进行离线分析。应用开发者可以使用此日志记录调试磁盘 I/O 过度使用问题。
- 减少磁盘 I/O 写入,直到过度使用计数器重置。
Java 客户端
- 通过继承
CarWatchdogManager.ResourceOveruseListener实现监听器:class ResourceOveruseListenerImpl implements CarWatchdogManager.ResourceOveruseListener { @Override public void onOveruse( @NonNull ResourceOveruseStats resourceOveruseStats) { // 1. Log/Upload resource overuse metrics. // 2. Reduce writes until the counters reset. IoOveruseStats ioOveruseStats = resourceOveruseStats.getIoOveruseStats(); // Stats period - [ioOveruseStats.getStartTime(), ioOveruseStats.getStartTime() // + ioOveruseStats.getDurationInSeconds()] // Total I/O overuses - ioOveruseStats.getTotalOveruses() // Total bytes written - ioOveruseStats.getTotalBytesWritten() // Remaining write bytes for the current UTC calendar day - // ioOveruseStats.getRemainingWriteBytes() } } }
- 通过调用
CarWatchdogManager.addResourceOveruseListener注册监听器实例private void addResourceOveruseListener() { CarWatchdogManager manager = (CarWatchdogManager) car.getCarManager(Car.CAR_WATCHDOG_SERVICE); // Choose a proper executor to handle resource overuse notifications. Executor