Android Automotive considers voice to be a crucial component for
drive-safe interactions and one of the safest ways for users to
interact with the Android Automotive OS while driving. As a result, we expanded the
Android voice assistant APIs (including VoiceInteractionSession)
to enable voice assistants to perform tasks for users
that can be difficult to accomplish while driving.
Tap-to-Read enables voice assistants to read and reply to text messages on
behalf of the user, when the user interacts with message notifications. To provide
this functionality, you can integrate a voice assistant with
CarVoiceInteractionSession.
In Automotive, notifications posted to the Notification Center identified
as INBOX
or INBOX_IN_GROUP (for example, SMS messages) include a
Play button. The user can click Play to have the selected
voice assistant read the notification aloud, and to optionally reply by voice.
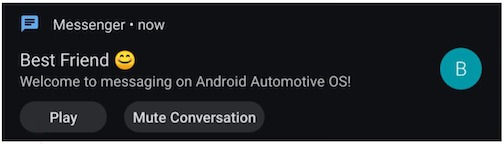
Figure 1. Tap-to-Read notification with Play button.
Integrate with CarVoiceInteractionSession
The next sections describe how to integrate a voice assistant with
CarVoiceInteractionSession.
Support voice interactions
Apps that provide car voice interaction services must
integrate with the existing Android voice interactions. To learn more, see Google Assistant for Android
(with the exception of VoiceInteractionSession). While all voice interaction API
elements remain the same as implemented on mobile devices, CarVoiceInteractionSession
(described in Implement CarVoiceInteractionSession) replaces
VoiceInteractionSession. For more information, see these pages:
Implement CarVoiceInteractionSession
CarVoiceInteractionSession
exposes APIs that you can use to enable voice assistants to read text messages aloud and then
reply to theose messages on behalf of the user.
The key difference between the CarVoiceInteractionSession and
VoiceInteractionSession classes is that
CarVoiceInteractionSession passes in the action in onShow
so the voice assistant can detect the context of the user's request as soon as
CarVoiceInteractionSession starts a session. The parameters for onShow
for each class are listed in the following table:
| CarVoiceInteractionSession | VoiceInteractionSession |
|---|---|
onShow takes these three parameters:
|
onShow takes these two parameters:
|
Changes in Android 10
Starting with Android 10, the platform calls VoiceInteractionService.onGetSupportedVoiceActions
to detect which actions are supported. The voice assistant overrides and
implements VoiceInteractionService.onGetSupportedVoiceActions,
as shown in the following example:
public class MyInteractionService extends VoiceInteractionService { private static final ListSUPPORTED_VOICE_ACTIONS = Arrays.asList( CarVoiceInteractionSession.VOICE_ACTION_READ_NOTIFICATION); @Override public Set onGetSupportedVoiceActions(@NonNull Set voiceActions) { Set result = new HashSet<>(voiceActions); result.retainAll(SUPPORTED_VOICE_ACTIONS); return result; } }
Valid actions are described in the following table. For details about each action, see Sequence diagrams.
| Action | Expected payload | Expected voice interaction action |
|---|---|---|
VOICE_ACTION_READ_NOTIFICATION |
Read messages aloud to the user and then fire the Mark as Read pending intent back when the messages are read successfully. Optionally, prompt the user for a reply. | |
VOICE_ACTION_REPLY_NOTIFICATION |
Parcelable with key.KEY_NOTIFICATION
that maps to StatusBarNotification.Requires android.permission.BIND_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SERVICE. |
Prompt the user to state the reply message, input the reply message into
the RemoteInputReply of the pending intent, and then fire the
pending intent. |
VOICE_ACTION_HANDLE_EXCEPTION |
String with key.KEY_EXCEPTION
that maps to ExceptionValue
(described in Exception values).KEY_FALLBACK_ASSISTANT_ENABLED that maps to a Boolean value. If the value
is true, the fallback assistant that can handle the user's request has been
disabled. |
The expected action to be taken for the exception is defined in the documentation for the exception. |
Exception values
EXCEPTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_PERMISSIONS_MISSING
indicates to the voice assistant that it's missing the Manifest.permission.BIND_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SERVICE permission and to get this permission from the user.
Request notification listener permission
If the default voice assistant doesn't have the notification listener
permission, the platform's FallbackAssistant
(if enabled by the car manufacturer) might read the message aloud before the voice assistant is
notifed to request the permission. To determine if FallbackAssistant is enabled and
has read the message, the voice assistant should check the
KEY_FALLBACK_ASSISTANT_ENABLED Boolean value in the payload.
