A media card is a self-contained ViewGroup that displays media metadata such as the title, album art, and more, and surfaces playback controls such as Play and Pause, Skip, and even custom actions provided by the third party media app. A media card can also show a queue of media items, such as a playlist.
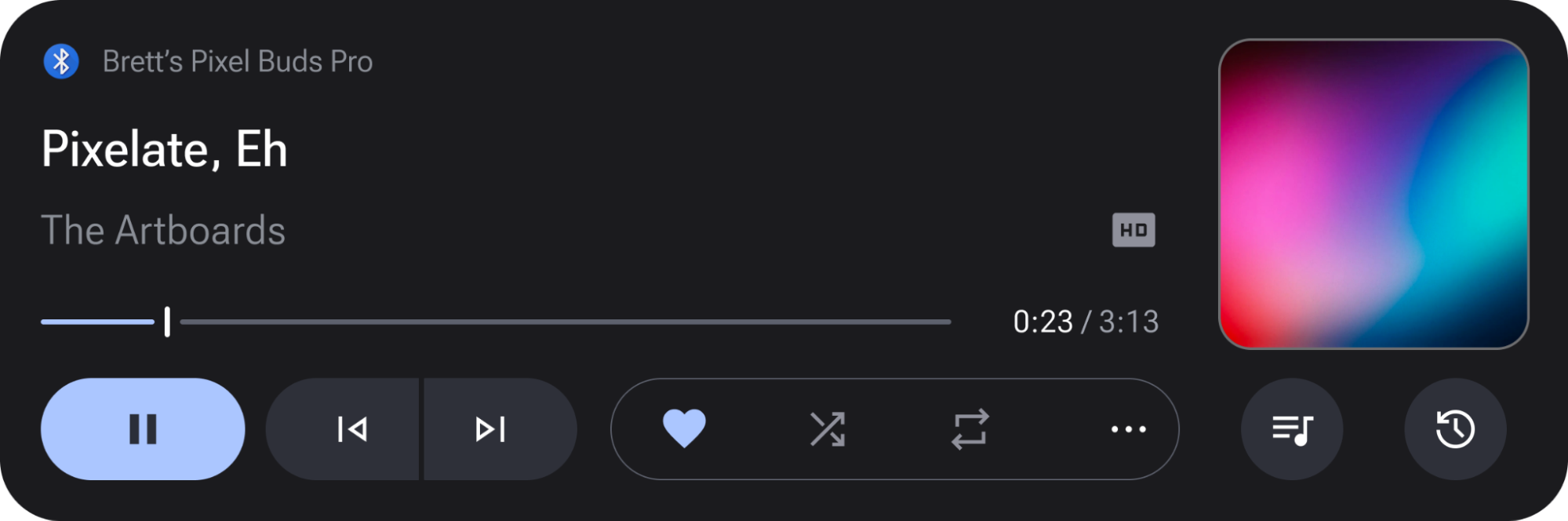
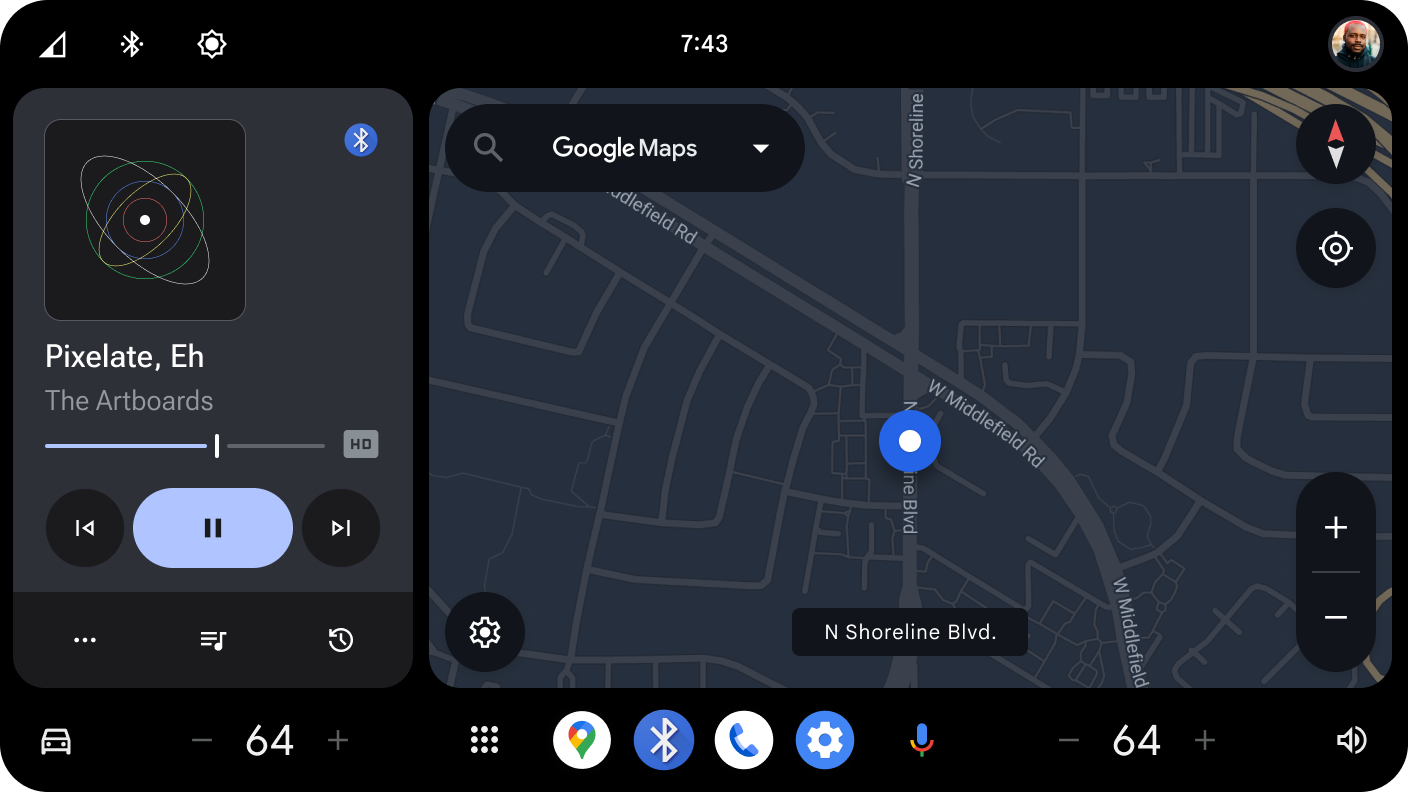
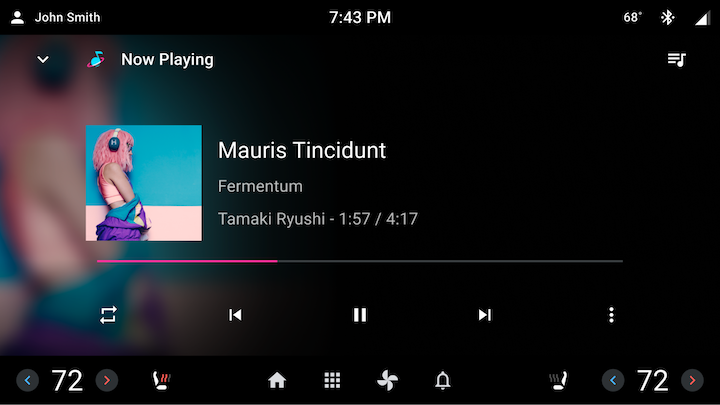
Figure 1. Media Card sample implementations.
How are media cards implemented in AAOS?
ViewGroups that show media information observe LiveData updates from the
car-media-common library data model, the PlaybackViewModel, to populate the
ViewGroup. Each LiveData update corresponds to a subset of media information
that has changed, such as MediaItemMetadata, PlaybackStateWrapper, and
MediaSource.