executor = mContext.getMainExecutor(); manager.addResourceOveruseListener( executor, CarWatchdogManager.FLAG_RESOURCE_OVERUSE_IO, mListenerImpl); } - 在应用完成监听后,取消注册监听器实例:
private void removeResourceOveruseListener() { CarWatchdogManager manager = (CarWatchdogManager) car.getCarManager(Car.CAR_WATCHDOG_SERVICE); mCarWatchdogManager.removeResourceOveruseListener( mListenerImpl); }
原生客户端
- 在 build 规则的
shared_libs依赖项中添加carwatchdog_aidl_interface-ndk_platform。Android.bpcc_binary { name: "sample_native_client", srcs: [ "src/*.cpp" ], shared_libs: [ "carwatchdog_aidl_interface-ndk_platform", "libbinder_ndk", ], vendor: true, } - 添加 SELinux 政策以允许供应商服务域使用 binder(
binder_user宏),并将供应商服务域添加到carwatchdog客户端域(carwatchdog_client_domain macro)中。请参阅sample_client.te和file_contexts的以下代码:sample_client.tetype sample_client, domain; type sample_client_exec, exec_type, file_type, vendor_file_type; carwatchdog_client_domain(sample_client) init_daemon_domain(sample_client) binder_use(sample_client)
file_contexts/vendor/bin/sample_native_client u:object_r:sample_client_exec:s0
- 通过继承