The platform recommends the voice assistant add rate-limiting logic for
the number of times this permission is requested. Doing so respects the user who doesn't
want to grant the voice assistant this permission and prefers the
FallbackAssistant to read text messages aloud. Prompting a
user for permission each time the user presses Play on a message notification
can be a negative user experience. The platform doesn't impose rate limits
on behalf of the voice assistant.
When requesting the notification listener permission, the voice assistant should
use CarUxRestrictionsManager
to determine if a user is parked or is driving. If the user is driving, the voice assistant
displays a notification that provides instructions on how to grant the permission. Doing so
helps (and reminds) the user to grant the permission when it's safer.
Work with StatusBarNotification
StatusBarNotification passed in with the Read and Reply
voice actions are always in a car-compatible messaging notification as described
in Notify
users of messages. While some notifications might not have the Reply Pending
intent, they all have Mark as Read pending intents.
To streamline interactions with notifications, use NotificationPayloadHandler,
which provides methods to extract messages from the notification and write the
reply messages to the appropriate pending intent of the notification. After the
voice assistant reads the message, the voice assistant must fires the Mark
as Read intent.
Satisfy Tap-to-Read preconditions
Only VoiceInteractionSession of the default voice
assistant is notified when a user triggers the voice action to read and
reply to messages. As mentioned above, this default voice assistant must also
have the notification listener permission.
Sequence diagrams
These figures display the logic flows of CarVoiceInteractionSession actions:
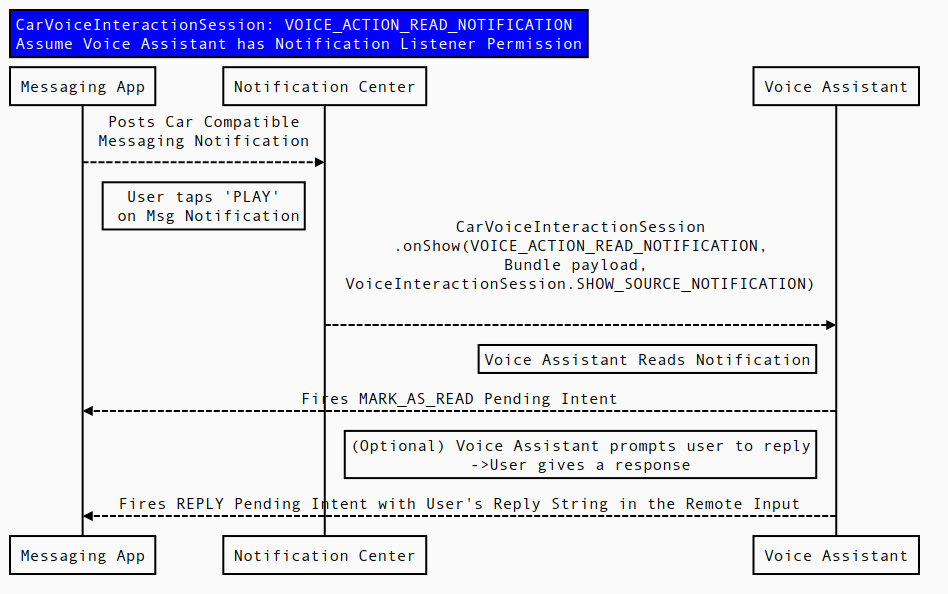
Figure 2. Sequence diagram for VOICE_ACTION_READ_NOTIFICATION.