Because this approach leads to repeated code (each client app adds Observers on
each piece of LiveData and many similar Views are assigned the updated data), we
created the PlaybackCardController.
PlaybackCardController
The PlaybackCardController has been added to the car-media-common library to
assist in creating a media card. This is a public class that is constructed with
a ViewGroup (mView), PlaybackViewModel (mDataModel), PlaybackCardViewModel
(mViewModel), and MediaItemsRepository instance (mItemsRepository).
In the setupController function, the ViewGroup is parsed for certain views by
ID, with mView.findViewById(R.id.xxx) and assigned to protected View objects.
private void getViewsFromWidget() {
mTitle = mView.findViewById(R.id.title);
mAlbumCover = mView.findViewById(R.id.album_art);
mDescription = mView.findViewById(R.id.album_title);
mLogo = mView.findViewById(R.id.content_format);
mAppIcon = mView.findViewById(R.id.media_widget_app_icon);
mAppName = mView.findViewById(R.id.media_widget_app_name);
// ...
}
Each LiveData update from the PlaybackViewModel is observed in a protected
method and performs interactions with the Views relevant to the data
received. For example, an observer on MediaItemMetadata sets the title on the
mTitle TextView and passes the MediaItemMetadata.ArtworkRef to the album
art ImageBinder mAlbumArtBinder. If the metadata is null, the Views are
hidden. Subclasses of the Controller can override this logic if need be.
mDataModel.getMetadata().observe(mViewLifecycle, this::updateMetadata);
// ...
/** Update views with {@link MediaItemMetadata} */
protected void updateMetadata(MediaItemMetadata metadata) {
if (metadata != null) {
String defaultTitle = mView.getContext().getString(
R.string.metadata_default_title);
updateTextViewAndVisibility(mTitle, metadata.getTitle(), defaultTitle);
updateTextViewAndVisibility(mSubtitle, metadata.getSubtitle());
updateMediaLink(mSubtitleLinker,metadata.getSubtitleLinkMediaId());
updateTextViewAndVisibility(mDescription, metadata.getDescription());
updateMediaLink(mDescriptionLinker, metadata.getDescriptionLinkMediaId());
updateMetadataAlbumCoverArtworkRef(metadata.getArtworkKey());
updateMetadataLogoWithUri(metadata);
} else {
ViewUtils.setVisible(mTitle, false);
ViewUtils.setVisible(mSubtitle, false);
ViewUtils.setVisible(mAlbumCover, false);
ViewUtils.setVisible(mDescription, false);
ViewUtils.setVisible(mLogo, false);
}
}
Extend the PlaybackCardController
Client apps that would like to create a media card should extend the
PlaybackCardController if they have additional capability they would like to
handle in each LiveData update. Existing clients in AAOS follow this pattern.
First, a PlaybackCardController subclass should be created, such as the
MediaCardController. Next, the MediaCardController should add a static inner
Builder class which extends that of the PlaybackCardController.
public class MediaCardController extends PlaybackCardController {
// extra fields specific to MediaCardController
/** Builder for {@link MediaCardController}. Overrides build() method to
* return NowPlayingController rather than base {@link PlaybackCardController}
*/
public static class Builder extends PlaybackCardController.Builder {
@Override
public MediaCardController build() {
MediaCardController controller = new MediaCardController(this);
controller.setupController();
return controller;
}
}
public MediaCardController(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
// any other function calls needed in constructor
// ...
}
}
Instantiate the PlaybackCardController or a subclass
The Controller class should be instantiated from a Fragment or Activity in order to have a LifecycleOwner for the LiveData observers.
mMediaCardController = (MediaCardController) new MediaCardController.Builder()
.setModels(mViewModel.getPlaybackViewModel(),
mViewModel,
mViewModel.getMediaItemsRepository())
.setViewGroup((ViewGroup) view)
.build();
mViewModel is an instance of the PlaybackCardViewModel (or subclass).