BnResourceOveruseListener实现资源过度使用监听器。替换BnResourceOveruseListener::onOveruse,以处理资源过度使用的通知。ResourceOveruseListenerImpl.hclass ResourceOveruseListenerImpl : public BnResourceOveruseListener { public: ndk::ScopedAStatus onOveruse( ResourceOveruseStats resourceOveruseStats) override; private: void initialize(); void terminate(); std::shared_ptr<ICarWatchdog> mWatchdogServer; std::shared_ptr<IResourceOveruseListener> mListener; }
ResourceOveruseListenerImpl.cppndk::ScopedAStatus ResourceOveruseListenerImpl::onOveruse( ResourceOveruseStats resourceOveruseStats) { // 1. Log/Upload resource overuse metrics. // 2. Reduce writes until the counters reset. if (stats.getTag() != ResourceOveruseStats::ioOveruseStats) { // Received resourceOveruseStats doesn't contain I/O overuse stats. } const IoOveruseStats& ioOveruseStats = stats.get(); // Stats period - [ioOveruseStats.startTime, // ioOveruseStats.startTime + ioOveruseStats.durationInSeconds] // Total I/O overuses - ioOveruseStats.totalOveruses // Total bytes written - ioOveruseStats.writtenBytes // Remaining write bytes for the current UTC calendar day - // ioOveruseStats.remainingWriteBytes return ndk::ScopedAStatus::ok(); }