In the case of Figure 3, the app of rate limits on permission requests is recommended:
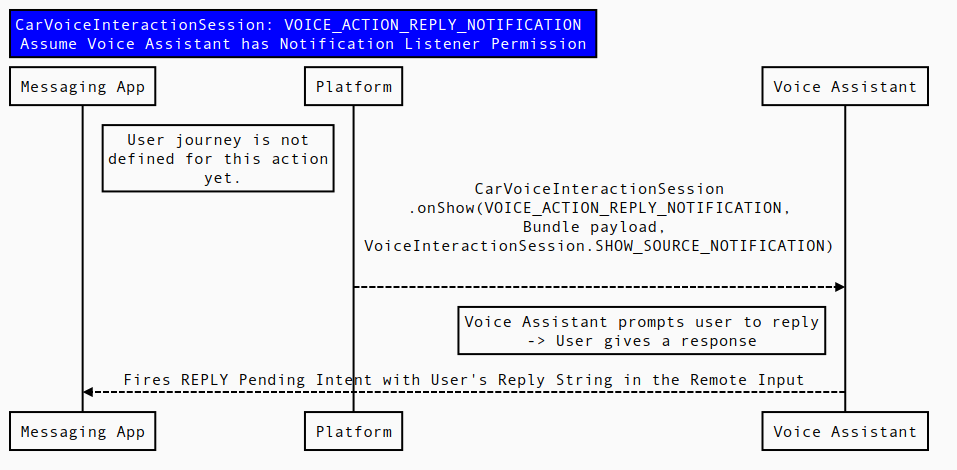
Figure 3. Sequence diagram for VOICE_ACTION_REPLY_NOTIFICATION.
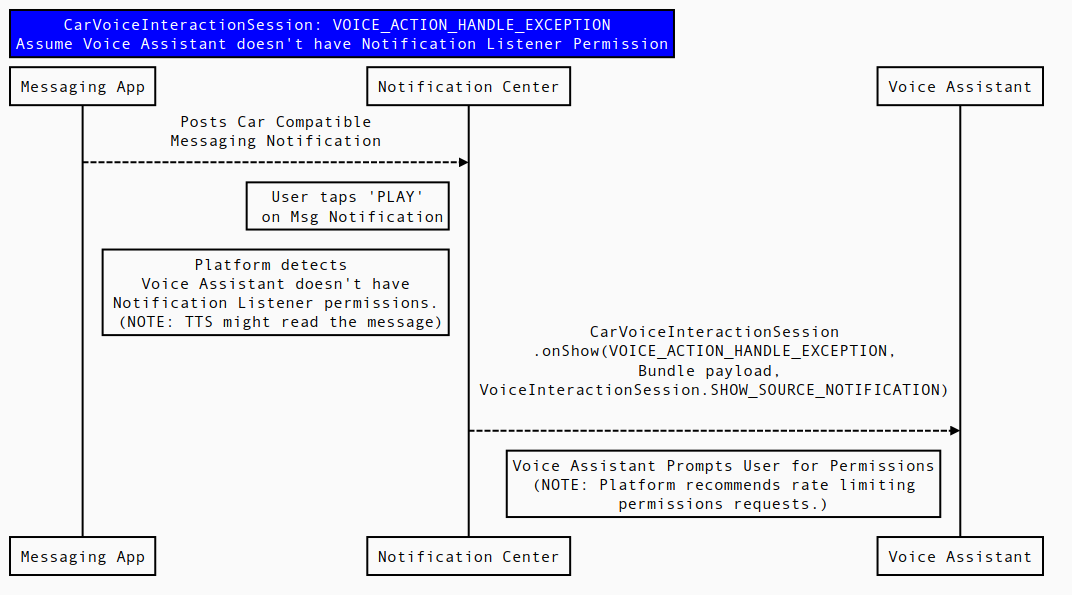
Figure 4. Sequence diagram for VOICE_ACTION_HANDLE_EXCEPTION.
Read name of app
If you want your voice assistant to read the messaging app's name aloud during the message readout (for example, "Sam from Hangouts said..."), create a function like that shown in the following code example to ensure the assistant is reading the correct name:
@Nullable String getMessageApplicationName(Context context, StatusBarNotification statusBarNotification) { ApplicationInfo info = getApplicationInfo(context, statusBarNotification.getPackageName()); if (info == null) return null; Notification notification = statusBarNotification.getNotification(); // Sometimes system packages will post on behalf of other apps, so check this // field for a system app notification. if (isSystemApp(info) && notification.extras.containsKey(Notification.EXTRA_SUBSTITUTE_APP_NAME)) { return notification.extras.getString(Notification.EXTRA_SUBSTITUTE_APP_NAME); } else { PackageManager pm = context.getPackageManager(); return String.valueOf(pm.getApplicationLabel(info)); } } @Nullable ApplicationInfo getApplicationInfo(Context context, String packageName) { final PackageManager pm = context.getPackageManager(); ApplicationInfo info; try { info = pm.getApplicationInfo(packageName, 0); } catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) { return null; } return info; } boolean isSystemApp(ApplicationInfo info) { return (info.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) != 0; }