PlaybackCardViewModel to Save State
The PlaybackCardViewModel is a state-saving ViewModel tied to a Fragment or
Activity that should be used to reconstruct the media card's contents if a
configuration change occurs (such as a switch from light to dark theme when a
user drives through a tunnel). The default PlaybackCardViewModel handles the
storing of instances of the MediaModels for playback, from which the
PlaybackViewModel and MediaItemsRepository can be retrieved. Use the
PlaybackCardViewModel to track the state of the queue, history, and overflow
menu through the provided getters and setters.
public class PlaybackCardViewModel extends AndroidViewModel {
private MediaModels mModels;
private boolean mNeedsInitialization = true;
private boolean mQueueVisible = false;
private boolean mHistoryVisible = false;
private boolean mOverflowExpanded = false;
public PlaybackCardViewModel(@NonNull Application application) {
super(application);
}
/** Initialize the PlaybackCardViewModel */
public void init(MediaModels models) {
mModels = models;
mNeedsInitialization = false;
}
/**
* Returns whether the ViewModel needs to be initialized. The ViewModel may
* need re-initialization if a config change occurs or if the system kills
* the Fragment.
*/
public boolean needsInitialization() {
return mNeedsInitialization;
}
public MediaItemsRepository getMediaItemsRepository() {
return mModels.getMediaItemsRepository();
}
public PlaybackViewModel getPlaybackViewModel() {
return mModels.getPlaybackViewModel();
}
public MediaSourceViewModel getMediaSourceViewModel() {
return mModels.getMediaSourceViewModel();
}
public void setQueueVisible(boolean visible) {
mQueueVisible = visible;
}
public boolean getQueueVisible() {
return mQueueVisible;
}
public void setHistoryVisible(boolean visible) {
mHistoryVisible = visible;
}
public boolean getHistoryVisible() {
return mHistoryVisible;
}
public void setOverflowExpanded(boolean expanded) {
mOverflowExpanded = expanded;
}
public boolean getOverflowExpanded() {
return mOverflowExpanded;
}
}
This class can be extended if additional states need to be tracked.
Show a queue in a media card
The PlaybackViewModel provides LiveData APIs to detect if the MediaSource
supports a queue and to retrieve the list of MediaItemMetadata objects in the
queue. Though these APIs can be used directly to populate a RecyclerView
object with the queue information, a PlaybackQueueController class has been
added to the car-media-common library to streamline this process. The layout
for each item in the CarUiRecyclerView is specified by the client app as well
as an optional Header layout. The client app can also opt to limit the number of
items shown in the queue during drive state with custom UXR restrictions.
The PlaybackQueueController constructor and setters are shown in the following
sample. The queueResource and headerResource layout resources can be passed
as Resources.ID_NULL if, in the former case, the container already contains a
CarUiRecyclerView with id queue_list and, in the latter case, the queue
does not have a Header.
/**
* Construct a PlaybackQueueController. If clients don't have a separate
* layout for the queue, where the queue is already inflated within the
* container, they should pass {@link Resources.ID_NULL} as the LayoutRes
* resource. If clients don't require a UxrContentLimiter, they should pass
* null for uxrContentLimiter and the int passed for uxrConfigurationId will
* be ignored.
*/
public PlaybackQueueController(
ViewGroup container,
@LayoutRes int queueResource,
@LayoutRes int queueItemResource,
@LayoutRes int headerResource,
LifecycleOwner lifecycleOwner,
PlaybackViewModel playbackViewModel,
MediaItemsRepository itemsRepository,
@Nullable LifeCycleObserverUxrContentLimiter uxrContentLimiter,
int uxrConfigurationId) {
// ...
}
public void setShowTimeForActiveQueueItem(boolean show) {
mShowTimeForActiveQueueItem = show;
}
public void setShowIconForActiveQueueItem(boolean show) {
mShowIconForActiveQueueItem = show;
}
public void setShowThumbnailForQueueItem(boolean show) {
mShowThumbnailForQueueItem = show;
}
public void setShowSubtitleForQueueItem(boolean show) {
mShowSubtitleForQueueItem = show;
}
/** Calls {@link RecyclerView#setVerticalFadingEdgeEnabled(boolean)} */
public void setVerticalFadingEdgeLengthEnabled(boolean enabled) {
mQueue.setVerticalFadingEdgeEnabled(enabled);
}
public void setCallback(PlaybackQueueCallback callback) {
mPlaybackQueueCallback = callback;
}
The layout for each queue item should contain the ids for the Views it would
like to show that correspond to those used in the QueueViewHolder inner class.