- 启动 binder 线程池,并向监控定时器服务器注册资源过度使用监听器。监控定时器服务器以服务名称
android.automotive.watchdog.ICarWatchdog/default进行注册。main.cppint main(int argc, char** argv) { ABinderProcess_setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(1); ABinderProcess_startThreadPool(); std::shared_ptr<ResourceOveruseListenerImpl> listener = ndk::SharedRefBase::make<ResourceOveruseListenerImpl>(); // The listener is added in initialize(). listener->initialize(); ... Run service ... // The listener is removed in terminate(). listener->terminate(); }
ResourceOveruseListenerImpl.cppvoid ResourceOveruseListener::initialize() { ndk::SpAIBinder binder(AServiceManager_getService( "android.automotive.watchdog.ICarWatchdog/default")); std::shared_ptr<ICarWatchdog> server = ICarWatchdog::fromBinder(binder); mWatchdogServer = server; std::shared_ptr<IResourceOveruseListener> listener = IResourceOveruseListener::fromBinder(this->asBinder()); mWatchdogServer->addResourceOveruseListener( std::vector<int>{ResourceType.IO}, listener); mListener = listener; } void ResourceOveruseListener::terminate() { mWatchdogServer->removeResourceOveruseListener(mListener); }
轮询资源过度使用统计信息
应用可以对 CarWatchdogManager 进行轮询,以了解最近 30 天内应用特定的 I/O 过度使用统计信息 ATS。
Java 客户端
使用 CarWatchdogManager.getResourceOveruseStats 可获取资源过度使用统计信息。传递 CarWatchdogManager.FLAG_RESOURCE_OVERUSE_IO 标志可获取磁盘 I/O 过度使用统计信息。
private void getResourceOveruseStats() {
CarWatchdogManager manager =
(CarWatchdogManager) car.getCarManager(Car.CAR_WATCHDOG_SERVICE);
// Returns resource overuse stats with I/O overuse stats for the past
// 7 days. Stats are available for up to the past 30 days.
ResourceOveruseStats resourceOveruseStats =
mCarWatchdogManager.getResourceOveruseStats(
CarWatchdogManager.FLAG_RESOURCE_OVERUSE_IO,
CarWatchdogManager.STATS_PERIOD_PAST_7_DAYS);
IoOveruseStats ioOveruseStats = resourceOveruseStats.getIoOveruseStats();
// Stats period - [ioOveruseStats.getStartTime(), ioOveruseStats.getStartTime()
// + ioOveruseStats.getDurationInSeconds()]
// Total I/O overuses - ioOveruseStats.getTotalOveruses()
// Total bytes written - ioOveruseStats.getTotalBytesWritten()
// Remaining write bytes for the UTC calendar day -
// ioOveruseStats.getRemainingWriteBytes()
}原生客户端
使用 CarWatchdogServer.getResourceOveruseStats 可获取资源过度使用统计信息。传递 ResourceType.IO 枚举可提取磁盘 I/O 过度使用统计信息。
void getResourceOveruseStats() { ndk::SpAIBinder binder(AServiceManager_getService( "android.automotive.watchdog.ICarWatchdog/default")); std::shared_ptr<ICarWatchdog> server = ICarWatchdog::fromBinder(binder); // Returns the stats only for the current UTC calendar day. const std::vector<ResourceOveruseStats> resourceOveruseStats; ndk::ScopedAStatus status = server.getResourceOveruseStats( std::vector<int>{ResourceType.IO}, &resourceOveruseStats); if (!status.isOk()) { // Failed to get the resource overuse stats. return; } for (const auto& stats : resourceOveruseStats) { if (stats.getTag() != ResourceOveruseStats::ioOveruseStats) { continue; } const IoOveruseStats& ioOveruseStats = stats.get(); // Stats period - [ioOveruseStats.startTime, // ioOveruseStats.startTime + ioOveruseStats.durationInSeconds] // Total I/O overuses - ioOveruseStats.totalOveruses // Total bytes written - ioOveruseStats.writtenBytes // Remaining write bytes for the current UTC calendar day - // ioOveruseStats.remainingWriteBytes } }