QueueViewHolder(View itemView) {
super(itemView);
mView = itemView;
mThumbnailContainer = itemView.findViewById(R.id.thumbnail_container);
mThumbnail = itemView.findViewById(R.id.thumbnail);
mSpacer = itemView.findViewById(R.id.spacer);
mTitle = itemView.findViewById(R.id.queue_list_item_title);
mSubtitle = itemView.findViewById(R.id.queue_list_item_subtitle);
mCurrentTime = itemView.findViewById(R.id.current_time);
mMaxTime = itemView.findViewById(R.id.max_time);
mTimeSeparator = itemView.findViewById(R.id.separator);
mActiveIcon = itemView.findViewById(R.id.now_playing_icon);
// ...
}
To show a queue in a media card created with the PlaybackCardController
(or a subclass), the PlaybackQueueController can be constructed in the
PlaybackCardController constructor using mDataModel and mItemsRepository
for the PlaybackViewModel and MediaItemsRepository instances, respectively.
Show history of previously played MediaSources
In this section, you learn how to show and surface history of previously played media sources.
Get history list with the PlaybackCardViewModel API
PlaybackCardViewModel provides a LiveData API called getHistoryList() to
retrieve the media history list. It returns a LiveData containing a list of
MediaSources that have been played before. This data can be used to populate
a CarUiRecyclerView object. Similar to PlaybackQueueController, a class
named PlaybackHistoryController has been added to the car-media-common
library to streamline the process.
public class PlaybackCardViewModel extends AndroidViewModel {
public PlaybackCardViewModel(@NonNull Application application) {
}
/** Initialize the PlaybackCardViewModel */
public void init(MediaModels models) {
}
public LiveData<List<MediaSource>> getHistoryList() {
return mHistoryListData;
}
}
Surface history UI with PlaybackHistoryController
Use the new PlaybackHistoryController to help populate the history data
to a CarUiRecyclerView. The constructors and main functions of this class are
as follows. The container passed from the client app should contain a
CarUiRecyclerView with the ID history_list. The CarUiRecyclerView
displays the list items and an optional header. Both layouts for the list item
and the header can be passed from the client app. If Resources.ID_NULL is set
as the headerResource, the header is not shown. After the
PlaybackCardViewModel is passed into the controller, it monitors the
LiveData<List<MediaSource>> retrieved from
playbackCardViewModel.getHistoryList().
public class PlaybackHistoryController {
public PlaybackHistoryController(
LifecycleOwner lifecycleOwner,
PlaybackCardViewModel playbackCardViewModel,
ViewGroup container,
@LayoutRes int itemResource,
@LayoutRes int headerResource,
int uxrConfigurationId) {
}
/**
* Renders the view.
*/
public void setupView() {
}
}
The layout for each item should contain the IDs for the Views it wants to
show that correspond to those used in the ViewHolder inner class.
HistoryItemViewHolder(View itemView) {
super(itemView);
mContext = itemView.getContext();
mActiveView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.history_card_container_active);
mInactiveView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.history_card_container_inactive);
mMetadataTitleView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.history_card_title_active);
mAdditionalInfo = itemView.findViewById(R.id.history_card_subtitle_active);
mAppIcon = itemView.findViewById(R.id.history_card_app_thumbnail);
mAlbumArt = itemView.findViewById(R.id.history_card_album_art);
mAppTitleInactive = itemView.findViewById(R.id.history_card_app_title_inactive);
mAppIconInactive = itemView.findViewById(R.id.history_item_app_icon_inactive);
// ...
}
To show a history list in a media card created with the
PlaybackCardController (or a subclass), the PlaybackHistoryController can be
constructed in the constructor of the PlaybackCardController.