资源过度使用时的用户体验
以下部分介绍了资源过度使用时的用户体验。
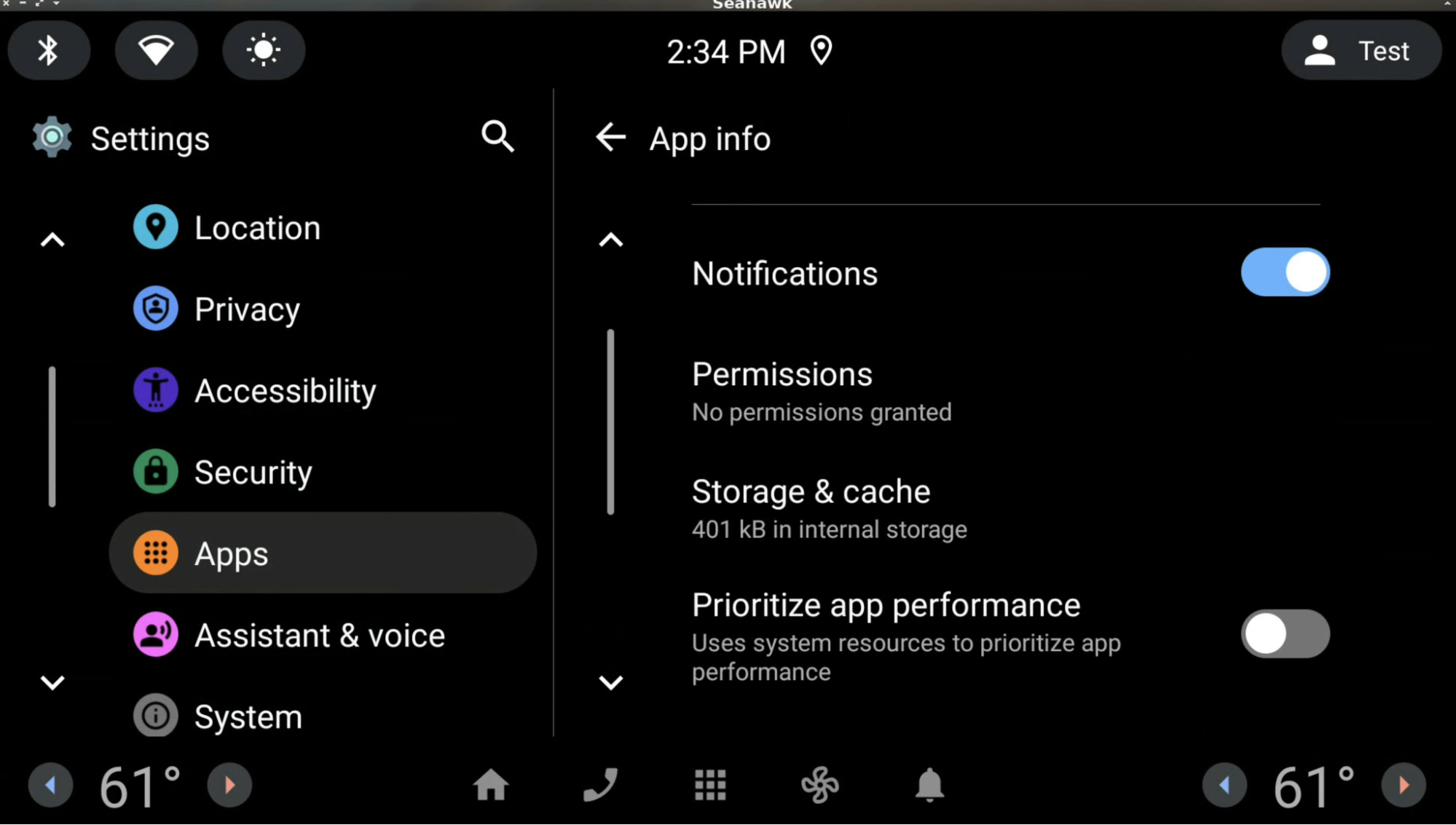
优先考虑应用性能的设置
应用设置页面包含 Prioritize app performance 方面的设置(见下图),这些设置让用户能够将系统资源优先用于保障应用性能,而不是优先保障系统性能和长期硬件性能。此设置仅适用于在资源过度使用时可以安全终止的应用。否则,此设置会处于停用状态。如果为某个应用关闭此设置(默认为关闭状态),系统可以在资源过度使用时终止该应用。否则,系统不会在资源过度使用时终止该应用。
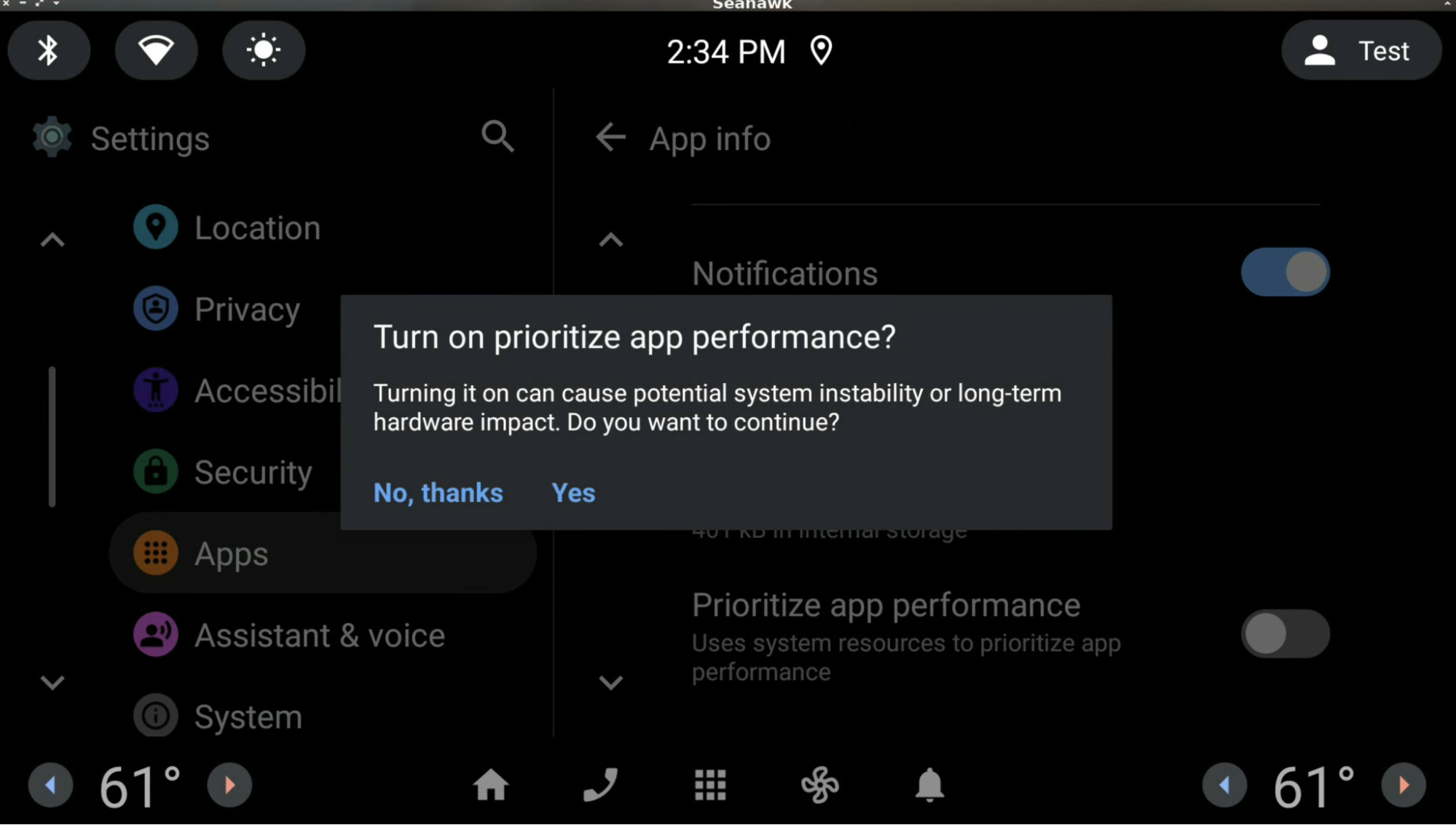
当用户开启此设置时,系统将会显示以下确认对话框,说明开启此设置的影响。
90 天后,此设置将自动重置为默认值。您可以使用 RRO 叠加层应用通过 watchdogUserPackageSettingsResetDays 修改每日上限,最长为 180 天。如需了解详情,请参阅在运行时更改应用资源的值。以下是一个示例叠加标记,该标记可包含在 AndroidManifest.xml 中:
<overlay android:priority="<insert-value>" android:targetPackage="com.android.car.updatable" android:targetName="CarServiceCustomization" android:resourcesMap="@xml/overlays" />
在 res/values/config.xml 中:
<resources> <integer name="watchdogUserPackageSettingsResetDays">value</integer> </resources>
在 res/xml/overlays.xml 中:
<overlay> <item target="integer/watchdogUserPackageSettingsResetDays" value="@integer/watchdogUserPackageSettingsResetDays" /> </overlay>
会影响性能的应用设置
设置应用包含会影响性能的应用部分(见图 1)。点按该部分可看到一个应用列表,其中会列出因闪存过度使用而受到限制的应用,以及会对系统性能产生负面影响的应用。这遵从 CDD 3.5.1 要求 [C-1-1]。
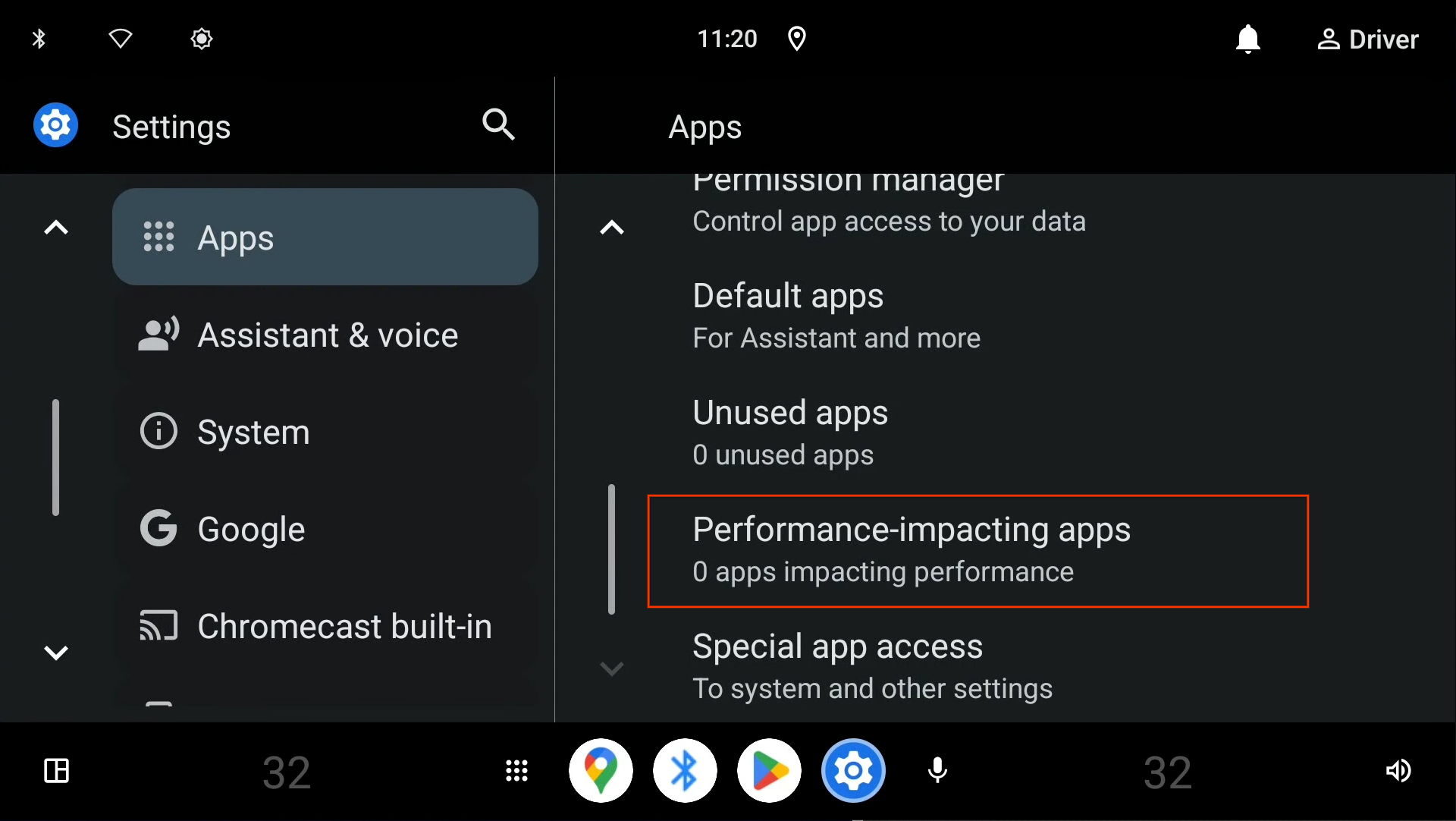
图 1. 会影响性能的应用
因资源过度使用而终止的应用会列在此处(见图 2)。所列应用可以优先考虑。如需了解详情,请参阅优先考虑应用性能的设置。
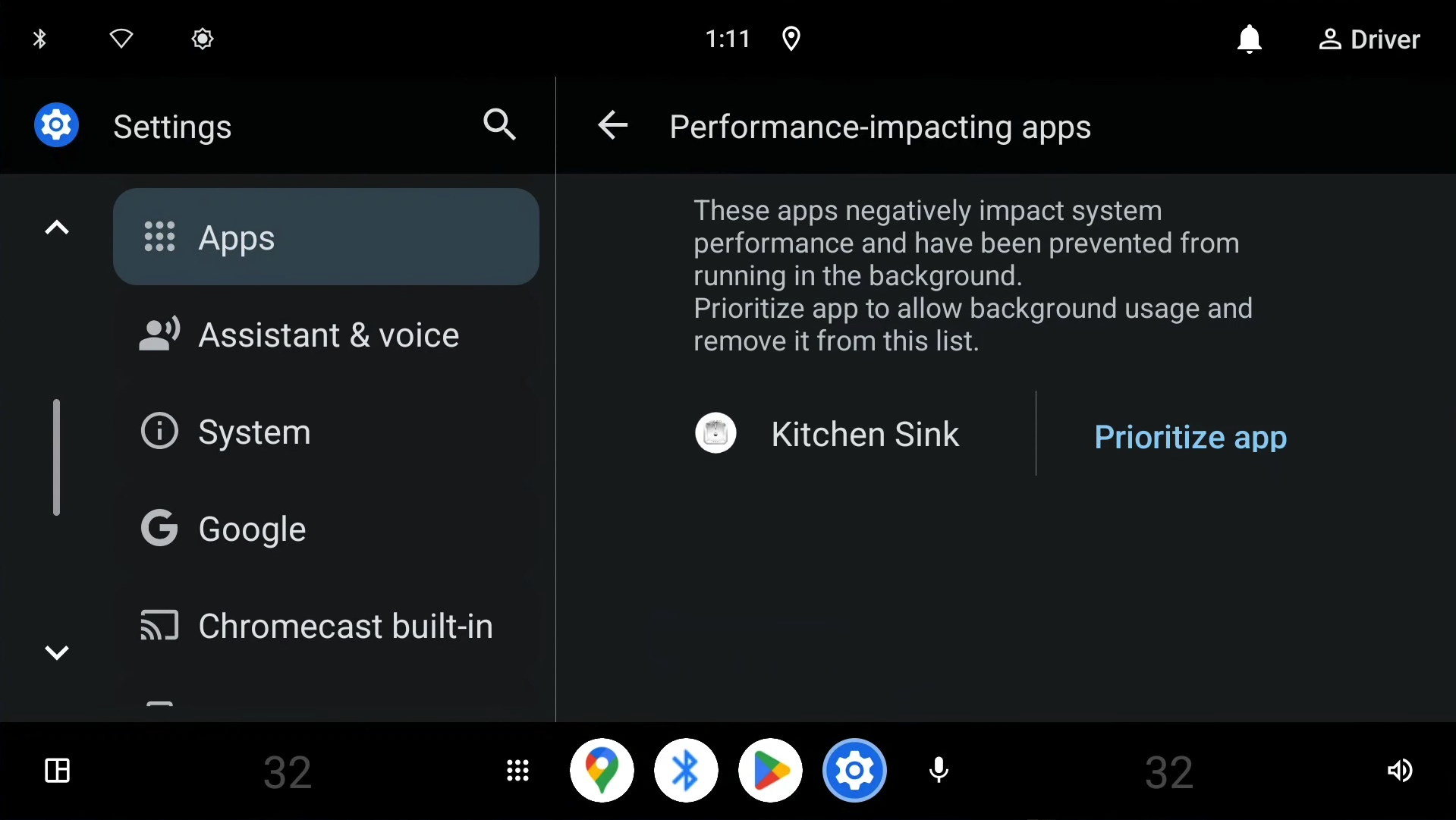
图 2. 因资源过度使用而被终止的应用的列表。
用户通知
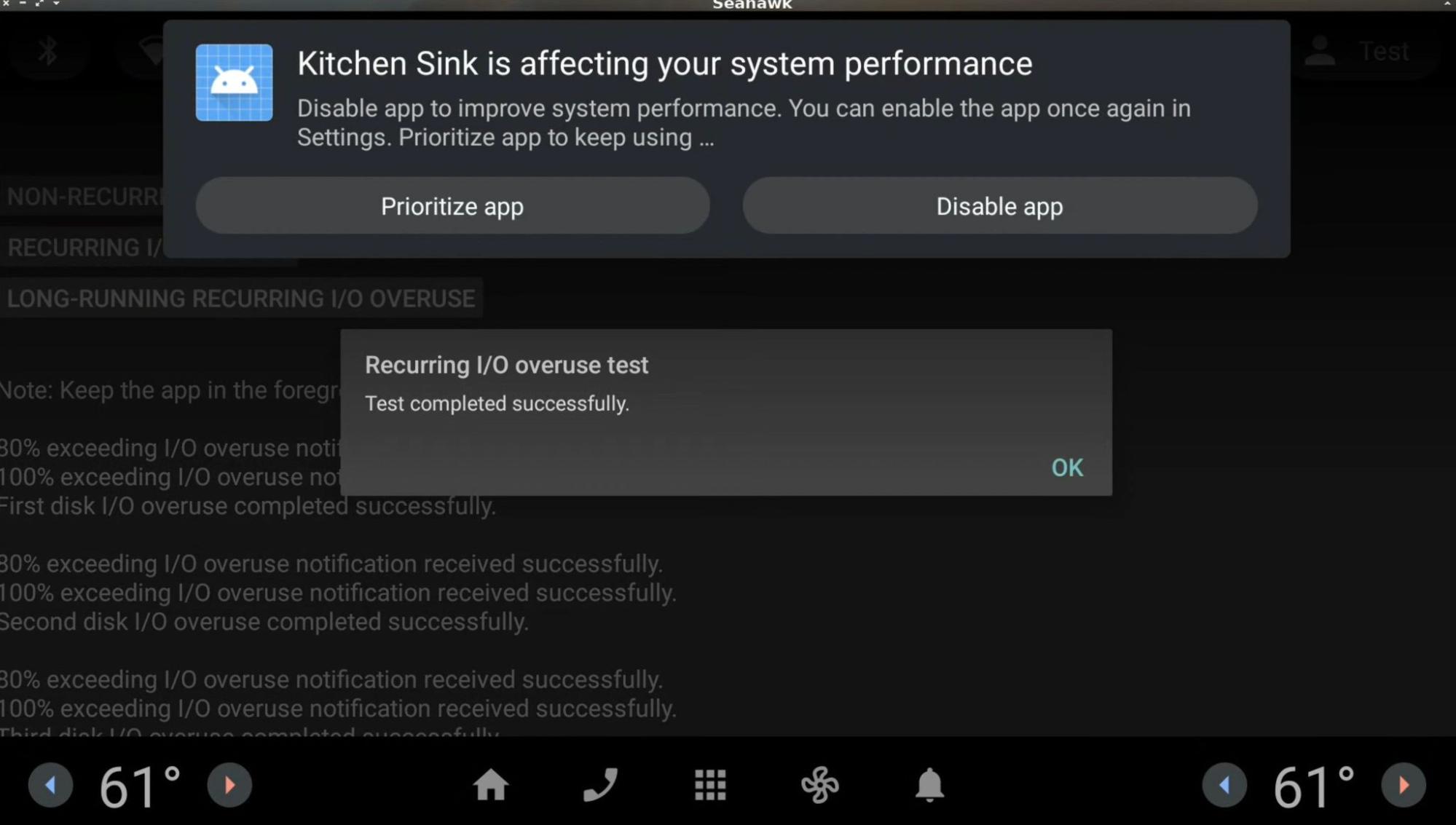
如果某个应用或服务在特定时间段内反复过度使用磁盘 I/O(例如,将数据写入磁盘但超出已定义的阈值),且在资源过度使用时可以安全终止,则系统会在车辆进入 allow-driver-distraction 状态时向用户发出通知。
第一个用户通知(在驾车期间)以浮动通知的形式发布,其他通知则在通知中心发布。
例如,当应用反复过度使用磁盘 I/O 时,用户会收到以下通知:
- 当用户点击将应用设为优先运行按钮时,系统会启动应用的设置页面,在该页面中可以开启或关闭优先应用性能设置。
- 当用户点击停用应用按钮时,应用将被停用,直至用户启动该应用或在应用的设置页面上启用该应用。
- 对于可卸载的应用,停用应用按钮会被替换为卸载应用按钮。当用户点击卸载应用按钮时,系统会启动应用的设置页面,用户可从中卸载应用。
启动器实现建议
当应用因资源过度使用而被停用时,应用会从默认启动器应用中消失,因为 CarService 会将应用的启用状态更新为 PackageManager.COMPONENT_ENABLED_STATE_DISABLED_UNTIL_USED。原始设备制造商 (OEM) 必须更新内置启动器实现以将这些应用显示为异常状态,以便用户在需要时使用。请根据 build 版本查看以下建议。
Android SC V2 版本
- 在检索要在启动器中显示的软件包列表时,启动器实现应使用
MATCH_DISABLED_UNTIL_USED_COMPONENTS标志。 - 当用户点击处于
PackageManager.COMPONENT_ENABLED_STATE_DISABLED_UNTIL_USED状态的应用时,启动器应用必须启用应用,方法是将启用状态设置为:
